Final ID: WP36
CTA versus DSA for the Detection of Mycotic Aneurysms in Infective Endocarditis
Abstract Body: Background: Up to 5% of patients with infective endocarditis (IE) develop intracranial mycotic aneurysms (MA) with nearly 25% of these patients having multiple intracranial aneurysms. Mortality rates have been reported up to 30% for unruptured and 80% for unruptured MA. Therefore, accurate diagnosis of intracerebral aneurysms is critical. CT angiography (CTA) is widely used to detect mycotic aneurysms (MA), yet data are sparse in the literature regarding diagnostic accuracy of CTA compared with the gold standard of 3D rotational digital subtraction angiography (DSA). In this study, we compare CTA to DSA particularly focusing on how the size of aneurysms may change sensitivity of CTA. Based on these results, we offer a practical strategy for the detection and monitoring of MAs.
Methods: This retrospective chart review included all patients admitted to Boston Medical Center between January 1, 2014 and December 31, 2023. 883 patients with IE were identified by ICD-9 and ICD-10 code. 77 intracranial aneurysms were identified by DSA with accompanying CTA within 1 month. An experienced neuroradiologist reviewed each CTA and DSA. Using DSA as the gold standard, sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, and likelihood ratios were calculated. To avoid bias and increase clinical relevance, these calculations were based on the final clinical interpretation at the time of the study. For the analysis based on aneurysm size, the review of our study neuroradiologist was used.
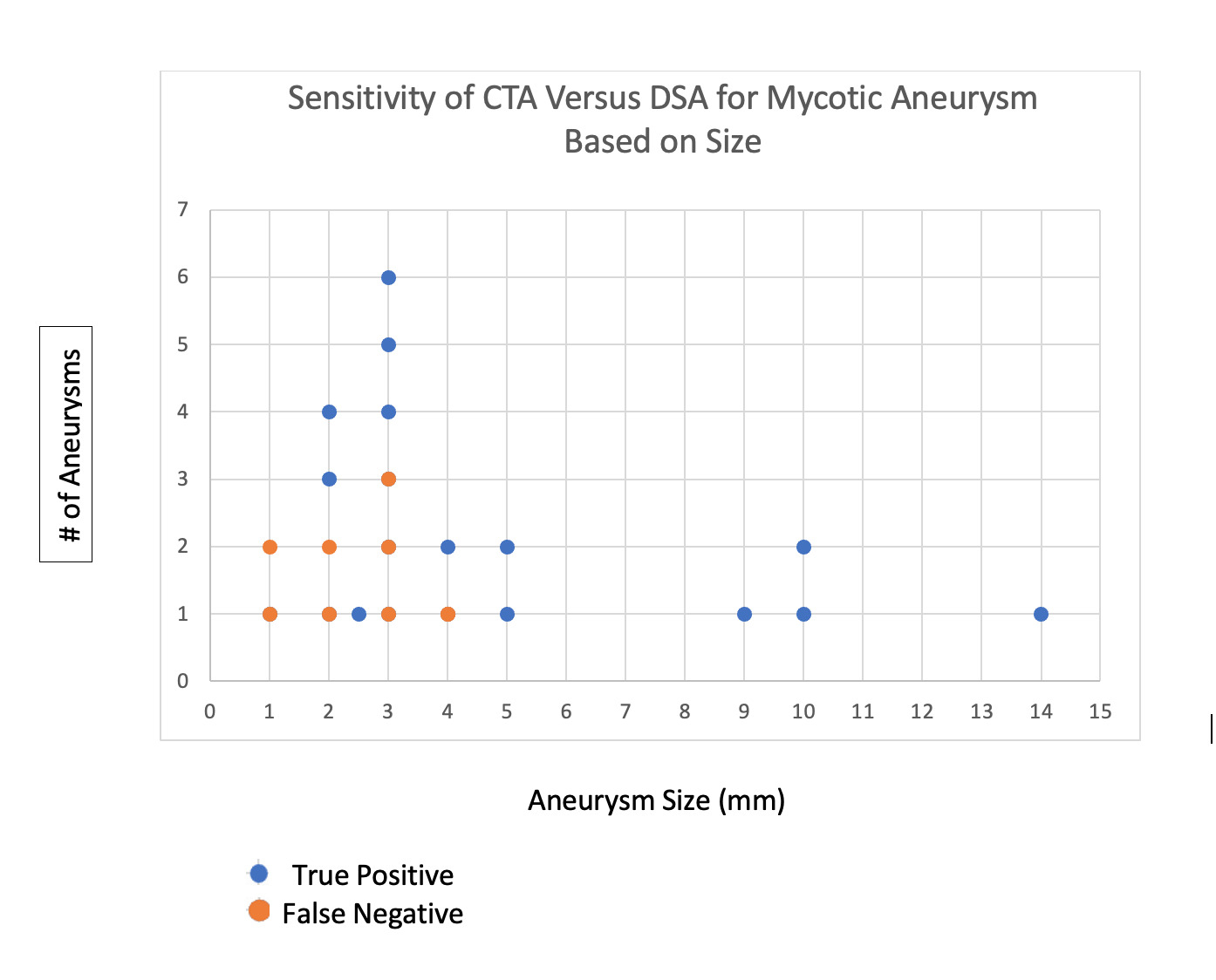
Results: Of the 77 aneurysms identified by CTA or DSA, test results were as follows: 53 true negative (CTA -, DSA-), 13 true positive (CTA +, DSA +), 5 false positive (CTA +, DSA -), and 8 false negative (CTA -, DSA +). Including all aneurysms, the sensitivity of CTA was (62%), and the specificity was (91%). The positive and negative predictive values were 72% and 87%, respectively. The sensitivity of CTA for aneurysms ≥ 5mm was 100%. For aneurysms ≥ 4, the sensitivity was 88%. For aneurysms ≤ 3mm, the sensitivity of CTA was 46%.
