Final ID: WP327
Identifying Novel Determinants of Death and Readmission Post-Stroke Using Explainable Machine Learning Algorithms
Identifying new determinants of death and hospital readmission can help inform target patient populations at high risk for poor transitions of care. Explainable machine learning (XML) algorithms are valuable tools to determine novel modifiable predictors in complex datasets. The goal of this study was to identify risk factors for death and readmission within 90 days post-stroke, focusing on novel non-clinical factors, including social determinants of health (SDOH), neighborhood characteristics, and post-stroke health behaviors. To achieve this goal, we explored the results of 11 distinct XML models, to identify predictors that were common and strong across models.
Methods
The study population included 1300 stroke survivors in the Transitions of Care Stroke Disparities Study (TCSD-S), a prospective cohort of patients from 10 comprehensive stroke centers who participated in the Florida Stroke Registry in 2018-2023 (mean age=63.8 (13.9), 56% male, 22% Hispanic, 23% Non-Hispanic Black,51% Non-Hispanic White; 92% ischemic stroke). 90-Day death and readmission (N=192) were obtained from patient interviews and review of medical records. Data on 65 potential risk factors were obtained from Get With The Guidelines-Stroke (demographics, clinical characteristics, medical history, acute care), as well as publicly available neighborhood characteristics (SES, race/ethnicity, business density), and patient interviews at discharge (SES, living