Final ID: TMP56
Comparison of HEmorrhage on CT versus MRI After ThrombEctomy: The HECATE study
The characterization of hemorrhage following acute stroke intervention has largely been CT-based. We sought to compare MRI- and CT-based scoring of hemorrhage after acute endovascular therapy (EVT) applying the Heidelberg Bleeding Classification (HBC) to assess inter-modal agreement and quantify inter-rater agreement.
Methods
Consecutive acute stroke patients were included in this retrospective study if they: i) had MRI and CT ≤12 hours of each other OR ii) had CT bracketed by MRI pre- and post-CT [i.e. MRI-CT-MRI] ≤7 days post-EVT. The concordance of the HBC ratings by consensus panel were compared between CT and T2*GRE MRI.
Results
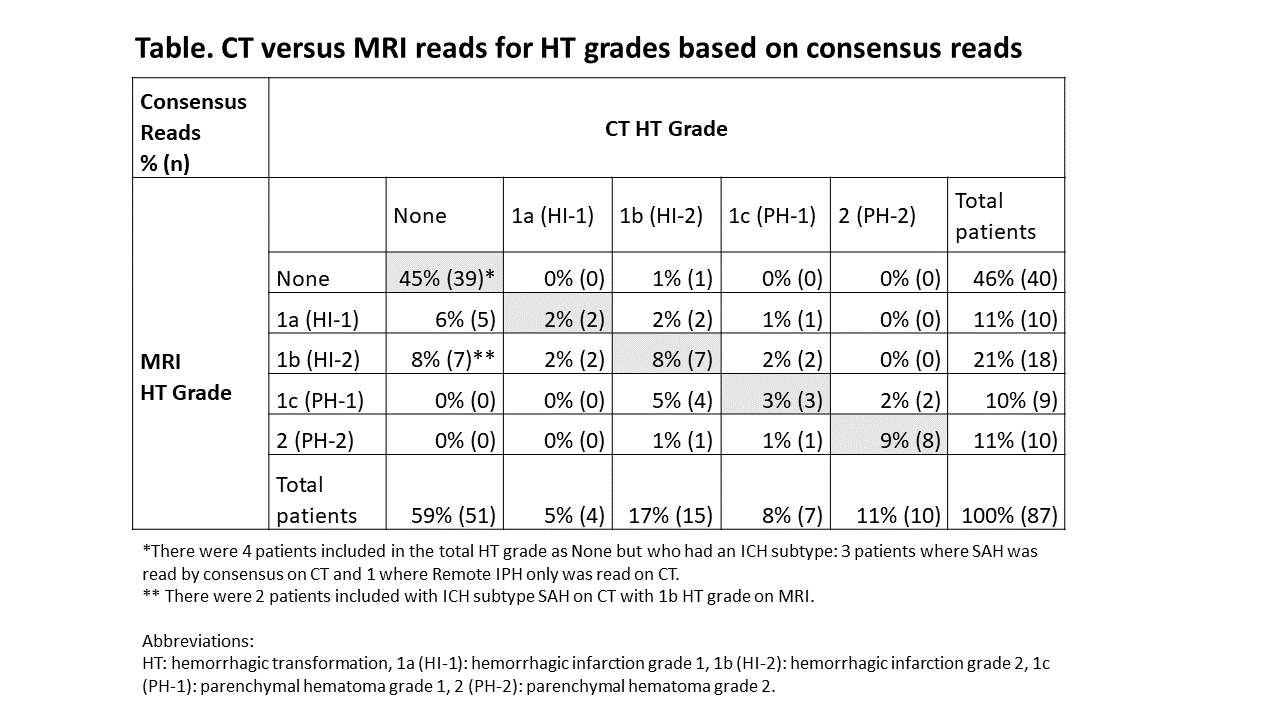
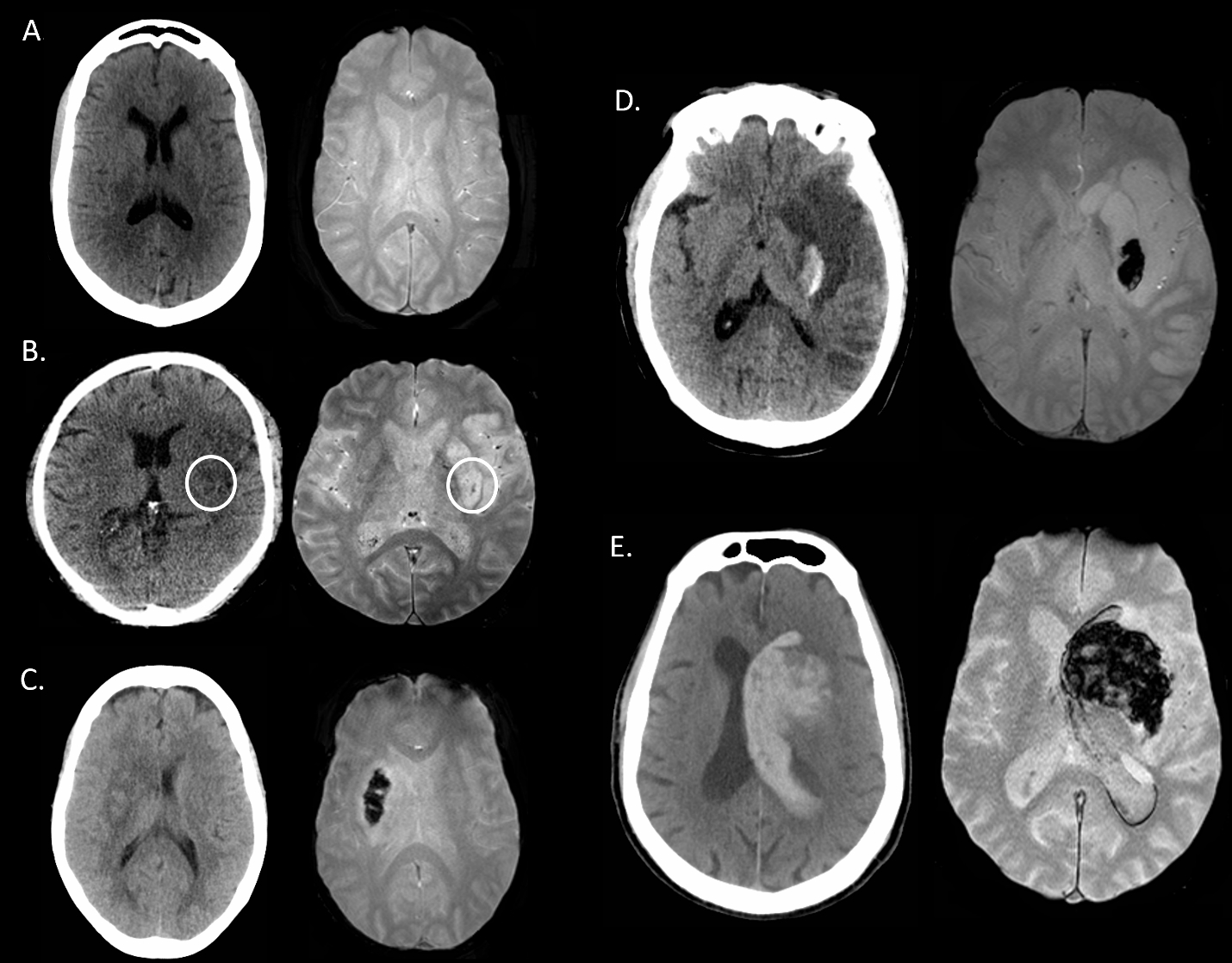
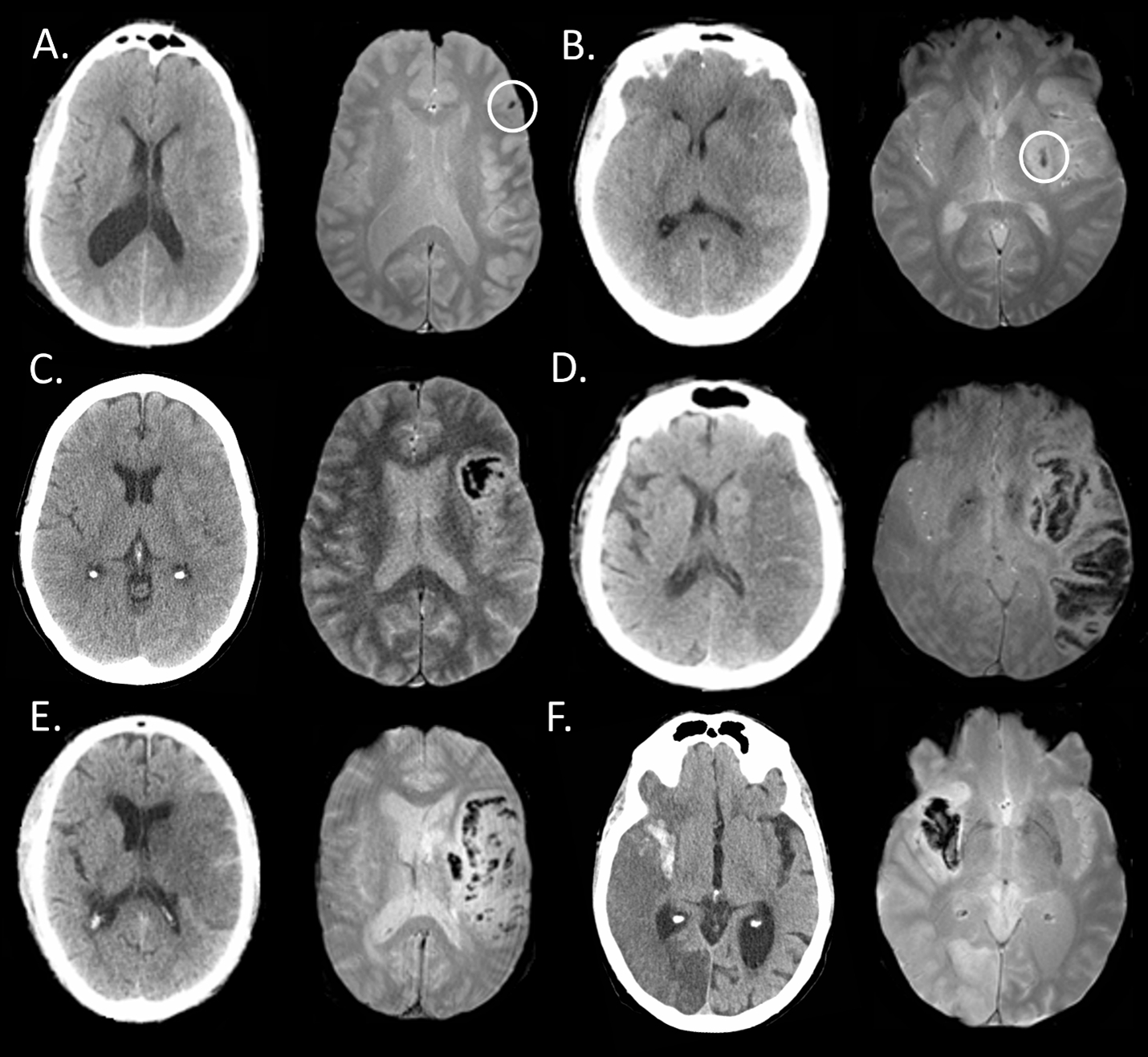
