Final ID: 96
Integrated Genomic and Proteomic Profiling Support Cathepsin-B as a Drug Repurposing Target in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease
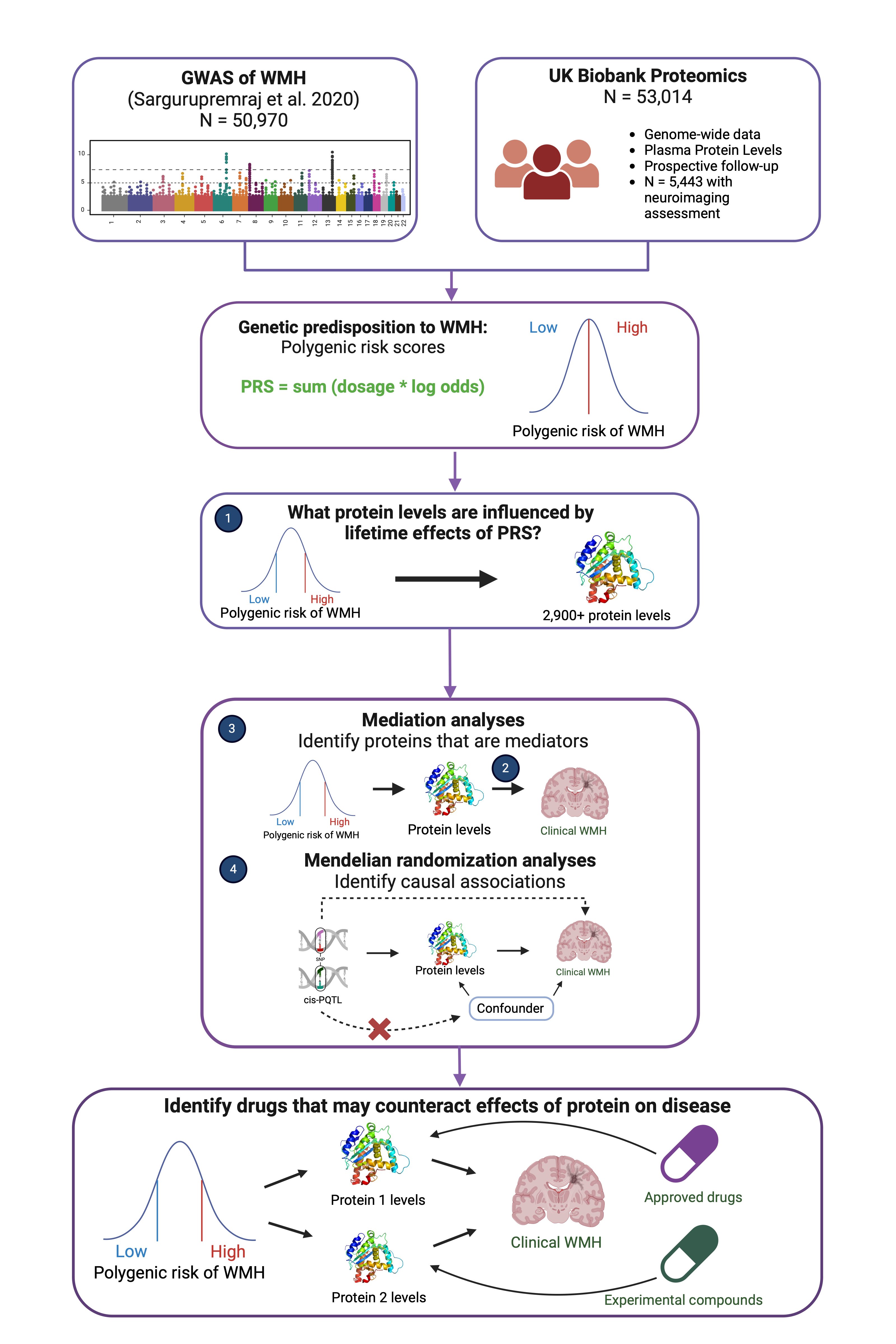
Methods: We analyzed data from 53,014 participants enrolled in the UK Biobank. The analytical pipeline involved (Figure 1): 1) linear regression analyses between a polygenic risk score of WMH (from 27 independent variants) and normalized levels of 2,923 proteins ascertained at baseline, adjusting for age, sex, and genetic principal components; 2) evaluation of proteins selected in step 1 for association with WMH volume, ascertained through dedicated research MRIs; 3) mediation analyses to confirm that proteins with significant and directionally concordant associations with both the polygenic score and WMH are indeed mediators of the polygenic score-WMH relationship; 4) Mendelian Randomization using cis-protein quantitative trait loci as instruments to evaluate the causality between selected proteins and WMH and other clinical manifestation of CSVD. Each step was adjusted for multiple testing using Bonferroni correction.
