Final ID: TH215
Association Between Supine Blood Pressure and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality; a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.
Abstract Body: Background
Supine hypertension, or elevated blood pressure while lying down, is often underrecognized in clinical settings. Though more common in older adults and those with autonomic dysfunction, its long-term cardiovascular impact remains unclear. Growing evidence suggests it may contribute to higher risks of cardiovascular disease (CVD), stroke, heart failure, and mortality.
Methods
A meta-analysis evaluated the association between supine hypertension and primary cardiovascular outcomes were searched using standard electronic databases. MeSh term including “supine hypertension” and “cardiovascular outcomes” were used for Search. Studies reporting hazard ratios for CVD events, stroke, heart failure, cardiovascular, and all-cause mortality were included. Random-effect models were used for pooled analysis, with heterogeneity assessed using the I2 statistic and p value <0.05 considered significant.
Results
A total of 13 studies were included in the analysis, comprising a combined study population of 241,765 individuals with a mean age of 59 years and follow up for 12.4 years.
Cardiovascular Events: Six studies showed a significant association between supine hypertension and increased CVD events (HR = 1.41, 95% CI: 1.28–1.55, p<0.05).
Cardiovascular Mortality: Five studies indicated elevated supine systolic BP was linked to higher cardiovascular mortality (HR = 1.57, 95% CI: 1.40–1.75, p<0.05).
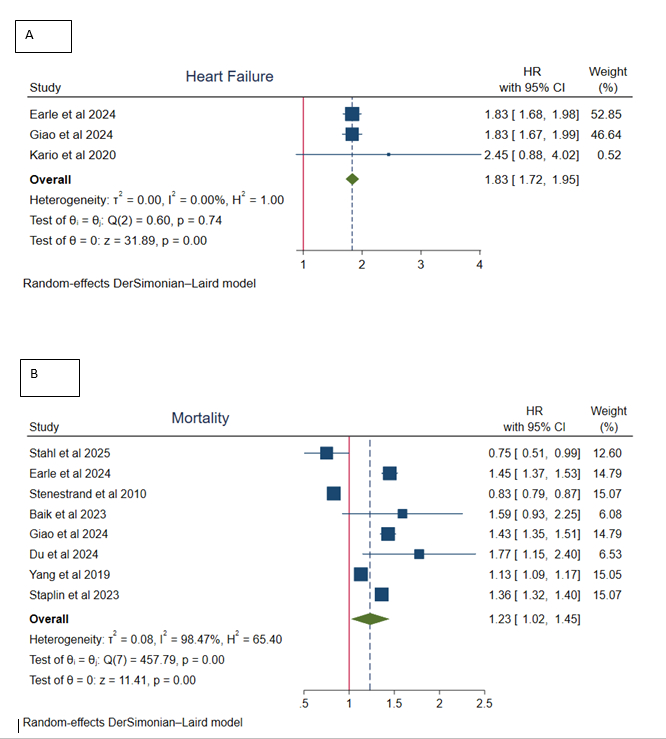
Heart Failure: Three studies demonstrated a strong, consistent association between supine hypertension and heart failure (HR = 1.83, 95% CI: 1.72–1.95, p<0.05).
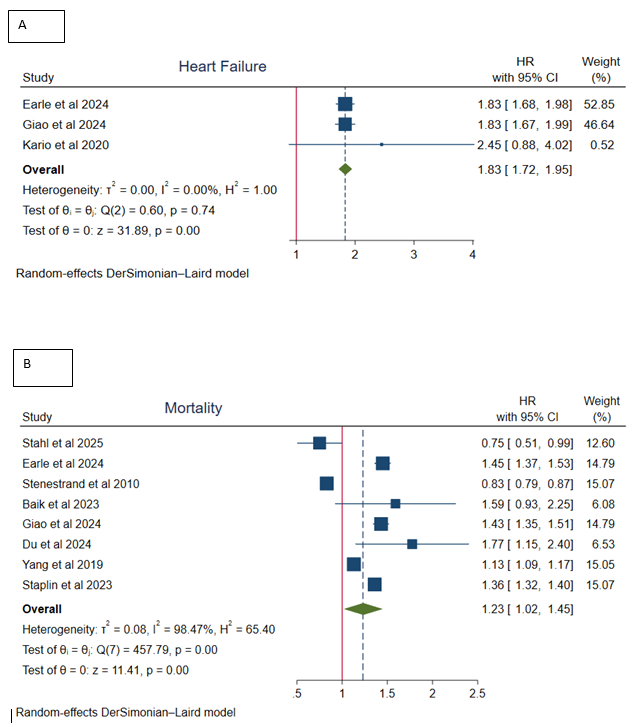
Mortality: Eight studies showed a modest but significant increase in all-cause mortality (HR = 1.23, 95% CI: 1.02–1.45, p<0.05).
