Final ID: FR598
Impact of Renal Denervation with Symplicity Spyral on Hypertension Management Stratified by Obesity: Findings from a Pilot Study in Kuwait
Abstract Body: Introduction/Background : Renal denervation (RDN) is an emerging therapy shown to significantly reduce BP.
Research Questions/Hypothesis : Impact of RDN on obese hypertensive Patients are unknown.
Goals/Aims : Aim of our study to analyze the Impact of RDN on obese hypertensive patients.
Methods/Approach : Patients were stratified into 2 groups Obese and non obese. Pre- and post-procedural
BP measurements were analyzed using repeated measures ANOVA to assess the changes in systolic (SYS)
and diastolic (DIA) BP over time.
Results/Data (descriptive and inferential statistics) : This retrospective study included 50 hypertensive
patients who underwent RDN with Symplicity Spyral from March 2023 to August 2024. The cohort had a mean
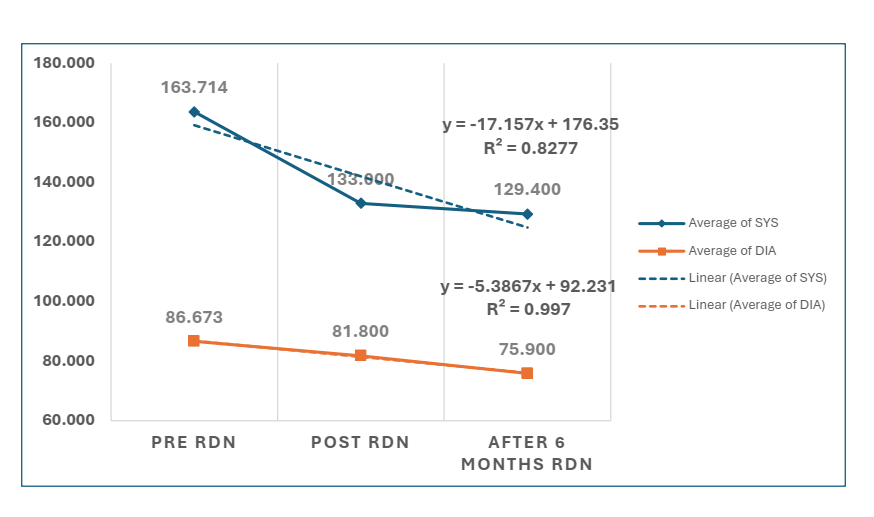
age of 61.7 years. Pre-RDN mean SYS and DIA BP were 163.7 mmHg and 86.7 mmHg, respectively. The
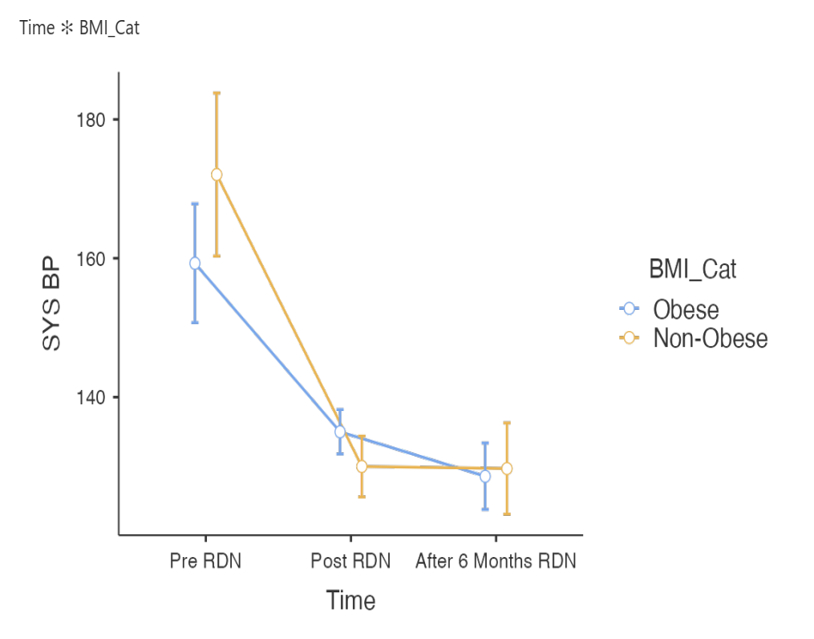
impact of renal denervation on blood pressure (BP) was examined in obese and non-obese groups. Initially,
the non-obese group had a higher SYS BP (180 mmHg) compared to the obese group (160 mmHg). Post-RDN, SYS BP decreased to 145 mmHg in the non-obese group and to 140 mmHg in the obese group. Six
months post-RDN, SYS BP stabilized at around 140 mmHg in both groups. RDN effectively reduced and
maintained lower SYS BP in both groups over six months.The forest plot analysis showed that Dyslipidemia
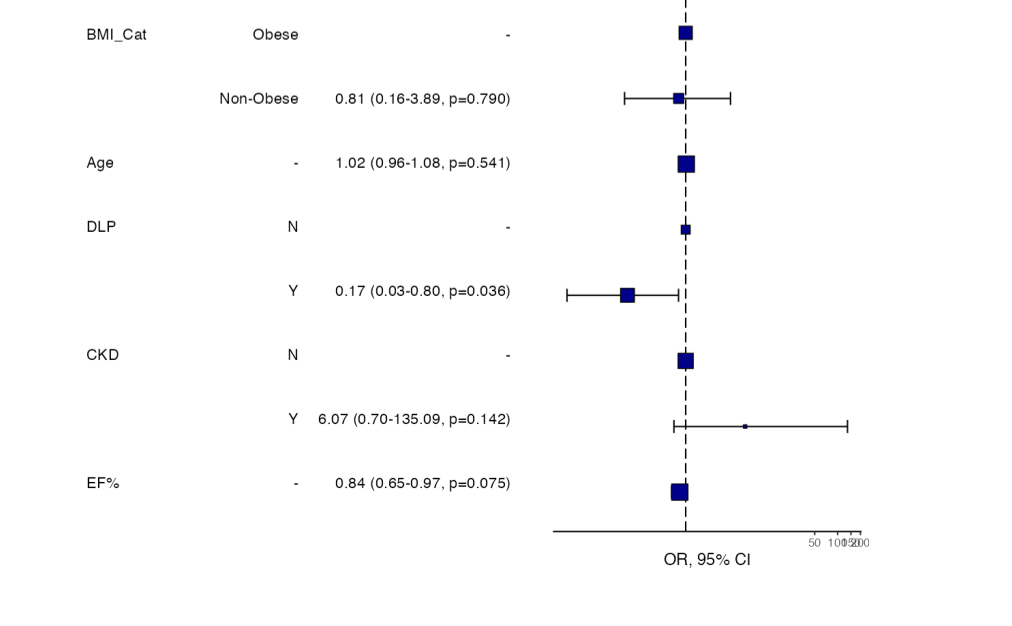
(DLP) significantly reduced the odds of achieving the SYS BP target (OR = 0.17, p = 0.036). Both regression
lines showed strong fits (SYS BP: R2 = 0.8277; DIA BP: R2 = 0.997). Repeated Measures ANOVA indicated
significant changes in SYS BP over time (p < .001, η2p = 0.590), with significant interaction between time and
BMI category (p = 0.038). Logistic regression analysis highlighted DLP as a significant predictor, reducing the
likelihood of achieving the systolic BP Target (OR = 0.17, p = 0.036). Other factors like BMI, age, CKD, and
EF% were not significant predictors.
Conclusion(s) : Renal denervation (RDN) with Symplicity Spyral effectively reduces blood pressure in both
obese and non-obese individuals, with sustained improvements over six months. Dyslipidemia significantly
decreases the likelihood of achieving target BP, while other factors such as BMI, age, chronic kidney disease
(CKD), and ejection fraction percentage (EF%) are not significant predictors. These findings support the use of
RDN as a viable intervention for managing hypertension, highlighting the importance of addressing
dyslipidemia in hypertensive patients.