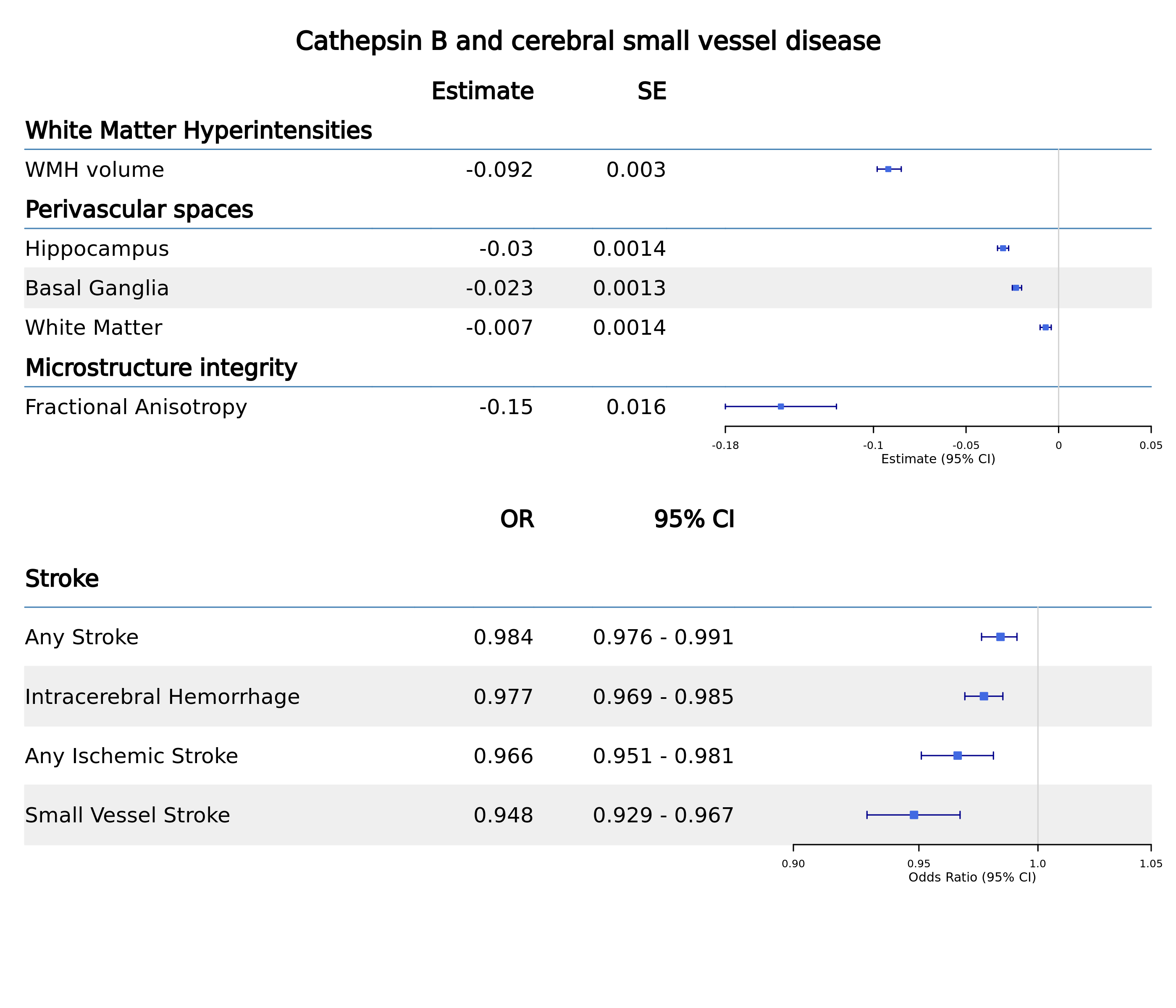
Results: Our analyses identified two proteins (Cathepsin B and ECHDC3) that met all the criteria to mediate the polygenic effect of CSVD on WMH. However, only one of these, Cathepsin B, was confirmed by Mendelian Randomization (Beta: -0.092, SE: 0.003, P<0.001). Mendelian Randomization also confirmed the association between Cathepsin B and the risk of intracerebral hemorrhage, small vessel stroke, perivascular spaces volumes, and alterations in white matter microstructure (Figure 2).
