Final ID: TP180
Deep Learning for Identifying Ischemic Core in Acute Ischemic Stroke Based on Non-contrast enhanced Computed Tomography
Although non-contrast enhanced CT (NCCT) is commonly used in emergency rooms and may be utilized to determine the extent of ischemic changes, its limited agreement between different raters prevents widespread use of NCCT in deciding whether to provide reperfusion therapies to patients with suspected acute ischemic stroke (AIS). Therefore, this study aimed to develop an automated approach for evaluating infarction in patients with AIS using NCCT.
Methods:
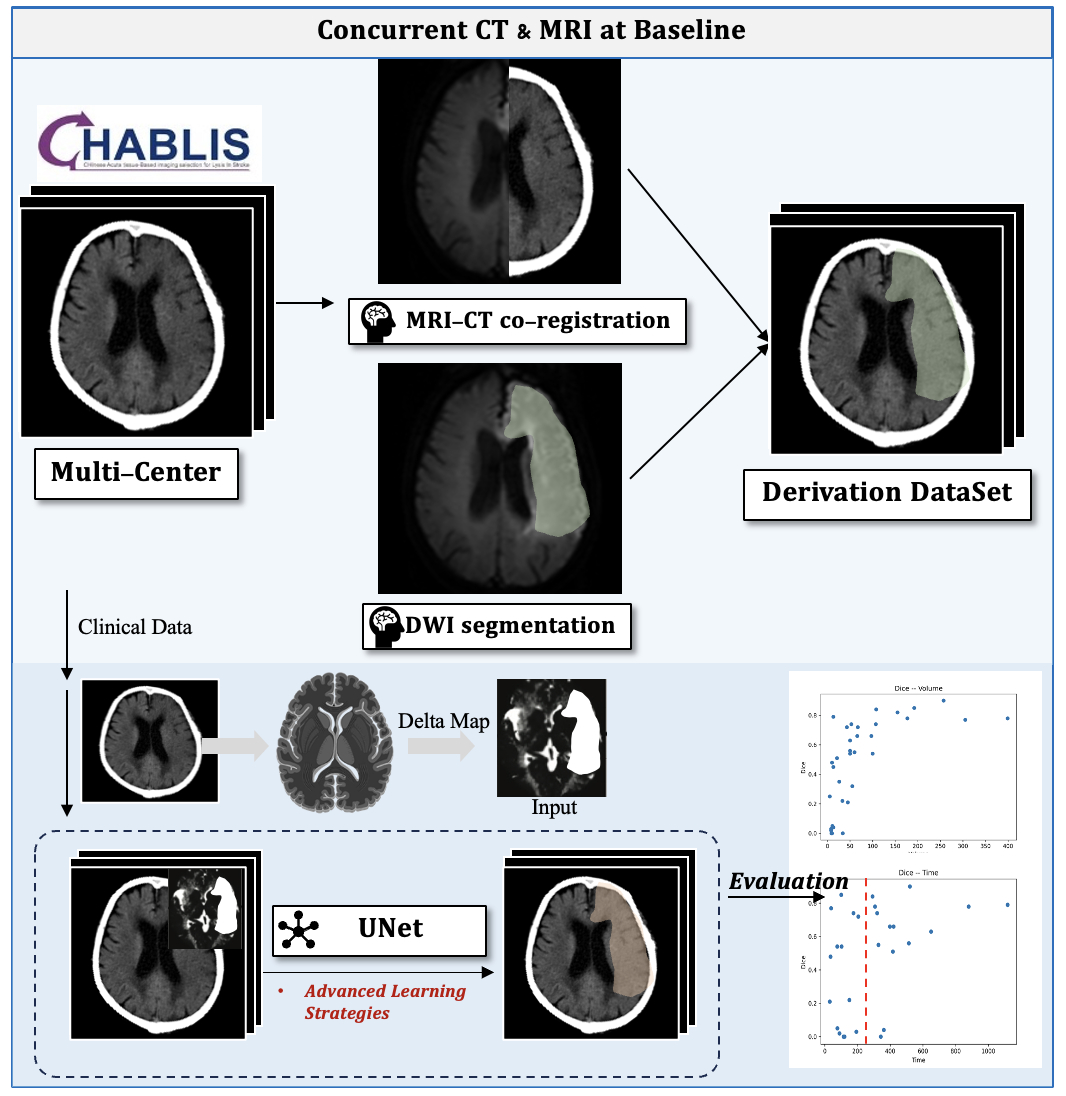
This multi-center retrospective study included patients with suspected AIS who presented within 24 hours from the last known well time and underwent NCCT and DWI (diffusion weighted imaging) within 3 hours between 2021 and 2024, regardless of occlusion sites and reperfusion therapies. The infarct lesions delineated on DWI were utilized as the golden reference. An UNet architecture-based infarction segmentation model was developed using data from 3 institutions (n = 949), which was divided into training and testing sets with an 8:2 split. The performance of the model was compared with the reference standard by using the Pearson correlation coefficient regarding the ischemic core volume and the Dice similarity coefficient regarding the spatial accuracy. Furthermore, the accuracy was provided to assess the discriminative ability to identify a large ischemic core.