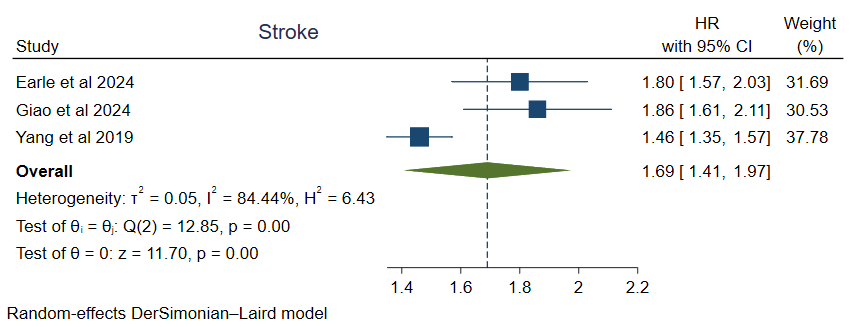
Stroke: Three studies revealed significantly increased stroke risk in individuals with supine hypertension versus standing hypotension (HR = 1.69, 95% CI: 1.41–1.97, p<0.05).
Conclusion
Supine hypertension was significantly associated with increased risks of CVD events, cardiovascular mortality, stroke, heart failure, and all-cause mortality. These findings highlight the need to consider supine blood pressure patterns in clinical evaluations to improve risk detection and guide preventive care strategies.
Supine hypertension, or elevated blood pressure while lying down, is often underrecognized in clinical settings. Though more common in older adults and those with autonomic dysfunction, its long-term cardiovascular impact remains unclear. Growing evidence suggests it may contribute to higher risks of cardiovascular disease (CVD), stroke, heart failure, and mortality.
Methods
A meta-analysis evaluated the association between supine hypertension and primary cardiovascular outcomes were searched using standard electronic databases. MeSh term including “supine hypertension” and “cardiovascular outcomes” were used for Search. Studies reporting hazard ratios for CVD events, stroke, heart failure, cardiovascular, and all-cause mortality were included. Random-effect models were used for pooled analysis, with heterogeneity assessed using the I2 statistic and p value <0.05 considered significant.
Results
A total of 13 studies were included in the analysis, comprising a combined study population of 241,765 individuals with a mean age of 59 years and follow up for 12.4 years.
Cardiovascular Events: Six studies showed a significant association between supine hypertension and increased CVD events (HR = 1.41, 95% CI: 1.28–1.55, p<0.05).
Cardiovascular Mortality: Five studies indicated elevated supine systolic BP was linked to higher cardiovascular mortality (HR = 1.57, 95% CI: 1.40–1.75, p<0.05).
Heart Failure: Three studies demonstrated a strong, consistent association between supine hypertension and heart failure (HR = 1.83, 95% CI: 1.72–1.95, p<0.05).
Mortality: Eight studies showed a modest but significant increase in all-cause mortality (HR = 1.23, 95% CI: 1.02–1.45, p<0.05).
Stroke: Three studies revealed significantly increased stroke risk in individuals with supine hypertension versus standing hypotension (HR = 1.69, 95% CI: 1.41–1.97, p<0.05).
Conclusion
Supine hypertension was significantly associated with increased risks of CVD events, cardiovascular mortality, stroke, heart failure, and all-cause mortality. These findings highlight the need to consider supine blood pressure patterns in clinical evaluations to improve risk detection and guide preventive care strategies.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Comparative Study Of Social Determinants, Hypertension, And Life Essential Factors In Alabama And Colorado From The 2021 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System
Chukwunyere Chibuike, Owuor Kevin
2 Dimensional Echocardiography versus 3 Dimentional Echocardiography to Assess Right Ventricular Function in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Systematic ReviewChaudhry Waleed Razzaq, Hajj Fatima, Bathula Satyamedha, Meghji Mohammed Askari, Pasupuleti Hemalatha, Kiyani Madiha, Shah Syeda Simrah, Neelakantan Ramaswamy Sanathanan, Mirzaeidizaji Nakisa, St. Jacques Jahnoy, Khan Khalil Ullah, Veluchamy Elakkiya, Jesse Joshanna