Final ID: WP73
Effect of Nurse Driven Stroke Alert Activation on Door to Needle Times
Abstract Body: Background: Research indicates that quicker response times from onset of stroke symptoms to the initiation of treatment result in better recovery outcomes. The purpose of this study is to determine if consistent nurse-led stroke alert activation improves door to needle (DTN) times, which frequently results in better patient outcomes.
Method: The method applied was a retrospective review of stroke alert records to evaluate the efficacy of different activation models. The period included in this review was January 2023 through December 2024. Each facility in this study is a primary stroke center with similar stroke alert volumes and treatment rates. The first facility reviewed (Facility “A”) used a physician-driven activation model in which a provider evaluated the patient to confirm appropriateness of neurological needs prior to stroke alert activation. The second facility included for review (Facility “B”) was consistently activating stroke alerts based on nursing evaluation alone. Taking the review a step further, the impact of implementing a nurse-driven activation process on door-to-needle times was included (Facility “C”).
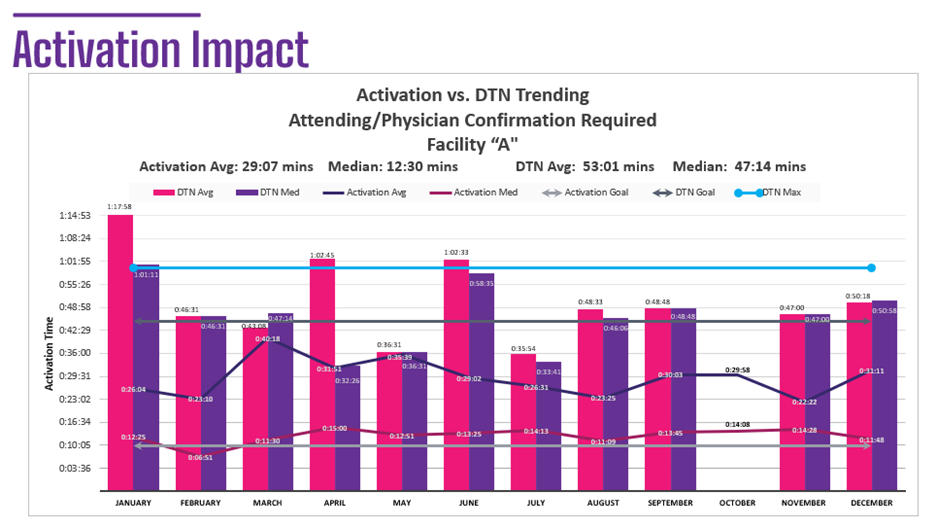
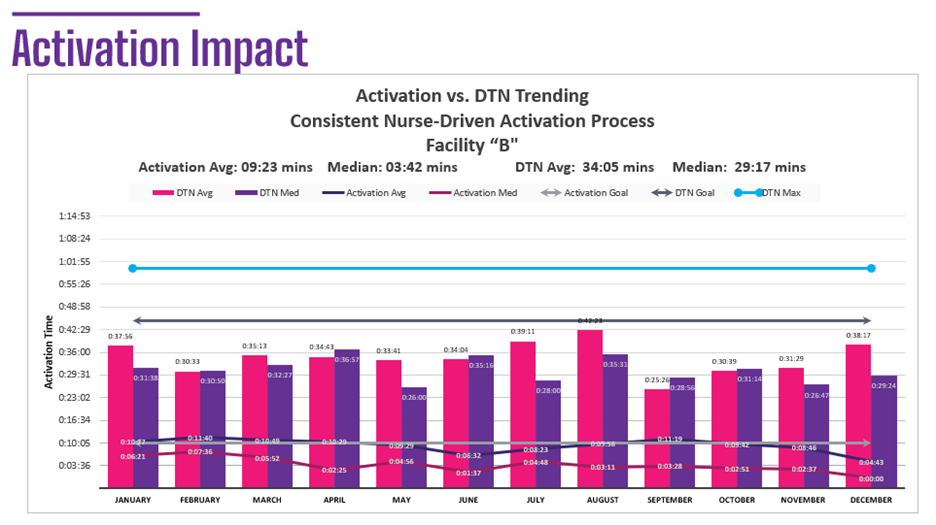
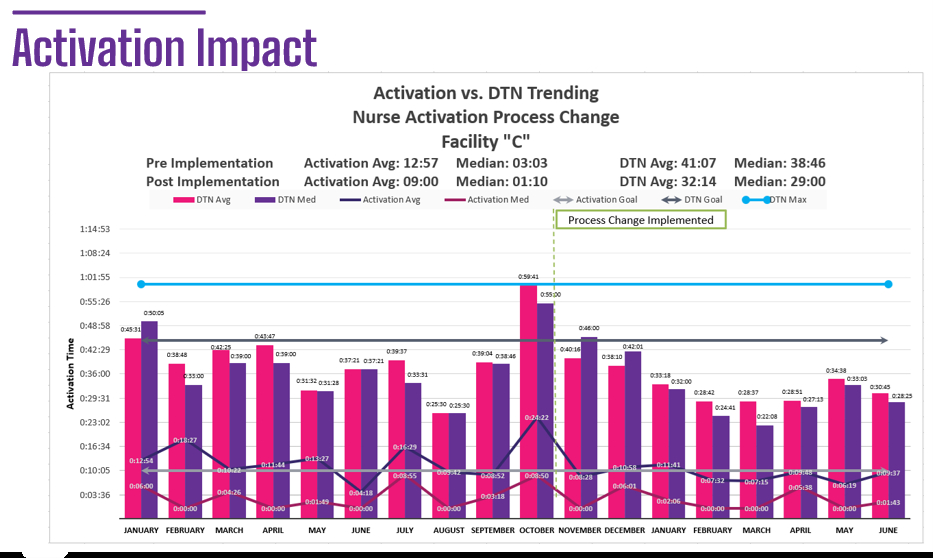
Results: Facility “A” had a physician-driven activation model. In the time evaluated, the activation average was 29 minutes with an average DTN of 53 minutes. Facility “B” had a consistent nurse-driven activation model. The activation average was 9 minutes with a DTN average of 34 minutes. The 68% faster activation time resulted in a 35% improvement in DTN. Finally, Facility “C” implemented a nurse-driven activation model as a process improvement project. From October 2023 (when process improvement implementation was initiated) through June 2024, their activation time average improved from 13 minutes to 10 minutes (23% improvement) and their DTN average improved from 41 minutes to 33 minutes (19% improvement).
Conclusion: The implementation of a nurse-driven activation model decreases DTN times. Our data supports that empowering nurses to activate the stroke team based on their independent assessment promotes earlier activation, improves DTN times and ultimately, patient outcomes.