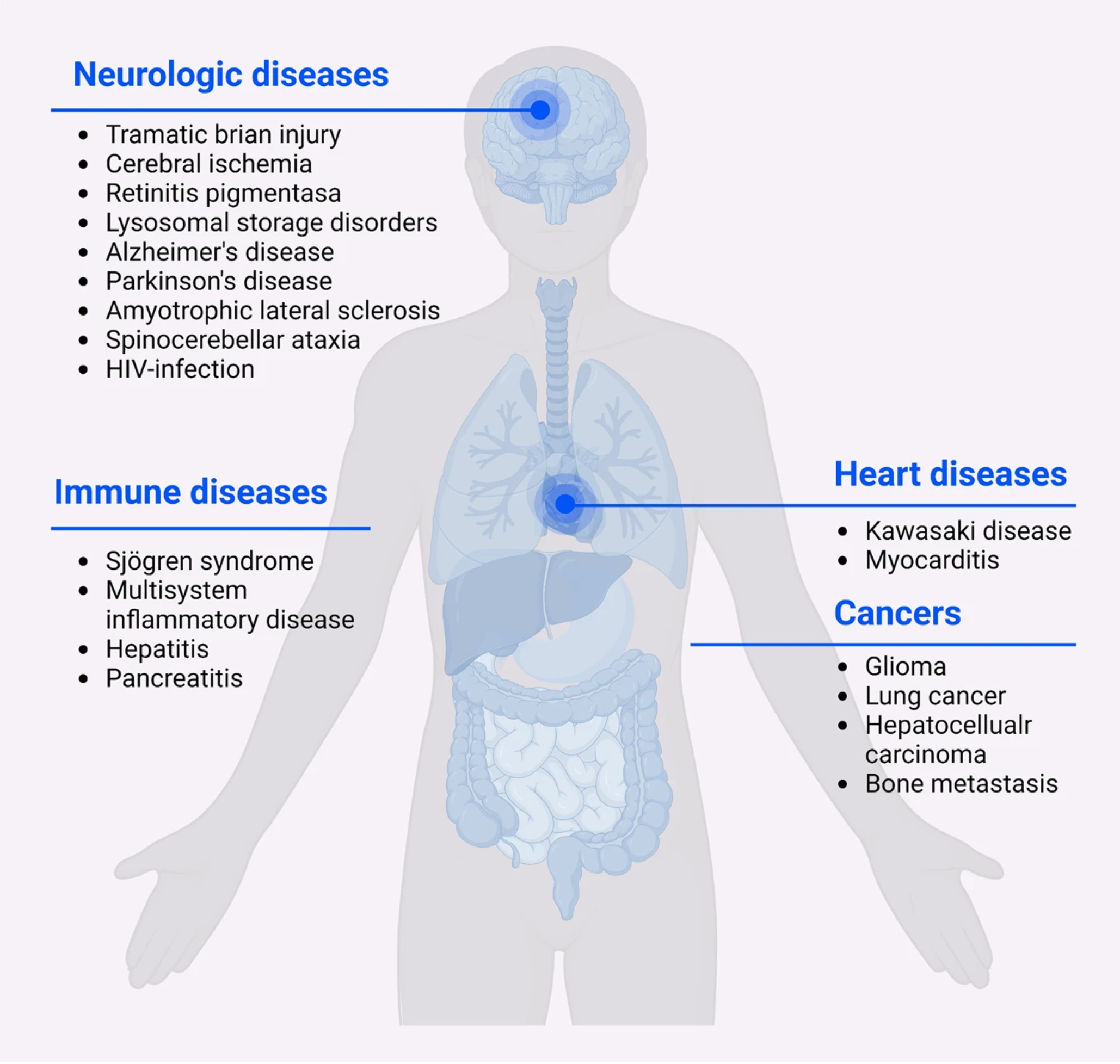
Conclusions: Our combined genetic and proteomic approach successfully identified Cathepsin B as a protein linked to WMH and other CSVD phenotypes. Cathepsin B, a lysosomal protease, is well-known for its involvement in programmed cell death, including hypoxia/ischemia-induced neuronal death, a key pathophysiological process leading to WMH (Figure 3). Compounds targeting Cathepsin B have shown promising results in reducing neuronal death and neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease models, where WMH often precedes disease onset. This finding provides a basis for repurposing Cathepsin B-targeting compounds to stabilize WMH burden.
More abstracts on this topic:
Zhang David, Ritchie Marylyn, Rader Daniel, Cuchel Marina
A new genetic model organism for primate-specific cardiac function and diseaseChang Stephen, Albertelli Megan, Quertermous Thomas, Wright Patricia, Terrien Jeremy, Aujard Fabienne, Wu Joseph, Krasnow Mark, Karanewsky Caitlin, Pendleton Jozeph, Ren Lu, Anzeraey Aude, Froelicher Victor, Liang David, Razafindrakoto Andriamahery, Ravelonjanahary Noeline
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.