Final ID: WP69
The effect of caregiver engagement in feeding practices on oral feeding resumption in rehabilitation among stroke survivors
Abstract Body: Objective:
Stroke patients with tube feeding have a high probability of feeding problems when they had regained oral intake ability. Assisting patients with eating is a major task for caregivers and they require better training. We developed an intervention to engage caregiver in feeding patients prior to feeding tube removal and examined the impact on oral feeding resumption in rehabilitation among stroke survivor.
Methods:
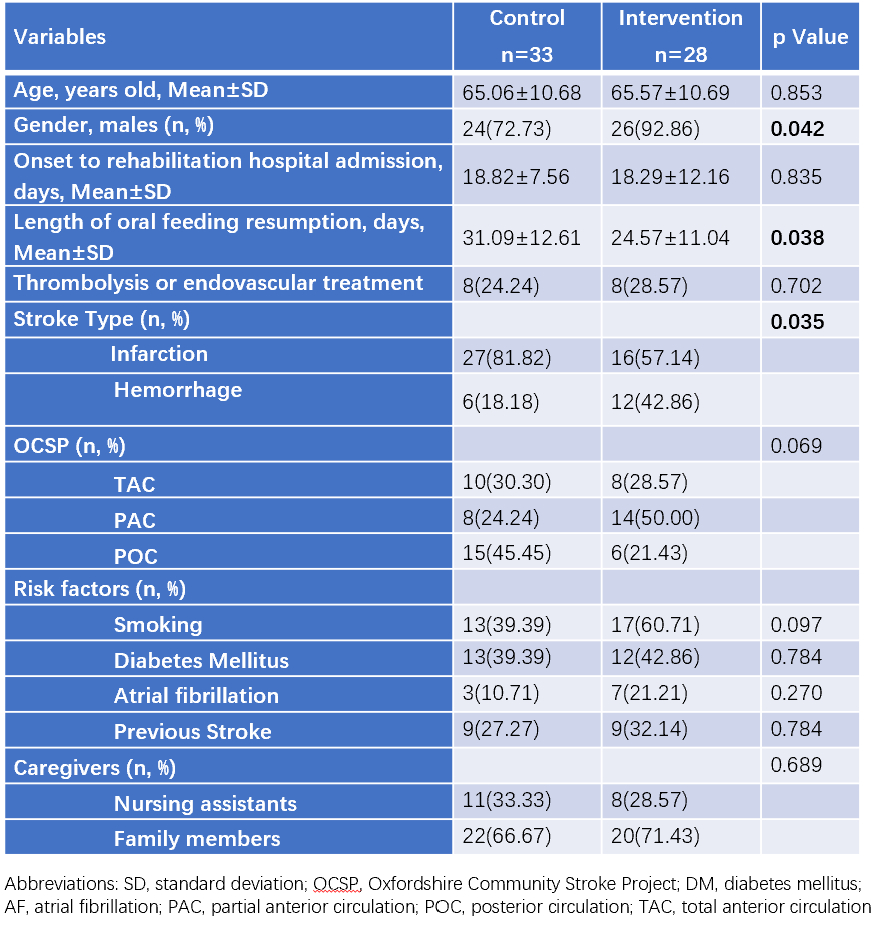
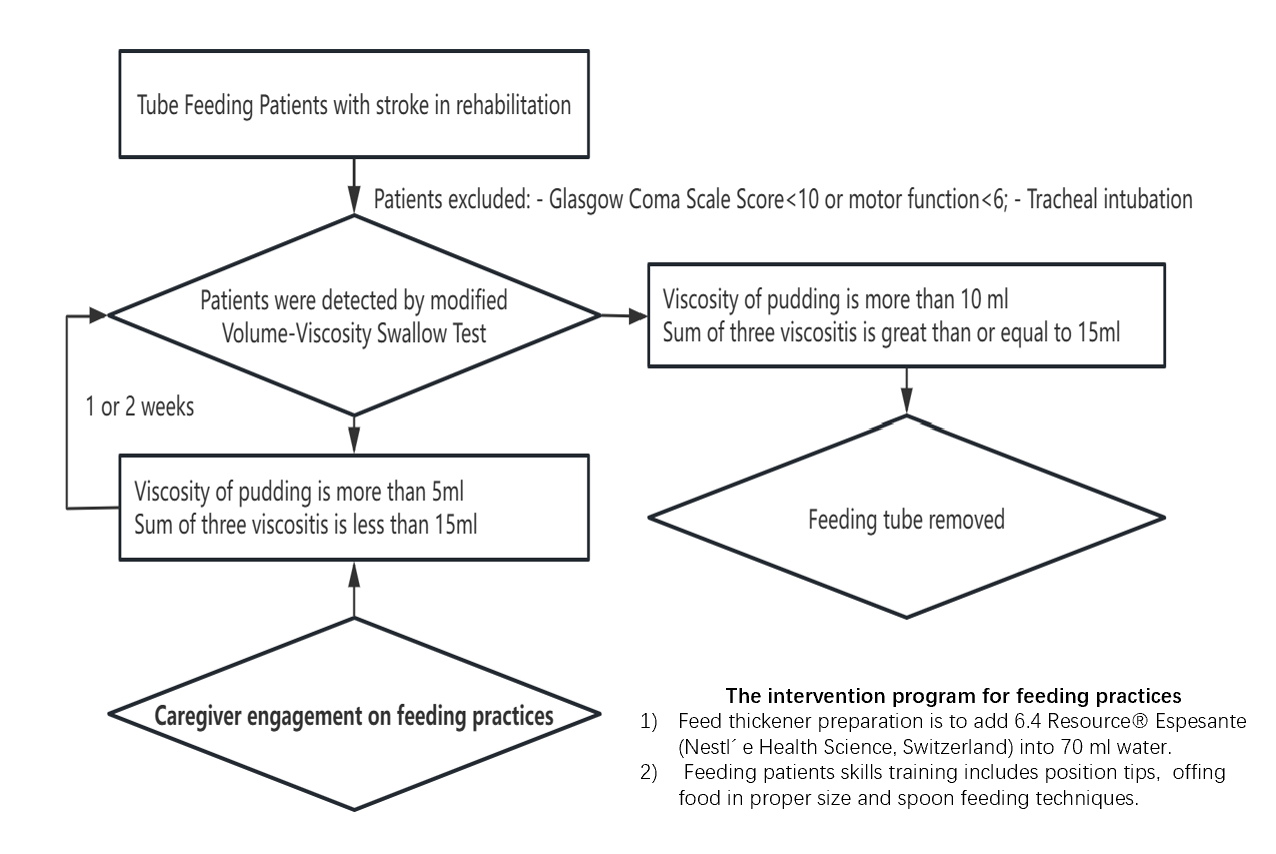
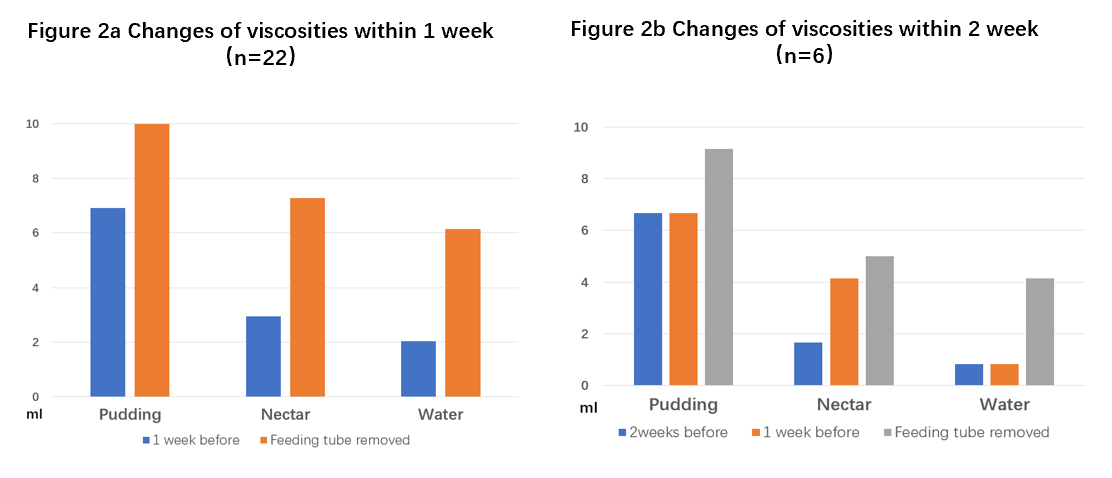
A total of 61 stroke patients with dysphagia recovery were enrolled in rehabilitation hospital from Jan. 2021 to Jul. 2024. They all recovered from tube feeding to complete oral feeding before discharge. Inclusion criteria included 1) Stroke patients with feeding tube. 2) Impaired oral intake which was defined as viscosity of pudding ≥5 ml and sum of three viscosities ≤15 ml based on the modified Volume-viscosity Swallow Test (V-VST). An intervention for caregivers, which engaged them on feeding practices was introduced from Jan 2023 to Jul 2024. The intervention program for feeding practices was primarily carried out by ward nurses. It consisted of thickener preparation and feeding patients skills training. Outcomes were compared between an intervention group of 28 patients and a historical control group of 33 patients recruited between Jan 2021 to Jul 2022. We compared the baseline characteristics and the length of oral feeding resumption between the groups. Volume change of three viscosities was represented by bar graphs.