Method: The method applied was a retrospective review of stroke alert records to evaluate the efficacy of different activation models. The period included in this review was January 2023 through December 2024. Each facility in this study is a primary stroke center with similar stroke alert volumes and treatment rates. The first facility reviewed (Facility “A”) used a physician-driven activation model in which a provider evaluated the patient to confirm appropriateness of neurological needs prior to stroke alert activation. The second facility included for review (Facility “B”) was consistently activating stroke alerts based on nursing evaluation alone. Taking the review a step further, the impact of implementing a nurse-driven activation process on door-to-needle times was included (Facility “C”).
Results: Facility “A” had a physician-driven activation model. In the time evaluated, the activation average was 29 minutes with an average DTN of 53 minutes. Facility “B” had a consistent nurse-driven activation model. The activation average was 9 minutes with a DTN average of 34 minutes. The 68% faster activation time resulted in a 35% improvement in DTN. Finally, Facility “C” implemented a nurse-driven activation model as a process improvement project. From October 2023 (when process improvement implementation was initiated) through June 2024, their activation time average improved from 13 minutes to 10 minutes (23% improvement) and their DTN average improved from 41 minutes to 33 minutes (19% improvement).
Conclusion: The implementation of a nurse-driven activation model decreases DTN times. Our data supports that empowering nurses to activate the stroke team based on their independent assessment promotes earlier activation, improves DTN times and ultimately, patient outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Assessing Social Vulnerability's Effect on Patient Outcomes in Los Angeles County Stroke Patients Among a Health System and Its Impact on Health Disparities
Mayorga Lina, Bohn Joe, Levin Dr Bruce L, Kim-tenser May, Sanossian Nerses, Towfighi Amytis
Digital Health Literacy and Levels of Stroke Literacy Among Thai Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Correlational StudyPotisopha Wiphawadee, Changrueang Orawee, Theeranut Ampornpan
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)