Conclusions: Sensitivity of CTA for intracranial aneurysms is low, however, it varies depending on size and is excellent for aneurysms ≥ 5mm. Based on this information, we present a strategy that uses a combination of DSA and CTA to detect and monitor MAs.
Methods: This retrospective chart review included all patients admitted to Boston Medical Center between January 1, 2014 and December 31, 2023. 883 patients with IE were identified by ICD-9 and ICD-10 code. 77 intracranial aneurysms were identified by DSA with accompanying CTA within 1 month. An experienced neuroradiologist reviewed each CTA and DSA. Using DSA as the gold standard, sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, and likelihood ratios were calculated. To avoid bias and increase clinical relevance, these calculations were based on the final clinical interpretation at the time of the study. For the analysis based on aneurysm size, the review of our study neuroradiologist was used.
Results: Of the 77 aneurysms identified by CTA or DSA, test results were as follows: 53 true negative (CTA -, DSA-), 13 true positive (CTA +, DSA +), 5 false positive (CTA +, DSA -), and 8 false negative (CTA -, DSA +). Including all aneurysms, the sensitivity of CTA was (62%), and the specificity was (91%). The positive and negative predictive values were 72% and 87%, respectively. The sensitivity of CTA for aneurysms ≥ 5mm was 100%. For aneurysms ≥ 4, the sensitivity was 88%. For aneurysms ≤ 3mm, the sensitivity of CTA was 46%.
Conclusions: Sensitivity of CTA for intracranial aneurysms is low, however, it varies depending on size and is excellent for aneurysms ≥ 5mm. Based on this information, we present a strategy that uses a combination of DSA and CTA to detect and monitor MAs.
More abstracts on this topic:
A ChatGLM-based stroke diagnosis and prediction tool
Song Xiaowei, Wang Jiayi, Ma Weizhi, Wu Jian, Wang Yueming, Gao Ceshu, Wei Chenming, Pi Jingtao
84 Immune checkpoint profiling in major aortic diseases leads to identification of potential roles of CD155-CD206 pathway in suppressing inflammation and immune responsesShao Ying, Saaoud Fatma, Xu Keman, Lu Yifan, Jiang Xiaohua, Wang Hong, Yang Xiaofeng
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)