Final ID: WP148
Assessment of the modified Rankin Scale in Electronic Health Records with Deep Learning
Acute ischemic stroke patients hospitalized within the M Health Fairview system between August 2020 and June 2023 had their charts reviewed at discharge and 90 days post-hospitalization. The mRS score at each clinical encounter was assessed by two independent researchers with any disagreements resolved through case discussion; a third researcher’s assessment was utilized when consensus could not be met. Additionally, each reviewer collected critical EHR text for mRS determination. Extracted EHR text and the corresponding mRS score for each encounter were used for model training and evaluation.
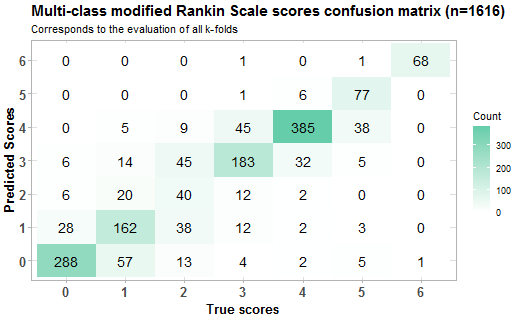
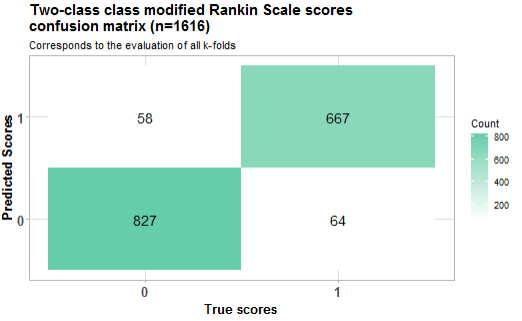
Two separate models were trained on the data: the first received all seven classes of the mRS, and the second received binomial mRS scores reflecting functional independence versus non-independence (mRS 0-2 vs. 3-6). Four-fold cross-validation was conducted, using accuracy and Cohen's kappa as model performance metrics. The base language model employed was Gatortron.
A total of 1616 EHR texts and mRS scores were included in the analysis. The first model—considering all seven classes of the mRS—presented with an accuracy of 74% and a Cohen's Kappa of 0.69. The highest class specific accuracy was achieved on mRS 4 determination (90%). The lowest class specific accuracy was achieved on mRS 2 determination (28%). The second model—considering only 2 classes—achieved an accuracy of 93% and Cohen's Kappa of 0.84.
Our findings demonstrate that large language models can be successfully trained to determine mRS scores through EHR text analysis. The multi-class model had the lowest class specific precision when determining an mRS score of 2, but the outstanding accuracy of the two-class model suggests that this could be improved with more training examples. Validation of our findings in different institutions is warranted to ensure model generalizability.
More abstracts on this topic:
Alkhaleefah Mohammad, Balakrishnan Guha, Li Shuo, Nasir Khurram, Al-kindi Sadeer, Gullapelli Rakesh, Bose Budhaditya, Rockers Elijah, Modanwal Gourav, Hoori Ammar, Madabhushi Anant, Wilson David, Patel Kershaw
A Machine Learning Algorithm to Detect Pediatric Supraventricular Tachycardia Risk from Baseline ECGsArezoumand Amirhossein, Danala Gopichandh, Masnadi Khiabani Parisa, Ebert David, Behere Shashank
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.