Final ID: WP196
Comparing hypodensity and volume measurements for ischemic stroke patients in admission CT between CTP ischemic core, DWI, and deep learning based CT regions of interest
Introduction:
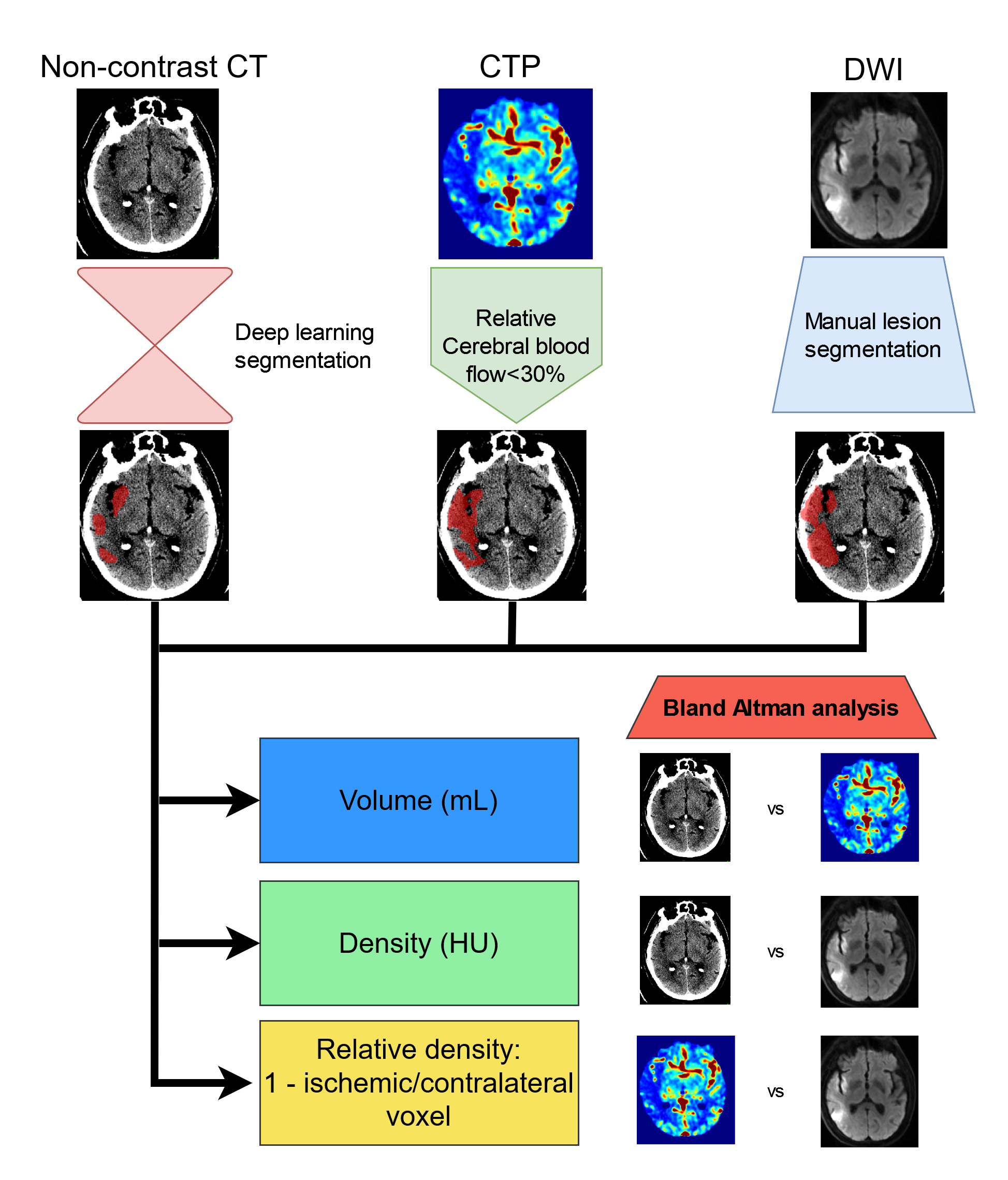
Non-contrast brain CT hypodensity and volume in acute ischemic stroke patients are associated with poor patient outcomes. Currently, abnormal hypodensities in CT are measured using coregistered CT Perfusion or DWI based region of interest (ROI) segmentations. We hypothesized that deep learning based ischemic lesion segmentation on admission CT (DLCT) could serve as an alternative to CTP or DWI ROIs for density and volume measurements in CT.
Methods:
Patients from the prospective CRISP 2 study with admission CT/CTP in the primary stroke center and DWI after transfer to a comprehensive stroke center were included (n=208). We trained a deep learning model for admission CT ischemic lesion segmentation using DEFUSE 3 patients (n=218). Besides this DLCT ROI, we used the admission CTP ischemic core (relative cerebral blood flow <30%) and manually segmented DWI lesion co-registered to the CT space. We report Bland-Altman analyses with mean difference between ROI methods and 95% confidence intervals (mean[95%CI]) for the following measurements: total volume, volume with <26 Hounsfield units (HU) and >26HU, volume with >10% and >20% relative hypodense voxels, average (avg), median, and standard deviation of density (HU) in the ROI, net water uptake (NWU=[1-mean density ischemic/contralateral ROI]), proportion of the total lesion with >10% and >20% relative hypodense voxels. Relative hypodensity was measured as the percentage difference between ischemic and contralateral voxels.
Results:
Mean differences for volume measures varied considerably for DLCT-CTP (total volume 1.6mL [-54.8;61.6]); volume<26HU 1.3mL [-16.5;19.0]), DLCT-DWI (total volume -22.0mL [-114.5; 70.6]; volume<26HU -3.0mL [-19.9; 13.9]), and CTP-DWI (total volume -23.6mL [100.6; 53.4]; volume<26HU -4.3mL [-22.4; 13.9]). However, DLCT-DWI and CTP-DWI had similar differences. Contrary to volume measure, average density and net water uptake measures had lower differences between DLCT-CTP (avg: -0.7HU [-5.1; 3.8]; NWU: 3% [-9;15]), DLCT-DWI (avg: -1.6HU [-6.8; 3.6]; NWU: 5% [-7; 18]), and CTP-DWI (avg: -1.6HU [-4.8; 1.7]; NWU: 2% [-8; 11]). Figure 2 describes all other variables.
Conclusion:
DLCT, CTP, and DWI techniques demonstrate relatively low mean differences for volume and hypodensity measurements, but substantial variability is present despite this agreement on average. Further research should identify if these variations alter associations with clinical outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Kesten Jamie, Mlynash Michael, Yuen Nicole, Seners Pierre, Wouters Anke, Schwartz Maya, Lansberg Maarten, Albers Gregory, Heit Jeremy
Attenuating Post-stroke Ischemia Reperfusion Injury: Establishing the Efficacy of Disodium Malonate in a Clinically Relevant Sheep ModelSorby-adams Annabel, Murphy Mike, Sharkey Jessica, Prag Hiran, Turner Renee, Skein Keziah, Guglietti Bianca, Pullan Caitlin, Williams Georgia, Krieg Thomas
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.