Final ID: TP310
The Shifting Evidence for Statin Use in the Setting of Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Intracerebral Hemorrhage (ICH) is associated with a high case fatality and survivors of ICH are at increased risk for ICH recurrence. Roughly 20-30% of patients with ICH take a statin at the time of ICH onset. The role of statins, whether protective or deleterious, in the setting of ICH remains unclear. The SPARCL (Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction of Cholesterol Level) study amongst others, have suggested that statin use may increase risk of ICH in those with prior history ICH, due to increased erythrocyte fragility and inhibition of platelet aggregation. However subsequent observational studies refuted these findings citing statins improve endothelial function and reduce oxidative stress thus theoretically. We reviewed relevant studies discussing the relationship between statin use and risk of ICH.
Methods
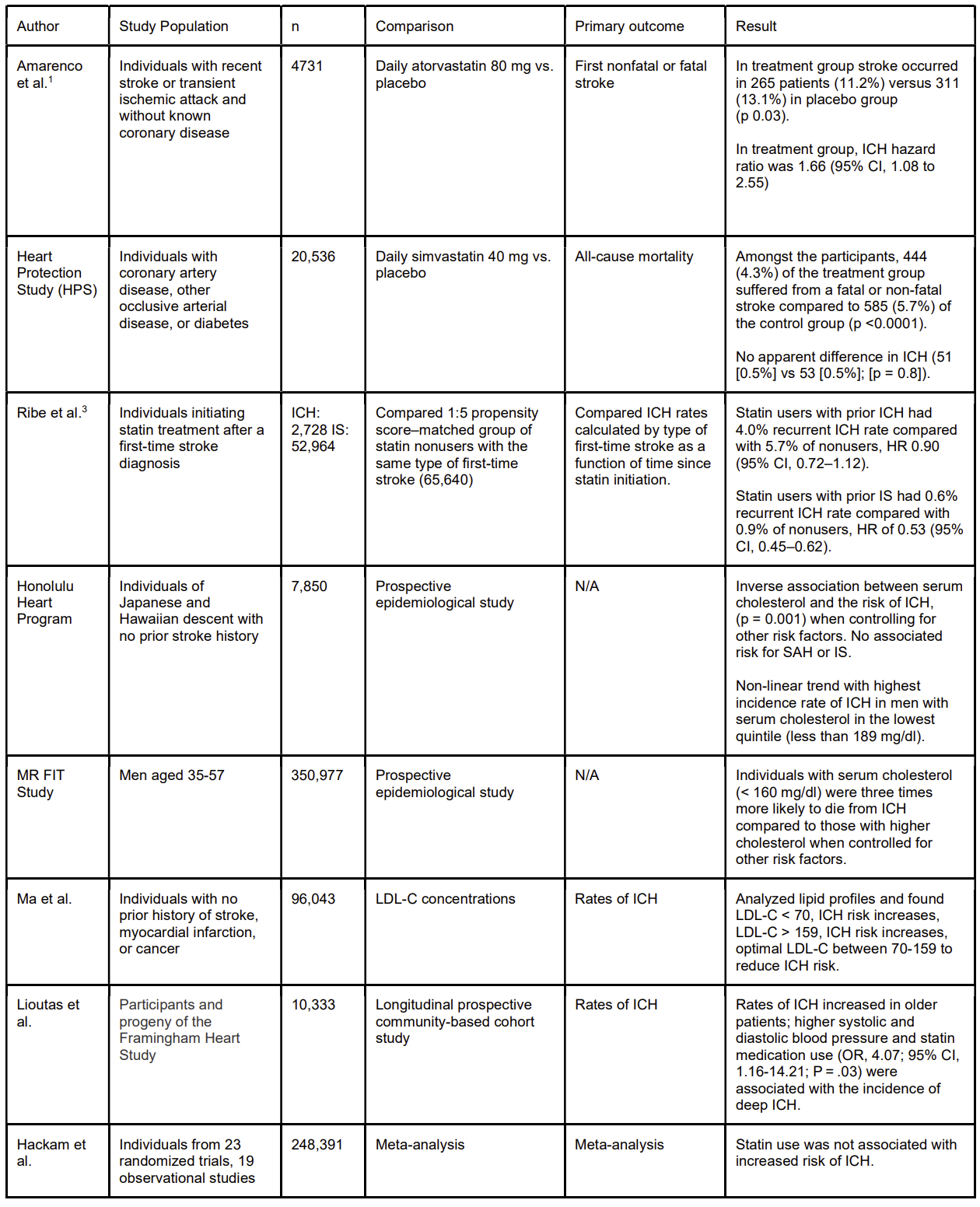
A comprehensive search strategy utilizing the key terms “statin use” and “intracerebral hemorrhage” was performed utilizing four electronic databases: Cochrane, Embase, Google Scholar, PubMed. The search was conducted by two authors (PM and CO). Following the search, articles citing a correlation between statin use and risk of intracerebral hemorrhage were included. Below is a table citing selected studies from our review (Table 1).
Discussion
There continues to be mixed evidence regarding statin use and risk of ICH. Current clinical guidelines do not provide a formal recommendation on statin use restriction in those with prior ICH. However, contrary to the SPARCL study, newer studies have suggested there is neither a statistically nor clinically significant relationship between LDL-C and ICH incidence. Our review also uncovered that one’s genetic signature may play a mediating role in this relationship as evidenced namely by the Honolulu Heart study, which analyzed a relatively monogenic study population. This implies a more nuanced relationship and we posit the burgeoning use of polygenic risk scoring may provide more utility here as well. Ultimately consideration of statin therapy should be determined by weighing one’s atherogenicity versus propensity to develop ICH. An optimal LDL-C goal has yet to be determined however many studies suggest targeting between 70-160 mg/dL is optimal. Additional studies should assess the role of other lipid lowering agents in the setting of ICH such as bempedoic acid and PCSK9 inhibitors, as well as discern optimal ranges for newer Apo-B and Lp(a) lipid biomarkers.
More abstracts on this topic:
Wang Fangfang, Li Haiyan, Zeng Jie, Shi Yibin, Li Hongmei
Adjunct middle meningeal artery embolization for chronic subdural hematoma: A meta-analysis to guide surgical decision makingMusheer Adeena, Faisal Noman, Haider Tehseen, Ahmed Ali, Arshad Usman, Ur Rehman Muneeb, Hassan Abbas Khan Muhammad, Said Sana, Iqbal Ahsan, Butt Abdur Rehman, Hassan Kazmi Zuha
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.