Final ID: FR429
Recent Advances in Hypertension Management: Systematic review and Meta-Analysis of Emerging Therapies (2023-2025).
Abstract Body: Introduction:
Hypertension is a major global health concern, contributing significantly to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular morbidity and mortality. Despite numerous available antihypertensive agents, a considerable number of patients remain uncontrolled or treatment-resistant. In recent years, innovative pharmacologic and procedural approaches have emerged to address these therapeutic gaps.
Objective:
To systematically review and analyse the efficacy of recent therapeutic innovations in hypertension management published between 2023 and 2025.
Methods:
We reviewed peer-reviewed publications, press releases, and clinical trial databases (PubMed, ClinicalTrials.gov, Nature) from Jan 2023 to May 2025. Eligible studies included adults (≥18 years) with hypertension, Phase II or higher trials, with ≥4 weeks of follow-up reporting changes in SBP/DBP. Keywords included terms like hypertension, clinical trial, and relevant drug or therapy names. Data extracted: intervention type, sample size, duration, BP changes, and adverse events. A random-effects model pooled weighted mean differences (WMD) in SBP. Heterogeneity was assessed using I2 statistics.
Results:
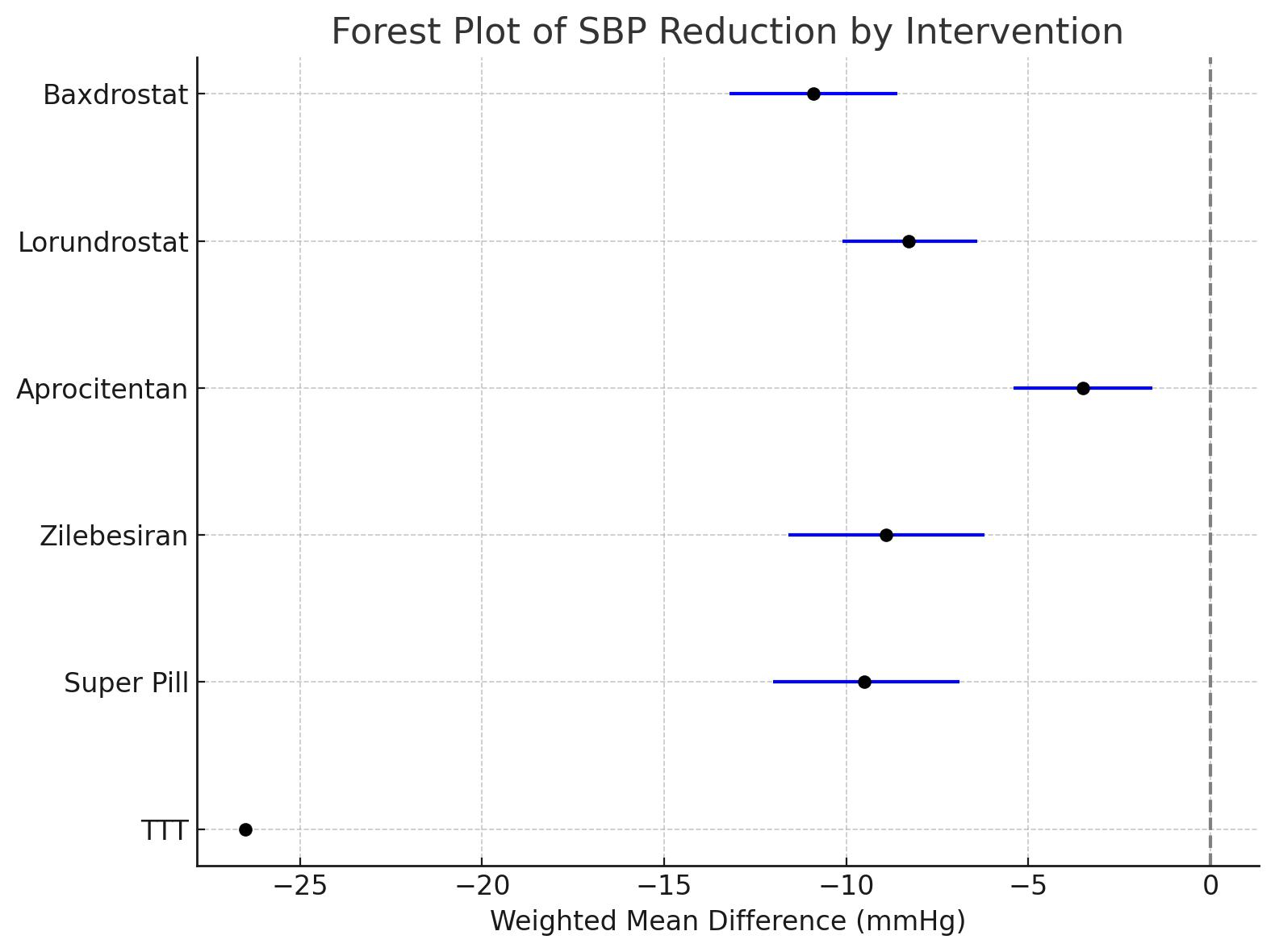
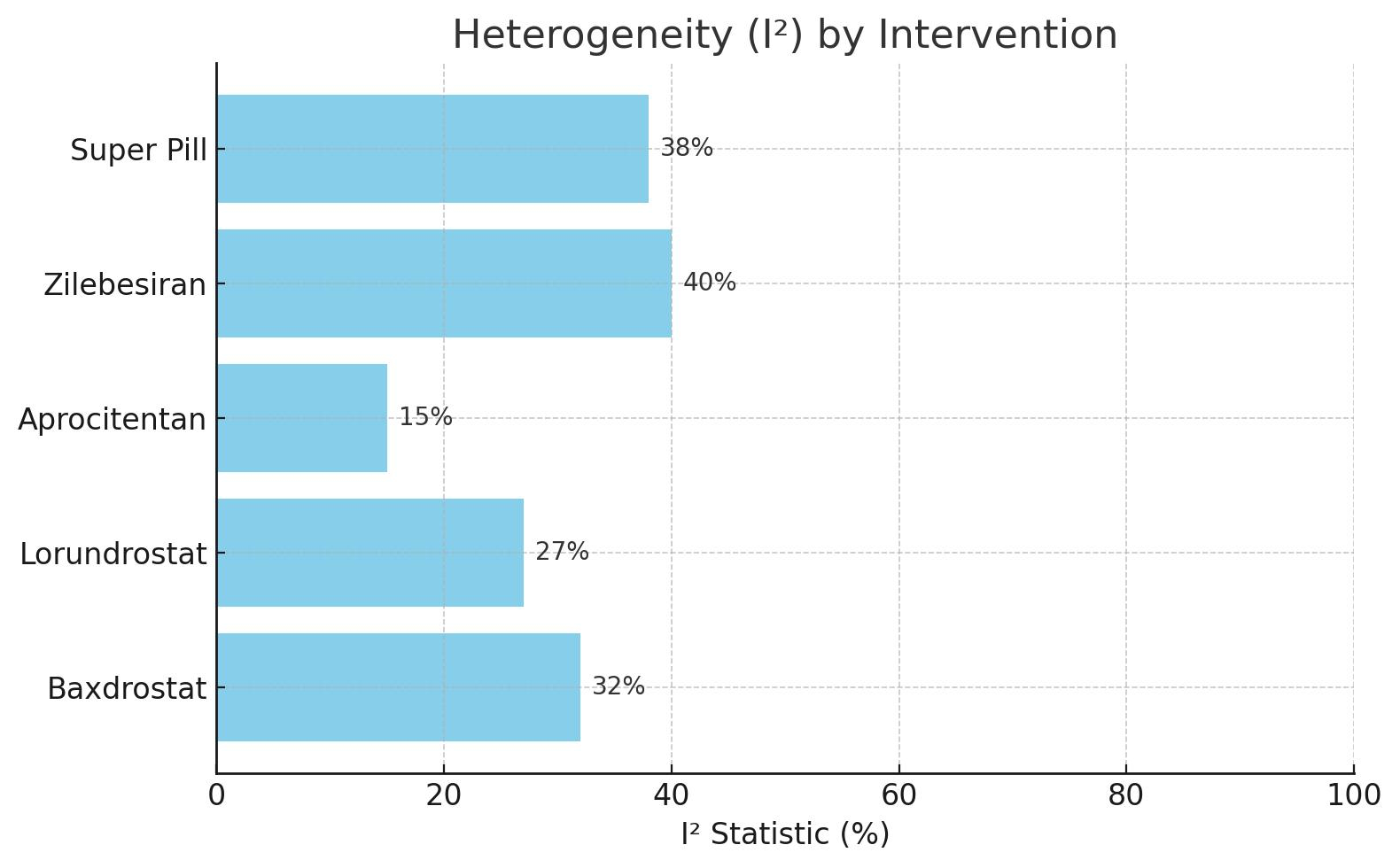
Six clinical trials involving 3,070 participants evaluated antihypertensive treatments: the BrigHTN trial (baxdrostat), Lorundrostat HTN-1 trial (lorundrostat), PRECISION trial (aprocitentan), KARDIA 1 trial (zilebesiran), the GMRx2 Super Pill trial, and a pilot study on Targeted Thermal Therapy (TTT). The pooled systolic blood pressure (SBP) reduction, excluding non-randomized TTT, was -8.5 mmHg (95% CI, -10.2 to -6.7; I2 = 33%). Aldosterone synthase inhibitors (baxdrostat and lorundrostat) and the Super Pill showed the most significant effects. Individually, SBP reductions versus placebo were: baxdrostat (-20.3 vs. -9.4 mmHg), lorundrostat (-15.3 vs. -7.0 mmHg), aprocitentan (-15.0 vs. -11.5 mmHg), zilebesiran (-13.9 vs. -5.0 mmHg), and the Super Pill (-18.2 mmHg). TTT reported the largest reduction (-26.5 mmHg) but lacked randomized control. Meta-analysis weighted mean differences (WMDs) supported these findings, with baxdrostat (-10.9 mmHg) and zilebesiran (-8.9 mmHg) demonstrating the strongest evidence.
