Final ID: 69
Both Infarct and Non-infarcted Brain Regions Drive Acute Deep Learning Based MRI Prediction of Stroke Outcome
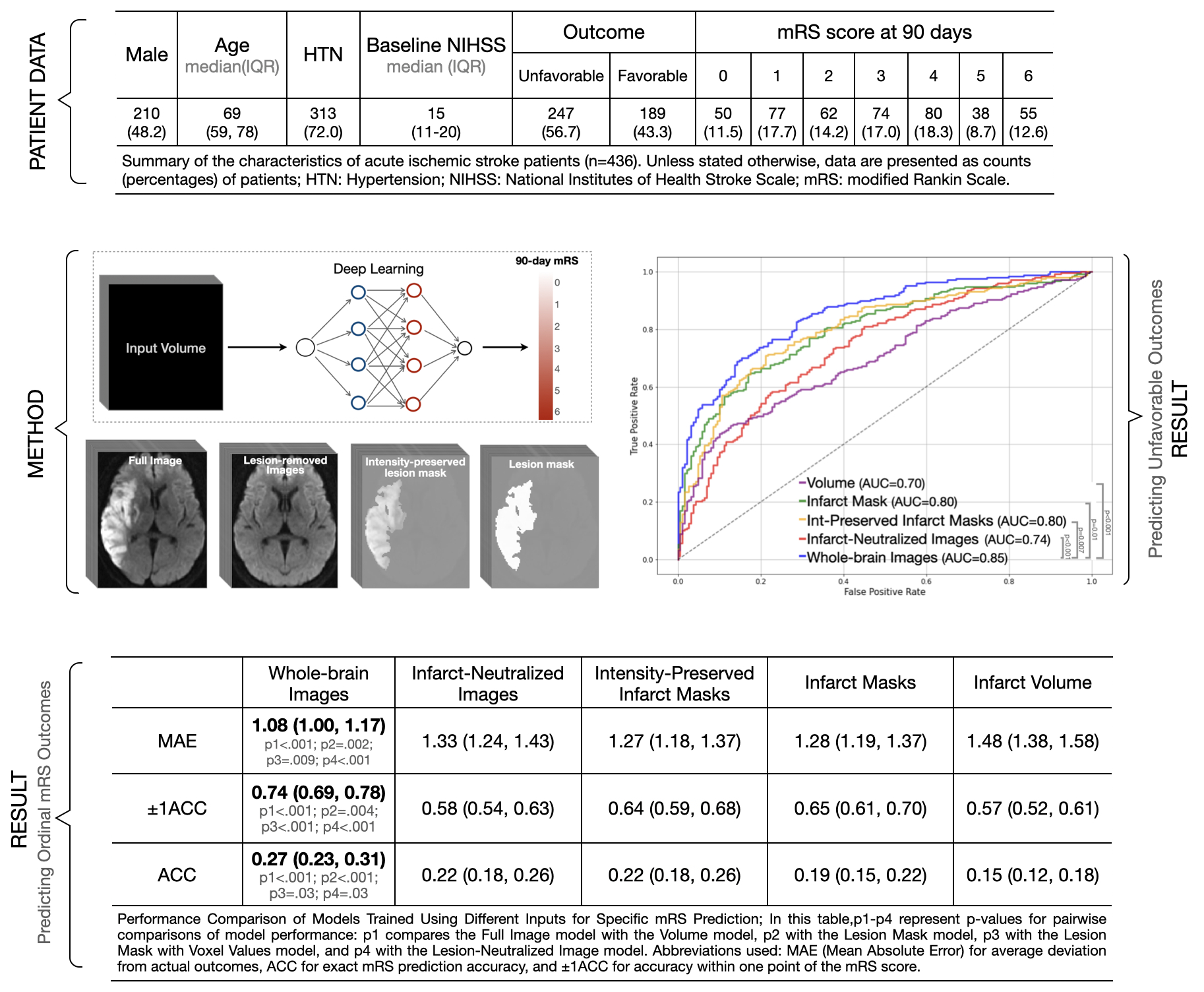
Materials and Methods: We developed and validated deep learning (DL) models on a cohort of 436 AIS patients, using MRI diffusion-weighted imaging scans from 1-7 days post-stroke and 90-day modified Rankin Scale (mRS) follow-up data. These models were trained on various inputs— infarct volumes, whole-brain images, infarct masks, intensity-preserved infarct masks, and images in which the infarct region is removed, which we call infarct-neutralized images, and which enable an assessment of overall brain health. Model performance was assessed based on the accuracy of predicting the specific mRS score, accuracy within ±1 mRS category, mean absolute error (MAE), and the ability to predict unfavorable outcomes (mRS > 2) using receiver operator curve (ROC) metrics.
Results: The infarct volume model had the highest (worst) MAE of 1.48 points (95% CI: 1.38-1.58, p < 0.001), while the whole-brain model achieved the lowest (best) MAE of 1.08 points (95% CI: 1.00-1.17). Models with intermediate imaging information—such as infarct masks (MAE 1.28, 95% CI: 1.19-1.37, p = .002), intensity-preserved infarct masks (MAE 1.27, 95% CI: 1.18-1.37, p = .009), and infarct-neutralized images (MAE 1.33, 95% CI: 1.24-1.43, p < .001)—improved upon the volume-only predictions. For predicting unfavorable outcomes, the infarct volume model had the lowest performance (AUC 0.70, 95% CI: 0.65-0.75; p < .001), while the whole-brain model achieved the highest AUC of 0.85 (95% CI: 0.82-0.89), outperforming the infarct mask (AUC 0.80, 95% CI: 0.76-0.84; p = .01), intensity-preserved infarct mask (AUC 0.80, 95% CI: 0.76-0.84; p = .007), and infarct-neutralized images (AUC 0.74, 95% CI: 0.69-0.79; p < .001)
Conclusions: The best predictive performance was achieved using voxel values from the entire brain, showing that both infarcted and non-infarcted regions contribute significantly to accuracy. Non-infarcted areas may reflect overall brain health and resilience, informing potential outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Thoroughman Rose, Riley Alan, De Loizaga Sarah, Adams David, Beaton Andrea, Buonfiglio Samantha, Danforth Kristen, Masyuko Sarah, Miller Mccall, Yadava Mrinal
A First-in-Class Humanized Antibody Fragment Targeting Platelet Glycoprotein Ibα: A Comprehensive Preclinical Study of CA1001 for the Treatment of Acute Ischemic StrokeXu Xiaohong, Preeti Preeti, Yu Ruoying, Shaykhalishahi Hamed, Zhang Cheng, Shen Chuanbin, Li Bei, Tang Naping, Chang Yan, Xiang Qian, Cui Yimin, Lei Xi, Ni Heyu, Zhu Guangheng, Liu Zhenze, Hu Xudong, Slavkovic Sladjana, Neves Miguel, Ma Wenjing, Xie Huifang
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.