Final ID: WP297
Sex-specific Trends in the Prevalence of Stroke Risk Factors and Medication Use in the GCNKSS
Abstract Body: Background: Existing data indicate recent increases in the prevalence of stroke and relevant risk factors as well as predicted continued increases in coming years. Our objective was to evaluate population-based data on the prevalence of stroke risk factors and related medication use by sex through 2021.
Methods: Data on the prevalence of stroke risk factors and medication use were taken from our general population random-digit dial survey conducted during 6 time periods: 1995, 2000, 2005, 2011, 2016, and 2021. Due to survey sampling design, survey participants' characteristics (sex, race, age) are representative of the Greater Cincinnati Northern Kentucky Stroke Study (GCNKSS) ischemic stroke study population. We examined the proportion of females vs. males who reported having hypertension (HTN), hyperlipidemia (HL), diabetes (DM), and current smoking and who reported using antihypertensive medications, lipid-lowering agents, aspirin, and anticoagulants (AC).
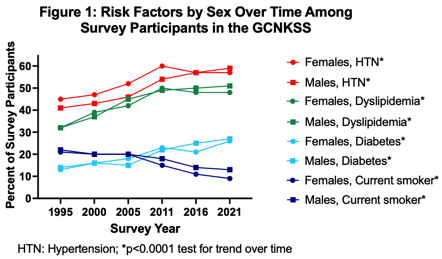
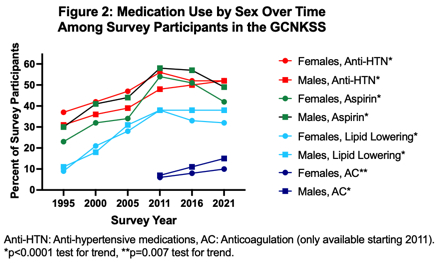
Results: Over 6 study periods, a total of 12,336 participants completed the survey; 59% were female, and 25% were Black. Mean age of participants (in years) went up over time in both females (64 [SD 16.3] in 1995 to 69 [SD 16.4] in 2021) and males (61 [SD 15.7] in 1995 to 67 [SD 16.8] in 2021), ptrend <0.0001 for both). Prevalence of HTN, DM, and HL increased over the 6 study periods in both females and males, and current smoking decreased (Figure 1, all ptrend <0.0001). All preventive medications (anti-hypertensives, lipid-lowering, aspirin, and AC) assessed increased over time (Figure 2). In 2021, similar proportions of females vs. males had HTN, DM, DL, and were current smokers (p>0.05). Further, similar proportions of females vs. males were on antihypertensives, lipid-lowering medications, and aspirin, though more men than women were on AC (15% vs. 10%, p<0.05).
Conclusions: In this population-based survey of residents of a 5-county region of southern Ohio and northern Kentucky, the reported prevalence of stroke risk factors increased over a 26-year period in both females and males, as did use of medications used to modify these risk factors. An increasing burden of cardiometabolic risk factors may increase stroke event rates in the future and points to the need for improved primordial prevention.
Methods: Data on the prevalence of stroke risk factors and medication use were taken from our general population random-digit dial survey conducted during 6 time periods: 1995, 2000, 2005, 2011, 2016, and 2021. Due to survey sampling design, survey participants' characteristics (sex, race, age) are representative of the Greater Cincinnati Northern Kentucky Stroke Study (GCNKSS) ischemic stroke study population. We examined the proportion of females vs. males who reported having hypertension (HTN), hyperlipidemia (HL), diabetes (DM), and current smoking and who reported using antihypertensive medications, lipid-lowering agents, aspirin, and anticoagulants (AC).
Results: Over 6 study periods, a total of 12,336 participants completed the survey; 59% were female, and 25% were Black. Mean age of participants (in years) went up over time in both females (64 [SD 16.3] in 1995 to 69 [SD 16.4] in 2021) and males (61 [SD 15.7] in 1995 to 67 [SD 16.8] in 2021), ptrend <0.0001 for both). Prevalence of HTN, DM, and HL increased over the 6 study periods in both females and males, and current smoking decreased (Figure 1, all ptrend <0.0001). All preventive medications (anti-hypertensives, lipid-lowering, aspirin, and AC) assessed increased over time (Figure 2). In 2021, similar proportions of females vs. males had HTN, DM, DL, and were current smokers (p>0.05). Further, similar proportions of females vs. males were on antihypertensives, lipid-lowering medications, and aspirin, though more men than women were on AC (15% vs. 10%, p<0.05).
Conclusions: In this population-based survey of residents of a 5-county region of southern Ohio and northern Kentucky, the reported prevalence of stroke risk factors increased over a 26-year period in both females and males, as did use of medications used to modify these risk factors. An increasing burden of cardiometabolic risk factors may increase stroke event rates in the future and points to the need for improved primordial prevention.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adrenal Zona Glomerulosa Long Form Leptin Receptor (LepRb) Protects from Leptin-Mediated Vascular Disorders in Female Mice
Ono Yoichi, Kennard Simone, Breault David, Belin De Chantemele Eric
A Case Series of Papillary Fibroelastomas on the Coumadin ridgeAboukhatwa Omar, Akiki Elias, Kurmann Reto, Larson Kathryn, Keeney Michael, Bois Melanie, Klarich Kyle
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)