Results:
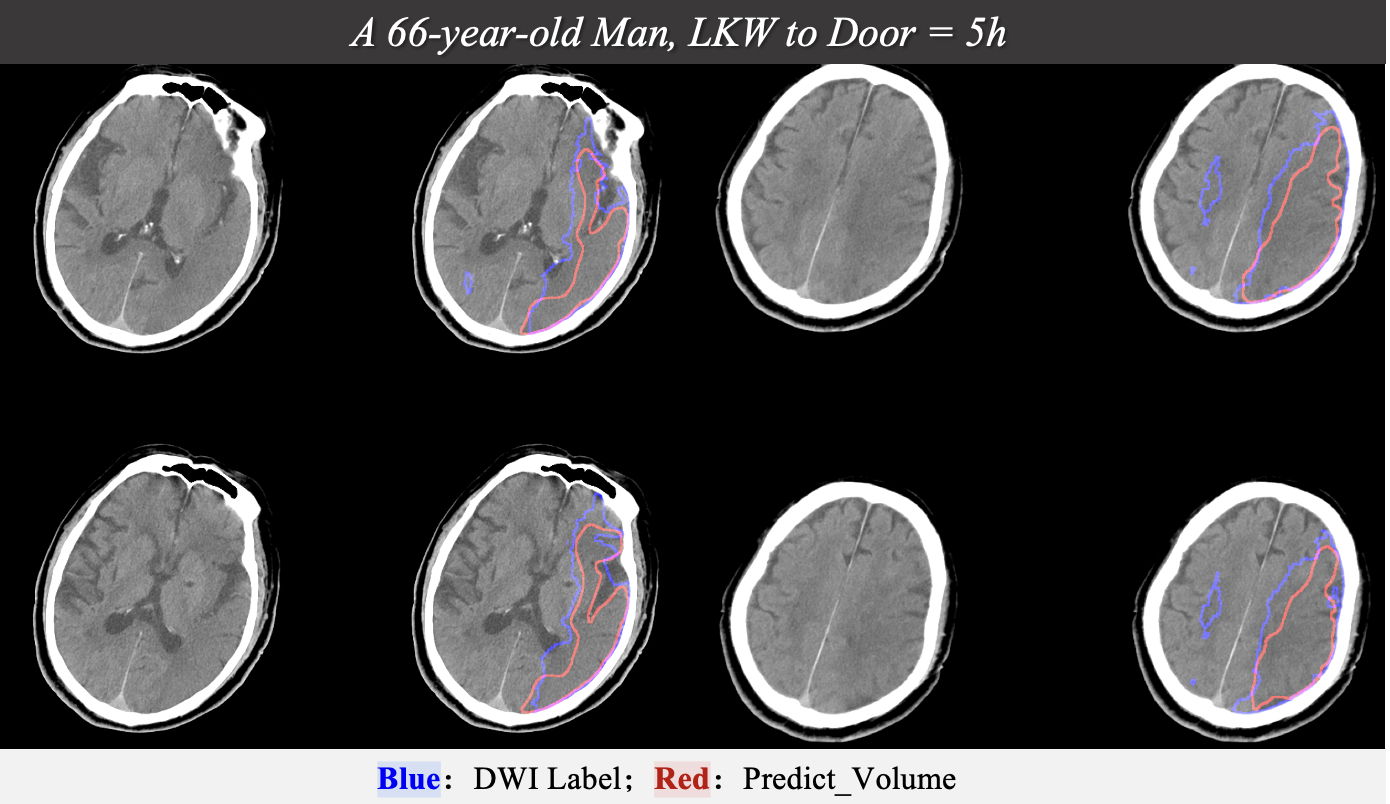
In the entire cohort, the median time interval between CT and DWI was 49 min, and approximately half of the patients (51.3%) arrived in the late window (>4.5 hours). To better differentiate patients with a large ischemic core, the model's performance was primarily assessed by excluding the subgroup of patients with a negative to small ischemic core (≤5 ml). The model's core volume showed a strong positive correlation with the reference standard, with a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.94 (P<0.01). Similarly, the Dice similarity coefficient indicated a strong spatial accuracy, with values of 0.601, 0.689, and 0.768 for cases >20 ml, >50 ml, and >70 ml, respectively. Moreover, the model demonstrated good performance in distinguishing a moderate to large ischemic core, with an accuracy of 83.3%, 72.2%, and 80.0% for cases >20 ml, >50 ml, and >70 ml, respectively.
Conclusion:
The UNet architecture-based infarction segmentation model on NCCT demonstrated good agreement with DWI, particularly in AIS patients with a large ischemic core, which is crucial for guiding treatment choices.
More abstracts on this topic:
Thangjui Sittinun, Trongtorsak Angkawipa, Kewcharoen Jakrin, Thyagaturu Harshith, Watson Hangyu, Mensah Samuel, Balla Sudarshan, Navaravong Leenhapong
A large-scale multi-view deep learning-based assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction in echocardiographyJing Linyuan, Metser Gil, Mawson Thomas, Tat Emily, Jiang Nona, Duffy Eamon, Hahn Rebecca, Homma Shunichi, Haggerty Christopher, Poterucha Timothy, Elias Pierre, Long Aaron, Vanmaanen David, Rocha Daniel, Hartzel Dustin, Kelsey Christopher, Ruhl Jeffrey, Beecy Ashley, Elnabawi Youssef
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.