Results:
The length of patients who could remove the tube feeding and completed oral feeding resumption was significantly shorter in the intervention group compared with the control group (24.57±11.04 days vs 31.09±12.61 days, P=0.038). 22/28 (78.6%) patients in the intervention group had their feeding tubes removed within one week. The volume growth of three different viscosities was demonstrated following the intervention. Swallowing function of stroke patients in the intervention group improved more quickly compared
Conclusion:
Our data indicated that effective caregiver engagement is necessary. Successful caregiver engagement has the potential to reduce costs and enhance patient outcomes.
Stroke patients with tube feeding have a high probability of feeding problems when they had regained oral intake ability. Assisting patients with eating is a major task for caregivers and they require better training. We developed an intervention to engage caregiver in feeding patients prior to feeding tube removal and examined the impact on oral feeding resumption in rehabilitation among stroke survivor.
Methods:
A total of 61 stroke patients with dysphagia recovery were enrolled in rehabilitation hospital from Jan. 2021 to Jul. 2024. They all recovered from tube feeding to complete oral feeding before discharge. Inclusion criteria included 1) Stroke patients with feeding tube. 2) Impaired oral intake which was defined as viscosity of pudding ≥5 ml and sum of three viscosities ≤15 ml based on the modified Volume-viscosity Swallow Test (V-VST). An intervention for caregivers, which engaged them on feeding practices was introduced from Jan 2023 to Jul 2024. The intervention program for feeding