Final ID: WP190
Predicting Intracranial Atherosclerosis-related Large Vessel Occlusion Using Deep Learning on Neuroimaging and Clinical Data.
Abstract Body: Background: Predicting recanalization in acute ischemic stroke (AIS) patients undergoing mechanical thrombectomy (MT) may help in optimizing treatment strategies but remains a critical challenge. Patients presenting intracranial atherosclerosis-related large vessel occlusion (ICAS-LVO) may benefit from performing an early bailout strategy after failed MT with conventional devices. Current predictive models often fail to effectively integrate complex interactions between clinical data and neuroimaging features. We aimed to explore predictive models for ICAS-LVO after an unsuccessful first pass, combining neuroimaging and clinical data.
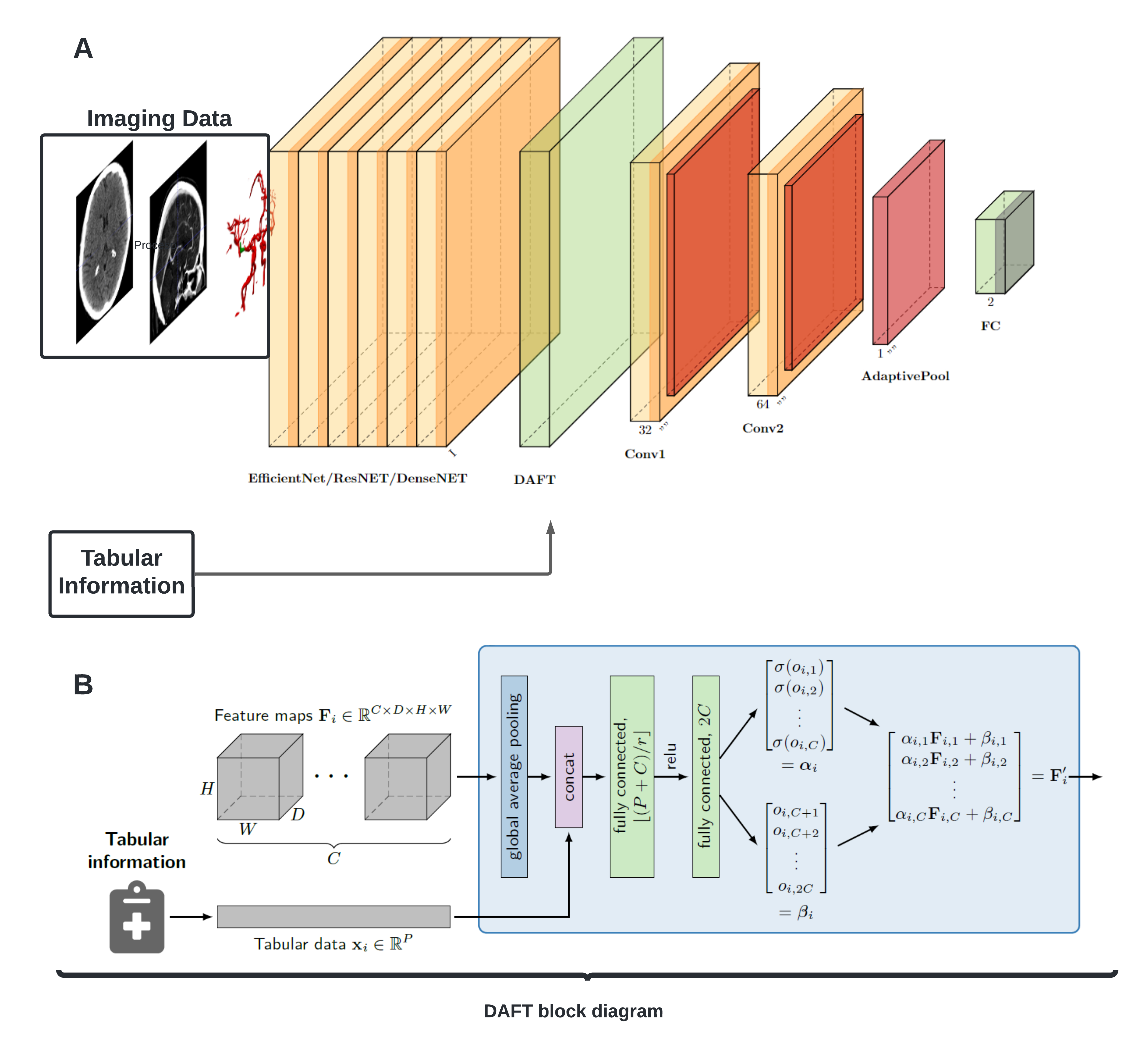
Methods: This retrospective, single-center study of patients presenting anterior LVO stroke from 2017 to 2023. ICAS-LVO was defined by fial angiographic stenosis >50% or failed MT (eTICI0-2a) with no evidence of other underlying etiology (i.e cardioembolic). Neuroimaging data included raw non-contrast CT and CTA volumes, automatic vascular segmentation, and CTP output values. Clinical data, such as patient demographics, stroke severity, and comorbidities, were incorporated into the model. A Dynamic Affine Feature Map Transform (DAFT) mechanism was used to integrate imaging data, encoded with a convolutional neural network, with clinical variables. A comparative analysis including several image-based deep learning models and known machine learning models trained on clinical data was performed. Data were split into 80% for training with four-fold cross-validation and 20% for testing.
