Final ID: WP379
Small Molecule Activator of the Sarcoendoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Ca(2+)-ATPase2 (SERCA2) Promotes Neuroprotection against Ischemic Stroke
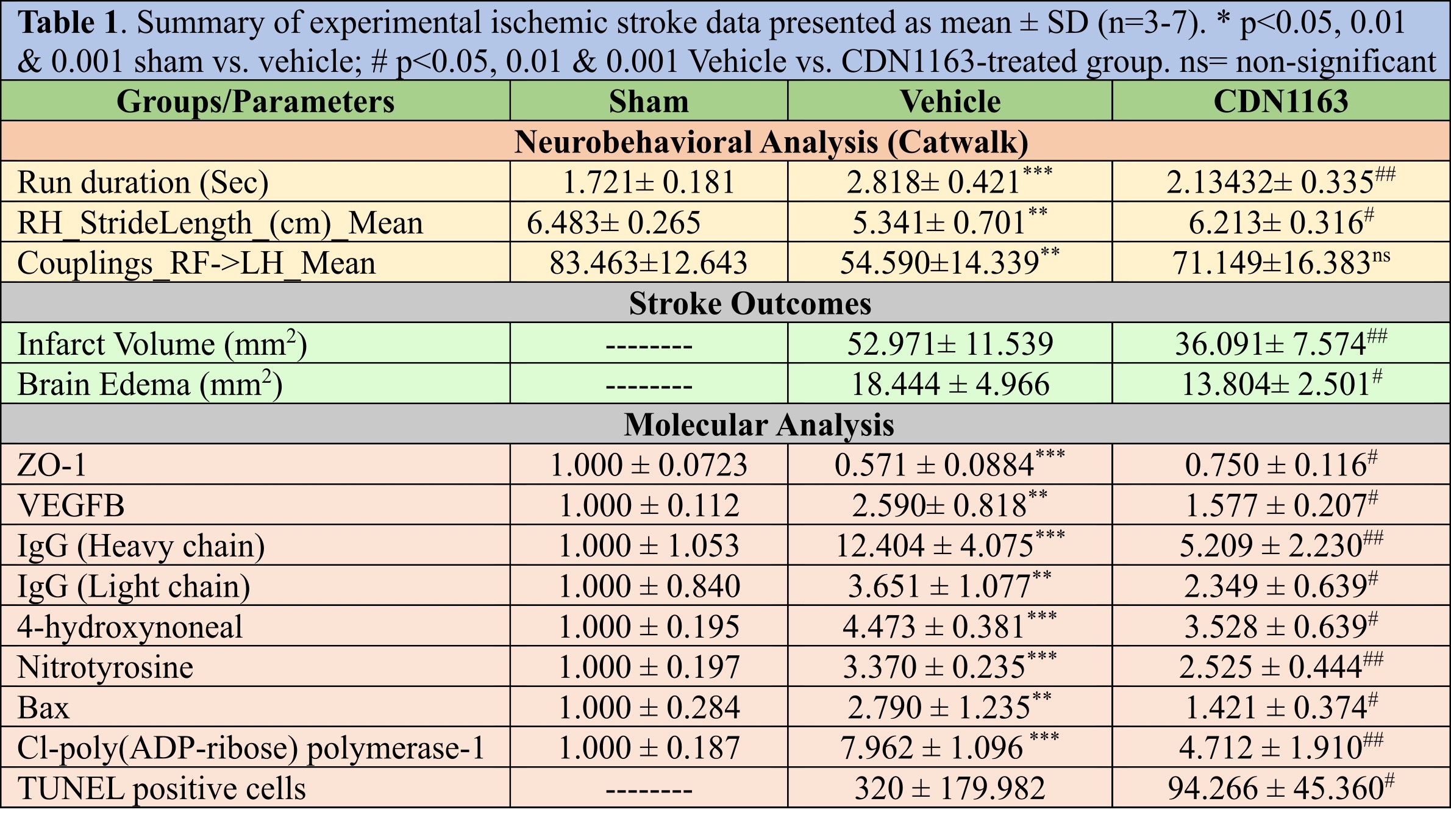
Methods: Ischemic stroke was induced in adult male mice using the Rose Bengal photothrombosis method. CDN1163 (50mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally at specific time points following the stroke. After 72 hours, the Catwalk test was performed to assess gait impairments. The mice were then euthanized, and their brain tissues were harvested for further analysis, including the measurement of infarct volume, brain edema, and molecular analysis. Neuronal apoptosis was determined using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeled (TUNEL) staining.
Results: CDN1163-treated mice showed a significant improvement in gait impairments and reduction in infarct volume and brain edema compared to the vehicle group. CDN1163 treatment also attenuated vascular damage by reducing immunoglobulin extravasation and restoring tight junction protein. In addition, CDN1163 treatment attenuated oxidative damage by reducing 4-hydroxynonenal and nitrotyrosine protein expression levels. Furthermore, the expression levels of apoptotic proteins and numbers of TUNEL-positive cells were significantly decreased in the CDN1163-treated group compared to the vehicle group (Table 1).
Conclusion: Our results indicate that CDN1163 reveals neuroprotection through attenuating vascular damage, oxidative stress, and neuronal loss against stroke pathogenesis. Further investigations into the therapeutic effects of CDN1163 are needed to determine whether it can be an effective therapeutic agent for stroke.
More abstracts on this topic:
Lee Ho-joon, Schwamm Lee, Turner Ashby, De Havenon Adam, Kamel Hooman, Brandt Cynthia, Zhao Hongyu, Krumholz Harlan, Sharma Richa
Clinical Benefit of Nerinetide at One Year in Early Window Participants Enrolled in ESCAPE-NEXTAdams Corey, Heard Kathy, Kohli Yatika, Vatanpour Shabnam, Menon Bijoy, Goyal Mayank, Hill Michael, Tymianski Michael
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.