Final ID: TMP98
Low-dose Rivaroxaban plus Antiplatelet Treatment in Patients With Symptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis:A Prospective Observational Study
Abstract Body: Background:
The secondary prevention of symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis (sICAS) remains a significant challenge. In the recent COMPASS (Cardiovascular Outcomes for People Using Anticoagulation Strategies) trial, the combination of low-dose rivaroxaban with antiplatelet therapy demonstrated better efficacy in preventing vascular events in patients with coronary atherosclerosis compared to antiplatelet therapy alone. This study aimed to evaluate the efficiency of dual pathway inhibition on recurrent stroke and vascular events in patients with sICAS.
Methods:
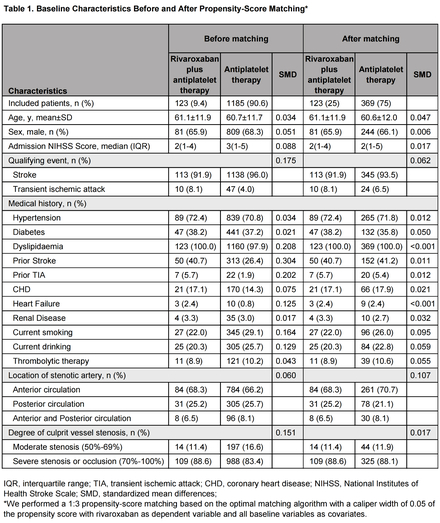
Patients with sICAS admitted within 7 days of symptom onset were identified from the hospital-based database from January 2019 to June 2023. We compared the clinical outcomes of low-dose rivaroxaban combined with antiplatelet therapy (Rivaroxaban 2.5mg bid plus asprin or clopidogrel) and antiplatelet therapy alone (dual antiplatelet therapy or antiplatelet monotherapy) among patients with sICAS. The primary outcome was a composite of all-cause death, ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack, and acute coronary syndrome within one year post-stroke. Propensity score matching was performed in a 1:3 ratio for the two groups of patients to mitigate confounders, adjusted hazard ratios (HR) were estimated using multivariate Cox regression model. The win-ratio method was employed to assess the composite outcome.
Results:
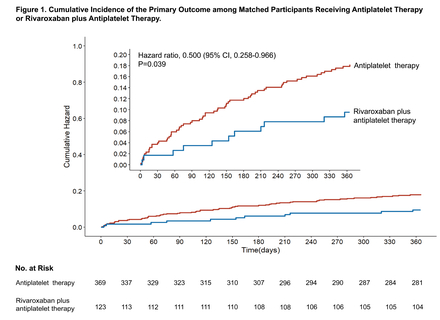
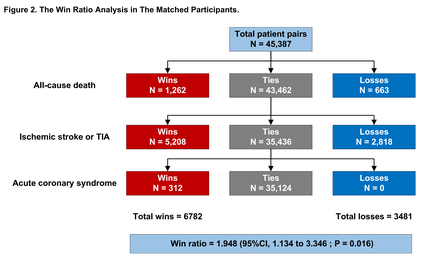
Among 1,308 patients, 123 (9.4%) were prescribed rivaroxaban and antiplatelet therapy. In the matched population, the primary endpoint event rate in this group was lower (11/123 [8.9%] vs. 63/369 [17.1%], P=0.029). Multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed a significant benefit from low-dose rivaroxaban (adjusted HR=0.459, 95% CI: 0.234-0.897, P=0.023). In addition, coronary heart disease (adjusted HR=1.674, 95% CI: 1.013-2.766, P=0.044) was identified as a risk factor associated with composite outcome during the 1-year follow-up. In the analysis of the hierarchical composite end point, the results for the primary end point favored rivaroxaban plus antiplatelet therapy (win ratio=1.948, 95% CI: 1.134-3.346, P=0.016).
Conclusions:
Low-dose rivaroxaban combined with antiplatelet therapy was superior to antiplatelet therapy alone for the prevention of all-cause death, recurrent stroke and acute coronary syndrome among patients with sICAS. These findings are preliminary and warrant further investigation through randomized controlled trials.
The secondary prevention of symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis (sICAS) remains a significant challenge. In the recent COMPASS (Cardiovascular Outcomes for People Using Anticoagulation Strategies) trial, the combination of low-dose rivaroxaban with antiplatelet therapy demonstrated better efficacy in preventing vascular events in patients with coronary atherosclerosis compared to antiplatelet therapy alone. This study aimed to evaluate the efficiency of dual pathway inhibition on recurrent stroke and vascular events in patients with sICAS.
Methods:
Patients with sICAS admitted within 7 days of symptom onset were identified from the hospital-based database from January 2019 to June 2023. We compared the clinical outcomes of low-dose rivaroxaban combined with antiplatelet therapy (Rivaroxaban 2.5mg bid plus asprin or clopidogrel) and antiplatelet therapy alone (dual antiplatelet therapy or antiplatelet monotherapy) among patients with sICAS. The primary outcome was a composite of all-cause death, ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack, and acute coronary syndrome within one year post-stroke. Propensity score matching was performed in a 1:3 ratio for the two groups of patients to mitigate confounders, adjusted hazard ratios (HR) were estimated using multivariate Cox regression model. The win-ratio method was employed to assess the composite outcome.
Results:
Among 1,308 patients, 123 (9.4%) were prescribed rivaroxaban and antiplatelet therapy. In the matched population, the primary endpoint event rate in this group was lower (11/123 [8.9%] vs. 63/369 [17.1%], P=0.029). Multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed a significant benefit from low-dose rivaroxaban (adjusted HR=0.459, 95% CI: 0.234-0.897, P=0.023). In addition, coronary heart disease (adjusted HR=1.674, 95% CI: 1.013-2.766, P=0.044) was identified as a risk factor associated with composite outcome during the 1-year follow-up. In the analysis of the hierarchical composite end point, the results for the primary end point favored rivaroxaban plus antiplatelet therapy (win ratio=1.948, 95% CI: 1.134-3.346, P=0.016).
Conclusions:
Low-dose rivaroxaban combined with antiplatelet therapy was superior to antiplatelet therapy alone for the prevention of all-cause death, recurrent stroke and acute coronary syndrome among patients with sICAS. These findings are preliminary and warrant further investigation through randomized controlled trials.
More abstracts on this topic:
Efficacy of Lipid-Lowering Therapies in Reducing Stroke Risk in Intracranial Atherosclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abdelkader Omar, Shourav Md Manjurul Islam, Vallamchetla Sai Krishna, Elnaggar Ali, Ramadan Doaa, Badi Mohammed, Meschia James, Lin Michelle
Age, Race, and Insurance Status Influences on Anticoagulation Therapy and Discharge Disposition: A Retrospective AnalysisTran Vi, Tjionas Panayiotis, Bowry Ritvij, Samuel Sophie
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)