For the 87 EVT-treated patients included, median age was 68 years [60-74], admit NIHSS 18 [13-23], 47% were treated with IV/IA thrombolytics, and 93% were successfully recanalized (mTICI 2b/3). Hemorrhage was detected on at least one modality in 60% (52/87) of patients. We found a 68% (59/87, 95% CI [57-77%]) agreement overall between CT and MRI for hemorrhage classification post-EVT. MRI had the best inter-rater agreement for HBC 0 (no hemorrhage) with excellent concordance (κ=0.882), compared to CT (κ=0.683). T2*GRE MRI tended to have increased sensitivity to scattered petechial hemorrhage (HBC 1a) as compared to CT with 17% (2/12) inter-modal agreement. The inter-rater agreement of HBC class 2 (i.e. PH-2) was substantial for MRI (κ=0.781) and excellent in CT (κ=0.951), with 67% (8 /12) inter-modal agreement. SAH was detected in 24% (21/87) of patients on CT and/or MRI with 29% (6/21) inter-modal agreement.
Conclusions
With the exception of SAH and minor petechial hemorrhagic transformation, we found that MRI and CT are overall interchangeable for detecting and classifying hemorrhage after endovascular therapy, reassuring findings for both clinical-decision making and research application. Given the complexity of hemorrhage subtypes post-EVT, work to further refine a post-EVT hemorrhage classification scale with clinical correlation would be beneficial.
More abstracts on this topic:
Stoehr Kaitlyn, Matouk Charles, Hebert Ryan, Gilmore Emily, Kim Jennifer, Petersen Nils, Jayasundara Sithmi, Vargas David, Thinzar Pwint, Rapuano Amedeo, Maarek Rafael, Beekman Rachel, Magid-bernstein Jessica, Okeefe Lena
Acute Ischemic Stroke Patient Factors Associated with Poor Outcomes in Patients with Favorable Collaterals and Successful ThrombectomyKesten Jamie, Mlynash Michael, Yuen Nicole, Seners Pierre, Wouters Anke, Schwartz Maya, Lansberg Maarten, Albers Gregory, Heit Jeremy
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.