Research Questions/Hypothesis : Impact of RDN on obese hypertensive Patients are unknown.
Goals/Aims : Aim of our study to analyze the Impact of RDN on obese hypertensive patients.
Methods/Approach : Patients were stratified into 2 groups Obese and non obese. Pre- and post-procedural
BP measurements were analyzed using repeated measures ANOVA to assess the changes in systolic (SYS)
and diastolic (DIA) BP over time.
Results/Data (descriptive and inferential statistics) : This retrospective study included 50 hypertensive
patients who underwent RDN with Symplicity Spyral from March 2023 to August 2024. The cohort had a mean
age of 61.7 years. Pre-RDN mean SYS and DIA BP were 163.7 mmHg and 86.7 mmHg, respectively. The
impact of renal denervation on blood pressure (BP) was examined in obese and non-obese groups. Initially,
the non-obese group had a higher SYS BP (180 mmHg) compared to the obese group (160 mmHg). Post-RDN, SYS BP decreased to 145 mmHg in the non-obese group and to 140 mmHg in the obese group. Six
months post-RDN, SYS BP stabilized at around 140 mmHg in both groups. RDN effectively reduced and
maintained lower SYS BP in both groups over six months.The forest plot analysis showed that Dyslipidemia
(DLP) significantly reduced the odds of achieving the SYS BP target (OR = 0.17, p = 0.036). Both regression
lines showed strong fits (SYS BP: R2 = 0.8277; DIA BP: R2 = 0.997). Repeated Measures ANOVA indicated
significant changes in SYS BP over time (p < .001, η2p = 0.590), with significant interaction between time and
BMI category (p = 0.038). Logistic regression analysis highlighted DLP as a significant predictor, reducing the
likelihood of achieving the systolic BP Target (OR = 0.17, p = 0.036). Other factors like BMI, age, CKD, and
EF% were not significant predictors.
Conclusion(s) : Renal denervation (RDN) with Symplicity Spyral effectively reduces blood pressure in both
obese and non-obese individuals, with sustained improvements over six months. Dyslipidemia significantly
decreases the likelihood of achieving target BP, while other factors such as BMI, age, chronic kidney disease
(CKD), and ejection fraction percentage (EF%) are not significant predictors. These findings support the use of
RDN as a viable intervention for managing hypertension, highlighting the importance of addressing
dyslipidemia in hypertensive patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Clinical Trial of Healthy Food Subsidies and Behavioral Interventions to Increase Fruit and Vegetable Purchasing in an Online Store
Hua Sophia, Klaiman Tamar, Dixon Erica, Volpp Kevin, Putt Mary, Coratti Samantha, White Jenna, Hossain Mohammad, Posner Hannah, Wang Erkuan, Zhu Jingsan, John Aileen
A durable reduction in blood pressure by ultrasound renal denervation: A real-world, single center experienceKing Jordan, Gharib Wissam