Final ID: TP288
Prevalence and Gender Differences in Carotid Atherosclerosis Among Adults: Evidence from a Cohort Study in China
Methods: From September 2021 to June 2022, we established a prospective cohort to study CAS and cardiovascular disease across 25 project sites in Henan, China, utilizing a multistage whole-population sampling method. Residents aged 18 years or older in the sampled areas were included in this study, and data were collected through questionnaires, physical examinations, laboratory tests, carotid ultrasound examinations, and biological sample collection. A consent information platform for data collection and quality control management was also developed. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee for Scientific Research and Clinical Trials of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (No. 2021-KY-1289-001).
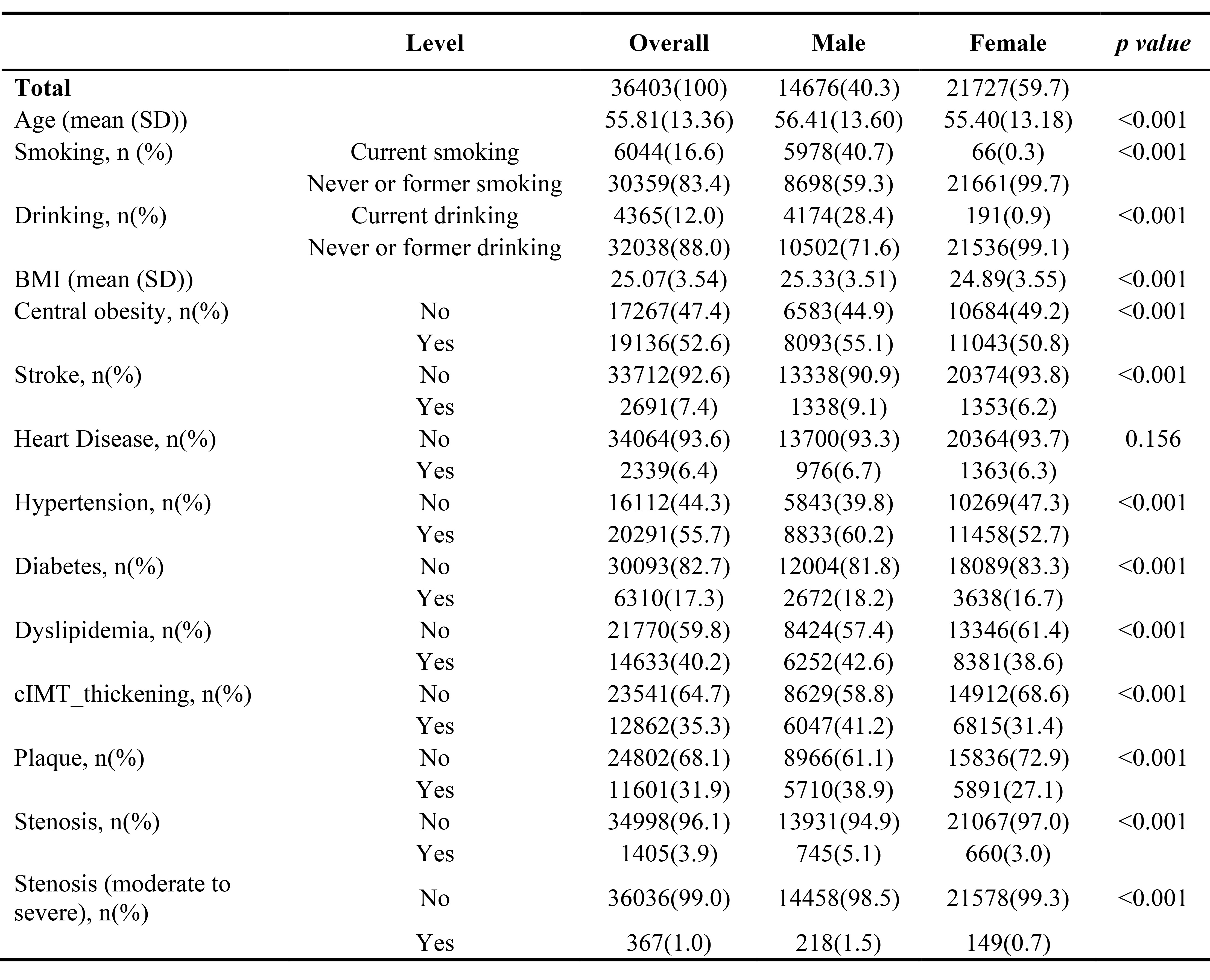
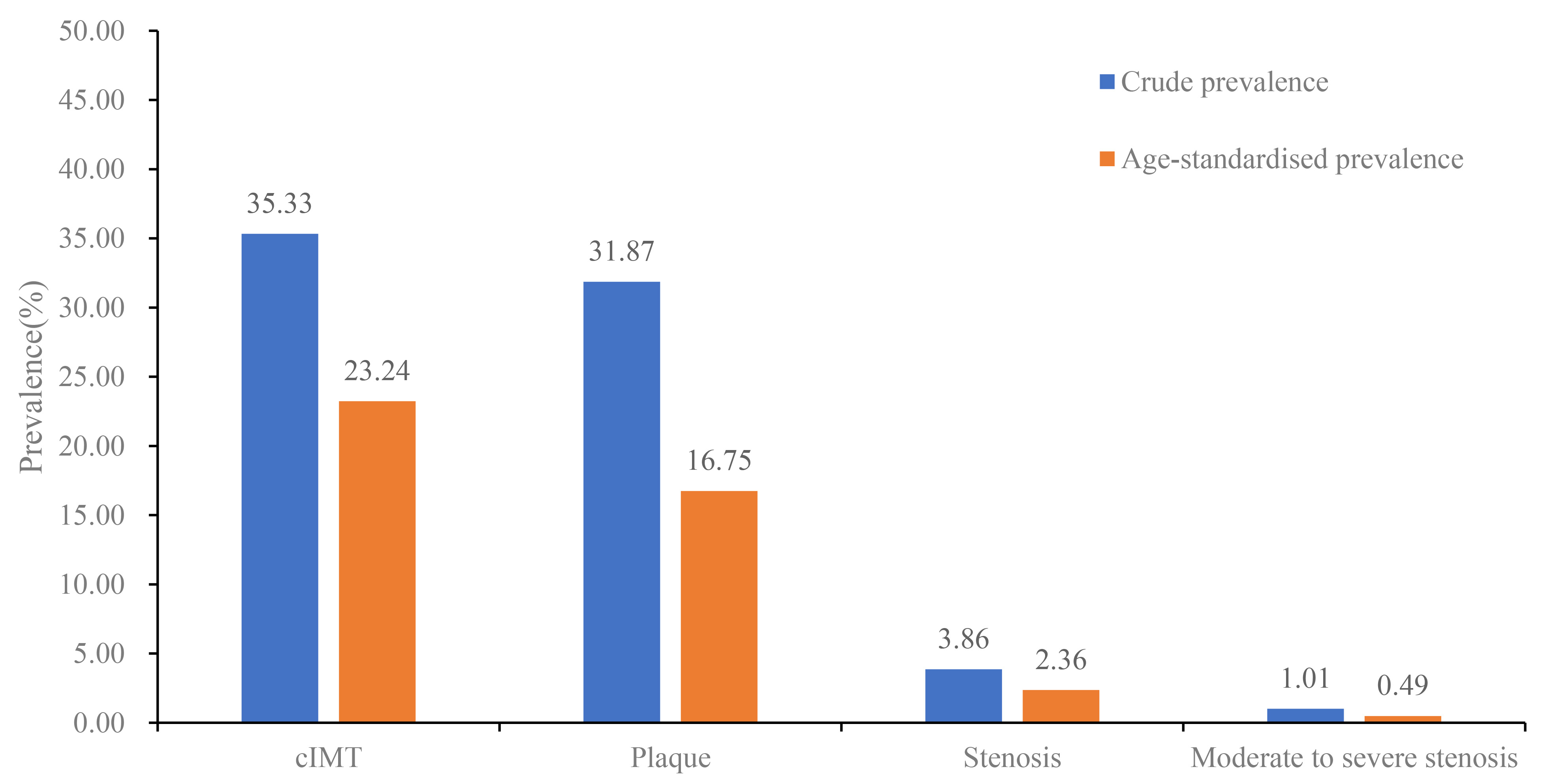
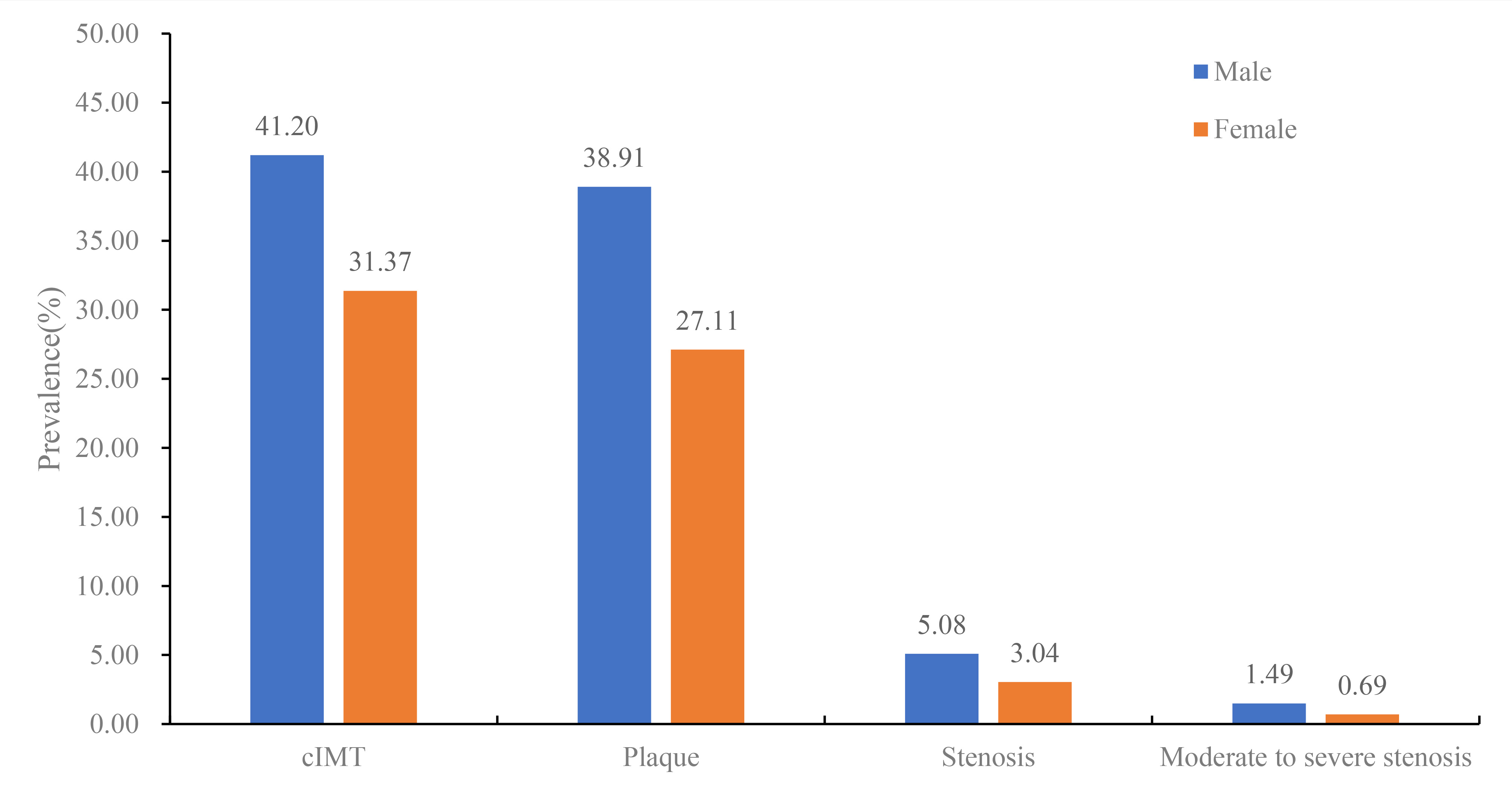
Results: Among the 36,403 participants (14,676 males, 40.3%), the prevalence of stroke, heart disease, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia was 7.4%, 6.4%, 55.7%, 17.3%, and 40.2% respectively. After age standardization, the prevalence of cIMT, carotid plaque, and carotid stenosis was 23.24%, 16.75%, and 2.36%, respectively, with moderate to severe carotid stenosis observed in 0.49% of all participants. Additionally, the gender-stratified analysis revealed that carotid atherosclerosis was more severe in males, who exhibited higher rates of cIMT, plaque, stenosis, and moderate to severe stenosis compared to females (41.20% vs. 31.37%, 38.91% vs. 27.11%, 5.08% vs. 3.04%, and 1.49% vs. 0.69%, respectively).
Conclusions: In conclusion, our study highlights that intima-media thickening and plaques are more prevalent in adult carotid arteries, with a significantly higher prevalence in males. These findings provide valuable evidence for authorities to implement health policies and identify high-risk populations, aiming to prevent the occurrence of stroke in both the general population and high-risk groups.
More abstracts on this topic:
Deitelzweig Steven, O'brien Ellen, Jiang Jenny, Schuleri Karl, Onorato Joelle, Elakoti Anupam, Li Xiaoyan, Kang Amiee
Characterization of Large Vessel Occlusion Stroke in Head and Neck Cancer Survivors treated with Endovascular TherapyAl-qudah Abdullah, Johnson Jonas, Al-bayati Alhamza, Nogueira Raul, Rocha Marcelo, Doheim Mohamed, Bhatt Nirav, Rios Rocha Lucas, Xkhalifax Xmoustafax, Starr Matthew, Nilsen Marci, Lang Michael, Gross Bradley
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.