Conclusions:
Emerging therapies from 2023 to 2025 show promise in improving blood pressure control, particularly in resistant hypertension. These results support integrating new agents into practice and highlight the need for larger, long-term studies to confirm efficacy and safety.
Hypertension is a major global health concern, contributing significantly to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular morbidity and mortality. Despite numerous available antihypertensive agents, a considerable number of patients remain uncontrolled or treatment-resistant. In recent years, innovative pharmacologic and procedural approaches have emerged to address these therapeutic gaps.
Objective:
To systematically review and analyse the efficacy of recent therapeutic innovations in hypertension management published between 2023 and 2025.
Methods:
We reviewed peer-reviewed publications, press releases, and clinical trial databases (PubMed, ClinicalTrials.gov, Nature) from Jan 2023 to May 2025. Eligible studies included adults (≥18 years) with hypertension, Phase II or higher trials, with ≥4 weeks of follow-up reporting changes in SBP/DBP. Keywords included terms like hypertension, clinical trial, and relevant drug or therapy names. Data extracted: intervention type, sample size, duration, BP changes, and adverse events. A random-effects model pooled weighted mean differences (WMD) in SBP. Heterogeneity was assessed using I2 statistics.
Results:
Six clinical trials involving 3,070 participants evaluated antihypertensive treatments: the BrigHTN trial (baxdrostat), Lorundrostat HTN-1 trial (lorundrostat), PRECISION trial (aprocitentan), KARDIA 1 trial (zilebesiran), the GMRx2 Super Pill trial, and a pilot study on Targeted Thermal Therapy (TTT). The pooled systolic blood pressure (SBP) reduction, excluding non-randomized TTT, was -8.5 mmHg (95% CI, -10.2 to -6.7; I2 = 33%). Aldosterone synthase inhibitors (baxdrostat and lorundrostat) and the Super Pill showed the most significant effects. Individually, SBP reductions versus placebo were: baxdrostat (-20.3 vs. -9.4 mmHg), lorundrostat (-15.3 vs. -7.0 mmHg), aprocitentan (-15.0 vs. -11.5 mmHg), zilebesiran (-13.9 vs. -5.0 mmHg), and the Super Pill (-18.2 mmHg). TTT reported the largest reduction (-26.5 mmHg) but lacked randomized control. Meta-analysis weighted mean differences (WMDs) supported these findings, with baxdrostat (-10.9 mmHg) and zilebesiran (-8.9 mmHg) demonstrating the strongest evidence.
Conclusions:
Emerging therapies from 2023 to 2025 show promise in improving blood pressure control, particularly in resistant hypertension. These results support integrating new agents into practice and highlight the need for larger, long-term studies to confirm efficacy and safety.
More abstracts on this topic:
Linking variability of leukocyte lipid metabolism to circulating lipids, lipoprotein composition and cardiovascular risk in the Finnish adult population
Hlushchenko Iryna, Pamilo Siina, Islam Mohammad Majharul, Lahdeniemi Iris, Tamlander Max, Ripatti Samuli, Pfisterer Simon
A First-In-Human Phase 1 Study of the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacodynamics of REGN7544, a Novel Natriuretic Peptide Receptor 1–Blocking Monoclonal AntibodyAhmed Mohsin, Morton Lori, Olenchock Benjamin, Herman Gary, Wynne Chris, Marin Ethan, Tuckwell Katie, Xu Meng, Cheng Xiping, Redington Emily, Koyani Bharatkumar, Mateo Katrina, Thakur Mazhar, Devalaraja-narashimha Kishor