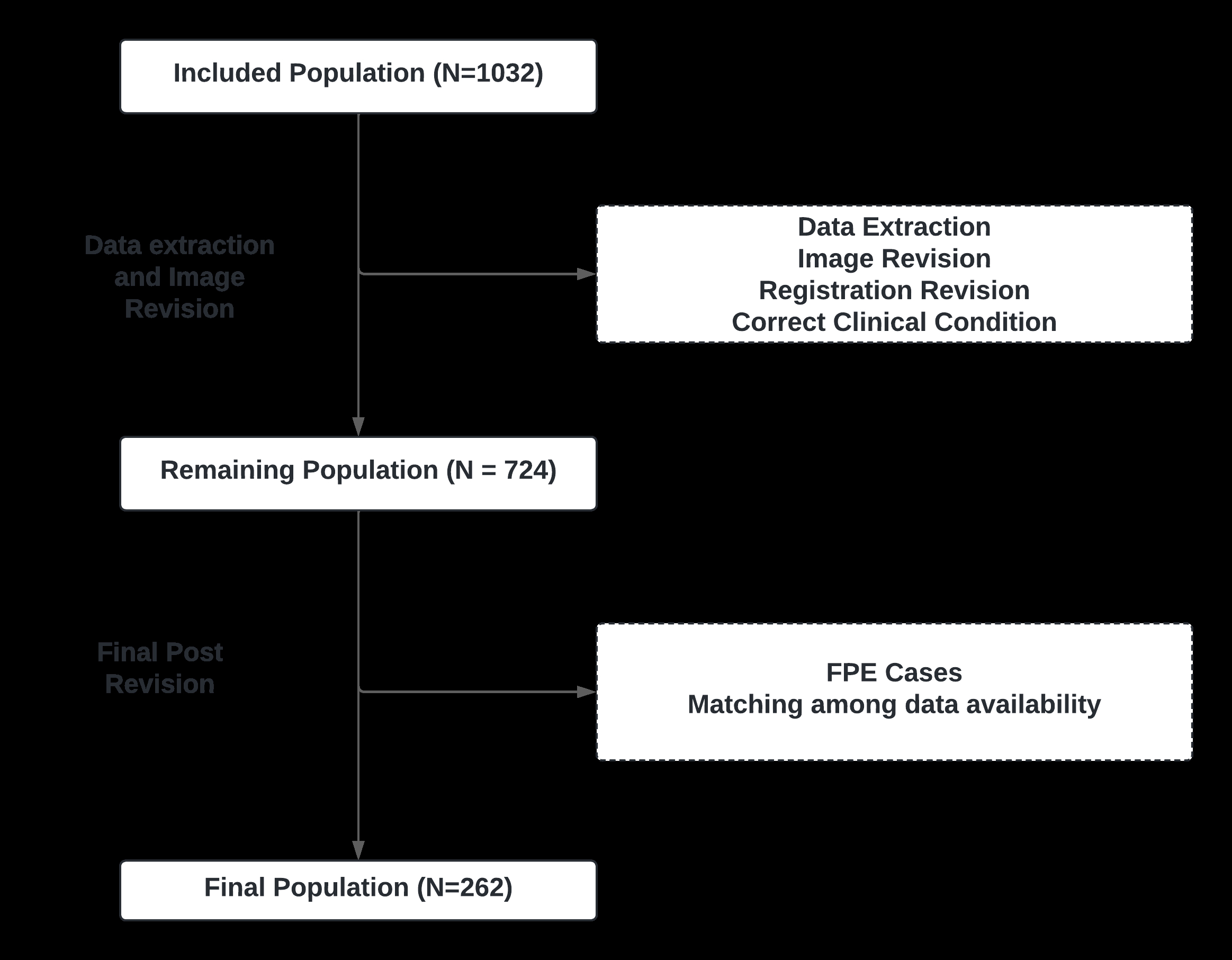
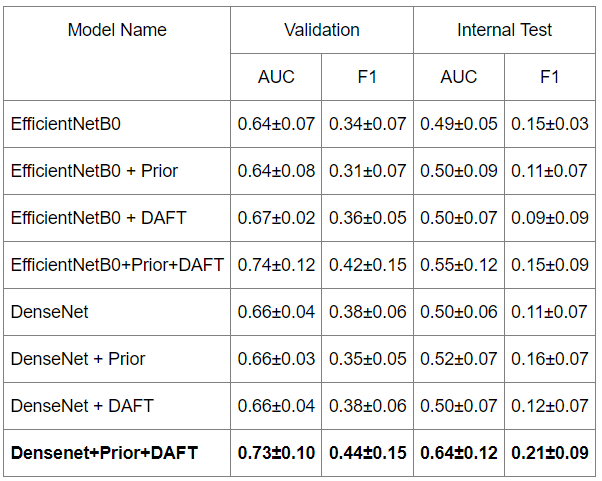
Results: A total of 262 patients (median age 81 IQR 69-88, 61% women; 11.83% with ICAS-LVO) with anterior LVO and failed MT first attempt (eTICI 0-2a) were included. Training sample was of 212 patients (12.73% with ICAS-LVO). A consecutive sample of 50 patients (8% with ICAS-LVO) was reserved for testing. The best-performing model achieved an AUC of 0.73 ± 0.10 (mean ± std), and a F1 of 0.44 ± 0.15 in validation and an AUC of 0.64 ± 0.12, and a F1 of 0.21 ± 0.09 on internal testing.
Conclusions: Although effective prediction of ICAS-LVO remains challenging, models using multi-modal data were superior to those using imaging or clinical data alone emphasizing the importance of combining multiple sources of data to enhance predictive capabilities. This model could be useful to rapidly identify patients with suspected ICAS-LVO prior to MT and optimize endovascular treatment strategy after the initial attempt.
Methods: This retrospective, single-center study of patients presenting anterior LVO stroke from 2017 to 2023. ICAS-LVO was defined by fial angiographic stenosis >50% or failed MT (eTICI0-2a) with no evidence of other underlying etiology (i.e cardioembolic). Neuroimaging data included raw non-contrast CT and CTA volumes, automatic vascular segmentation, and CTP output values. Clinical data, such as patient demographics, stroke severity, and comorbidities, were incorporated into the model. A Dynamic Affine Feature Map Transform (DAFT) mechanism was used to integrate imaging data, encoded with a convolutional neural network, with clinical variables. A comparative analysis including several image-based deep learning models and known machine learning models trained on clinical data was performed. Data were split into 80% for training with four-fold cross-validation and 20% for testing.