arrangement, social support) and 30 days post-stroke (health behaviors). We used 11 distinct XML models to identify the top 12 predictors of death or readmission in each model, resulting in 38 out of 65 distinct predictors across models. Predictors were ranked based on strength of association and consistency across models using feature agreement.
Results
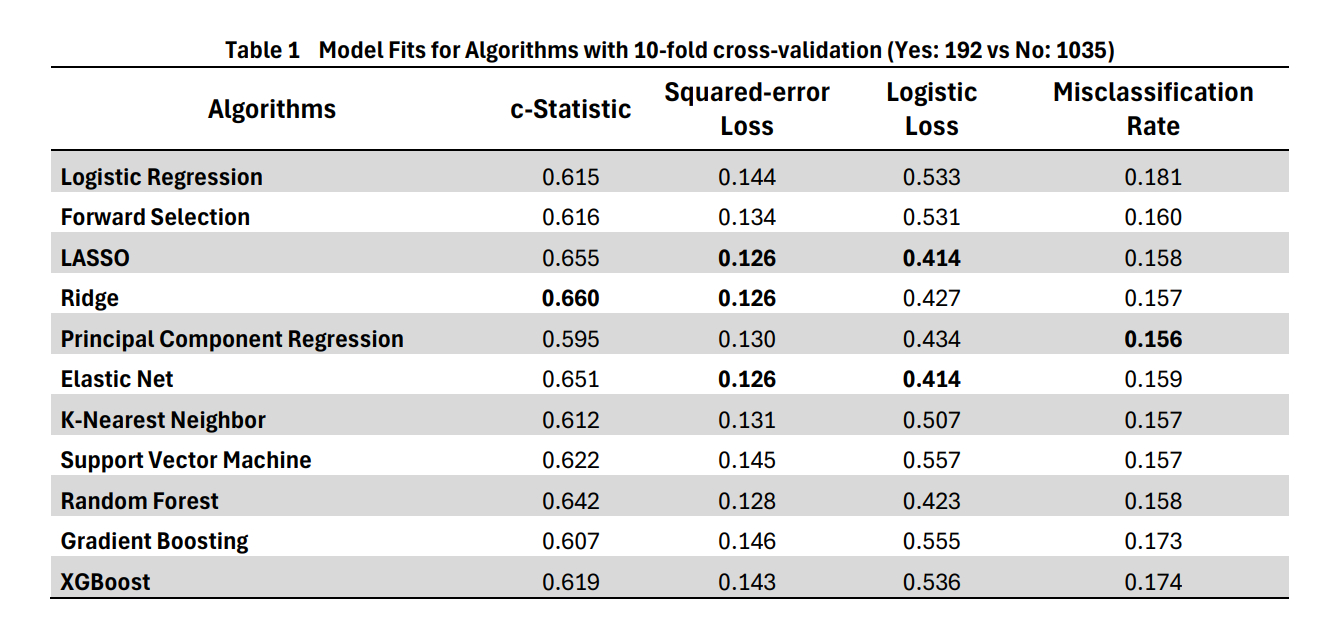
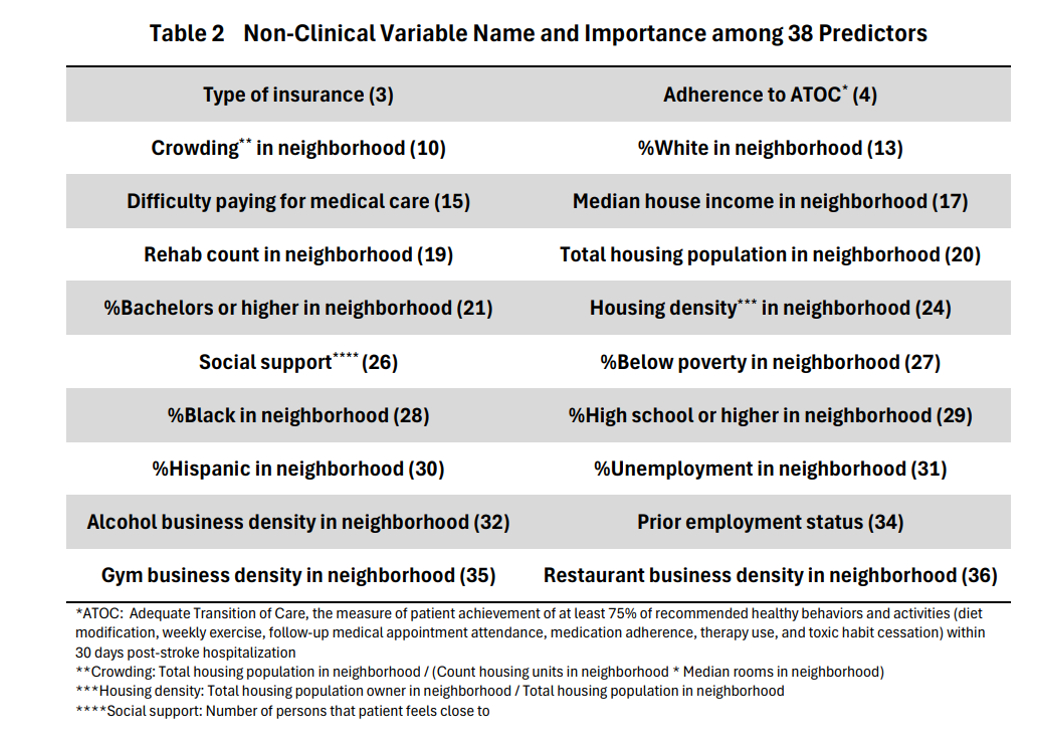
Table 1 shows model fit statistics across all XML models with best values in bold. Out of 38 identified predictors, 20 are non-clinical variables. Table 2 shows their rank order. The identified variables reflect the importance of SDH, environmental factors, and behavioral modifications, beyond traditional clinical predictors of death/readmission.
Conclusion
XML methods emphasized the importance of non-clinical factors, including SDOH, environmental factors, and behavioral modifications, in transitions of stroke care and stroke outcomes. This illustration of the ability of XML models to find novel and nonobvious predictors may increase the trust in results produced by XML.
More abstracts on this topic:
Marrero Natalie, Thanassoulis George, Rotter Jerome, Blaha Michael, Whelton Seamus, Jha Kunal, Grant Jelani, Razavi Alexander, Budoff Matthew, Shah Sanjiv, Blumenthal Roger, Post Wendy, Shaw Leslee
A Comprehensive Study on Machine Learning Models Combining with Oversampling for One-year Persistent Coronary Artery Aneurysm in Kawasaki DiseaseLiang Kaizhi, Pang Yusheng, Su Danyan
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.