Final ID: TMP108
Incidence and Characteristics of Acute Ischemic Stroke after Cardiac Arrest
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of brain MRI reports from patients with cardiac arrest in a multicenter cohort to evaluate the incidence of acute ischemic stroke and HIBI. Patients with MRI in the first 7 days after cardiac arrest were included. Patients with traumatic brain injury, intracranial hemorrhage, recent neurosurgical procedures, or ischemic stroke at admission were excluded. A secondary manual review by a board-certified vascular neurologist was pursued if the MRI report did not specify the absence of ischemic stroke. Univariate and multivariable analysis was performed to explore the characteristics of the ischemic lesions and to evaluate if it was related to poor functional outcomes (i.e., Cerebral Performance Category of 4-5).
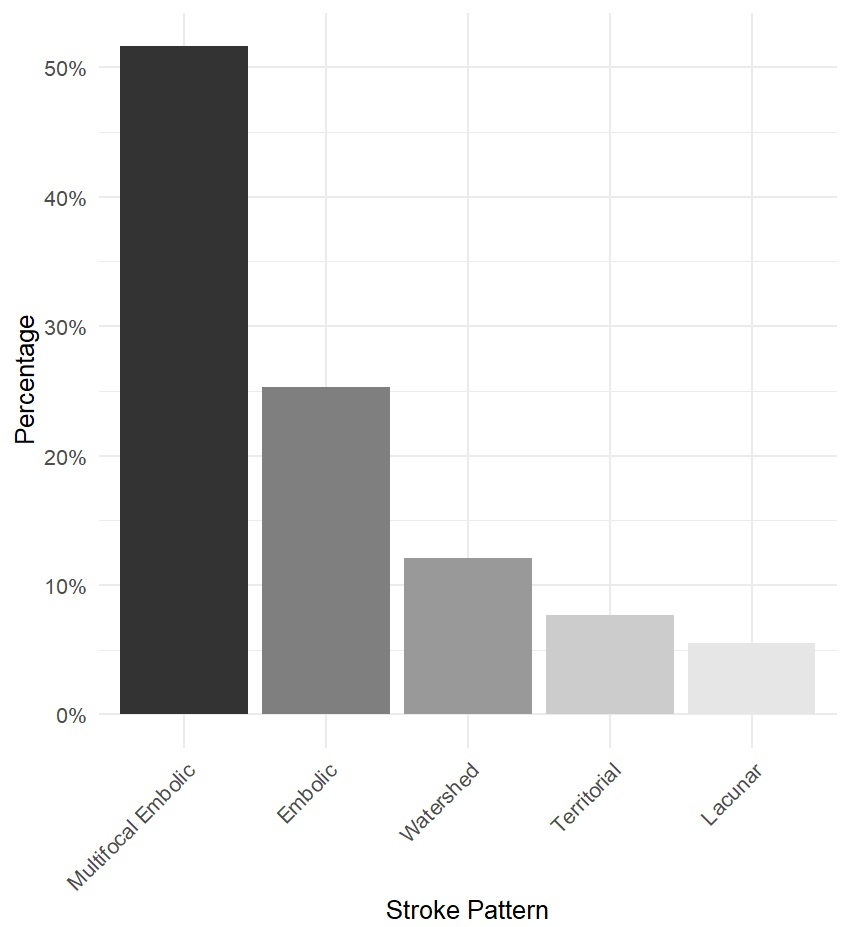
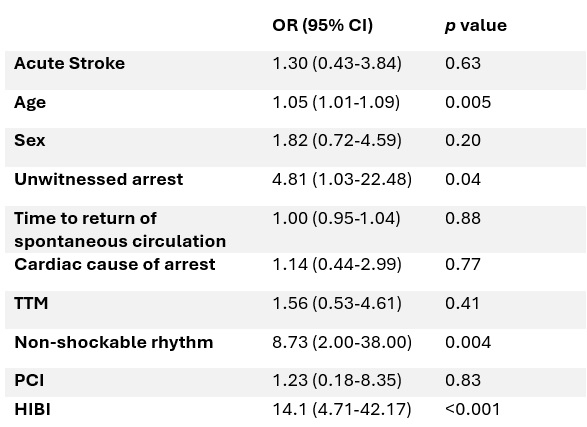
Results: Among 396 patients who met the inclusion criteria, 91 had cerebral infarction based on MRI (22.9%). The most common pattern of stroke was multifocal small embolic (51.6%), followed by single embolic (25.3%), watershed (12.1%), territorial (7%), and lacunar (5%). The patients with acute ischemic stroke were older (p<0.01). In the logistic regression, older age, non-witnessed cardiac arrest, and non-shockable rhythm were associated with worse prognosis (p<0.05). The presence of acute ischemic stroke was not significantly associated with the cause of arrest, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), or the use of targeted temperature management (TTM). Individuals with acute ischemic stroke had lower rates of HIBI (odds ratio [OR] 0,55 [0.34-0.87], p<0.01). In univariate and multivariate analysis, the presence of acute ischemic stroke was not associated with outcome, as opposed to the presence of HIBI (p<0.01).
Conclusion: More than one-fifth of the comatose patients after cardiac arrest present acute ischemic stroke on MRI. The most common pattern is multifocal embolic, which may be related to cardiac embolism and hypercoagulable state after the arrest and not from PCI or cardiac arrest rhythm. The detection of acute ischemic stroke is higher among individuals without HIBI and is not associated with worse outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Riker Richard, Chessa Frank, Sawyer Douglas, Seder David B., Weatherbee Mary, Daley Alison, Searight Meghan, Lord Christine, Lessard Amanda, Feutz Catherine, May Teresa, Gagnon David
A Hospital-Wide Multidimensional Approach to Pediatric In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Review: Early Identification and PreventionLoeb Daniel, Collins Kelly, Ortega Karina, Dewan Maya
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.