Results: A total of 262 patients (median age 81 IQR 69-88, 61% women; 11.83% with ICAS-LVO) with anterior LVO and failed MT first attempt (eTICI 0-2a) were included. Training sample was of 212 patients (12.73% with ICAS-LVO). A consecutive sample of 50 patients (8% with ICAS-LVO) was reserved for testing. The best-performing model achieved an AUC of 0.73 ± 0.10 (mean ± std), and a F1 of 0.44 ± 0.15 in validation and an AUC of 0.64 ± 0.12, and a F1 of 0.21 ± 0.09 on internal testing.
Conclusions: Although effective prediction of ICAS-LVO remains challenging, models using multi-modal data were superior to those using imaging or clinical data alone emphasizing the importance of combining multiple sources of data to enhance predictive capabilities. This model could be useful to rapidly identify patients with suspected ICAS-LVO prior to MT and optimize endovascular treatment strategy after the initial attempt.
More abstracts on this topic:
3D Statistical Shape Analysis Predicts Type A Aortic Dissection Better Than Aortic Diameters
with intracranial arterial disease
Marway Prabhvir, Campello Jorge Carlos Alberto, Wagner Catherine, Baker Timothy, Burris Nicholas
Impact of eicosapentaenoic acids and cilostazol in patientswith intracranial arterial disease
Takeishi Yusuke, Watanabe Yosuke, Matsuda Shingo, Okada Yoshio, Dowaki Ryosuke, Kuroki Kazuhiko
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)