practices was primarily carried out by ward nurses. It consisted of thickener preparation and feeding patients skills training. Outcomes were compared between an intervention group of 28 patients and a historical control group of 33 patients recruited between Jan 2021 to Jul 2022. We compared the baseline characteristics and the length of oral feeding resumption between the groups. Volume change of three viscosities was represented by bar graphs.
Results:
The length of patients who could remove the tube feeding and completed oral feeding resumption was significantly shorter in the intervention group compared with the control group (24.57±11.04 days vs 31.09±12.61 days, P=0.038). 22/28 (78.6%) patients in the intervention group had their feeding tubes removed within one week. The volume growth of three different viscosities was demonstrated following the intervention. Swallowing function of stroke patients in the intervention group improved more quickly compared
Conclusion:
Our data indicated that effective caregiver engagement is necessary. Successful caregiver engagement has the potential to reduce costs and enhance patient outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Bleeding Risks for Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients on Serotonergic Antidepressants and Anticoagulation/Dual Anti-Platelet Therapy
Simmonds Kent, Chavez Audrie, Ifejika Nneka
Cost or Benefit? Analysis of a Virtual Health Coaching Intervention for Caregivers of Patients with Heart FailureSun Chuxuan, Riegel Barbara, Coe Norma, Hirschman Karen, Matus Austin, Stawnychy Michael, Goba Miatta, Thomas Gladys, Ashare Rebecca, Gordon Deborah, Bowles Kathy
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)