Final ID: 029
Comprehensive Resistant Hypertension Clinic Improves Access to Care and Blood Pressure Control
Abstract Body: Resistant hypertension is a leading risk factor for adverse cardiovascular events including stroke, heart failure, and death. It is defined as blood pressure (BP) that remains above guideline-specified goals despite using maximum tolerated doses of at least three antihypertensives or controlled while on four or more. Given that this is a significant health crisis in regions that lack specialized programs, we established a Resistant Hypertension Clinic at an academic medical center to meet the needs of this high-risk patient population.
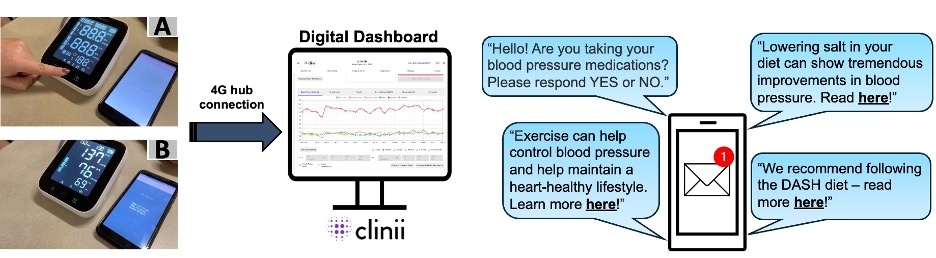
A population health-based registry was created to identify patients in large health systems who have uncontrolled BP while on three medications via EMR. A retrospective chart review was conducted to confirm that patients were appropriately identified. Their PCP then received a pended referral to Resistant Hypertension Clinic where patients are screened for secondary causes of hypertension, enrolled in remote BP monitoring and text-messaging for medication adherence, and evaluated for advanced therapies. The mean change in systolic BP and clinical outcomes were assessed longitudinally.
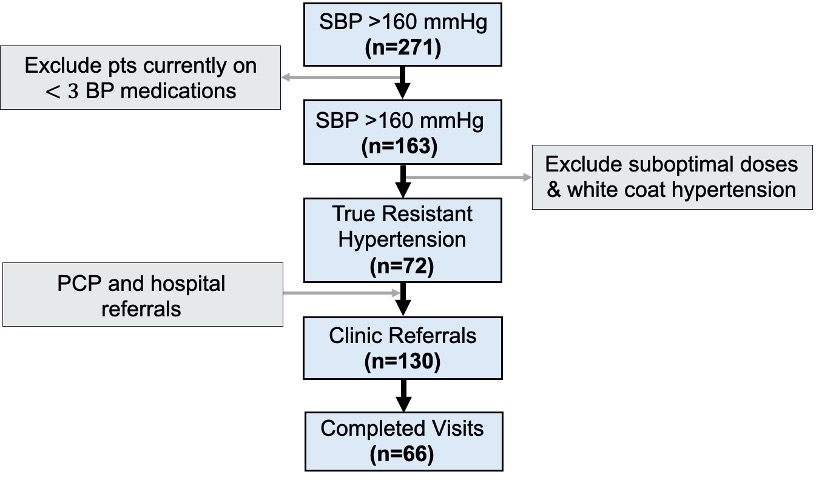
A cohort of 271 patients aged 29-86 years (66 ±15 years) with systolic BP above 160 mmHg while on three or more antihypertensives were screened. Those with suboptimal doses and white-coat hypertension were excluded and a total of 130 clinic referrals were received. Of those identified with resistant hypertension, only 24% had any workup for secondary causes, therefore, screening was initiated in 100% of referred patients. After completing 66 initial clinic visits, medication changes were implemented for 76% of patients, specialty referrals were made to nephrology or endocrinology for 30%, remote BP monitoring was offered to 26%, and advanced renal therapies including denervation, stenting and angioplasty were provided to 26%. Of those screened for secondary causes, elevated aldosterone/renin ratio (36%), documented obstructive sleep apnea (64%), and renal artery stenosis (20%) were detected. To date, 75% of patients have achieved BP control, with 65% experiencing 10 mmHg or more decrease in mean systolic BP.
These results reflect the positive impact of a health systems QI initiative. Here, we show the development and outcomes of a comprehensive program that increases screening for secondary causes, improves access to specialty care and helps patients take active control of their hypertension through remote BP monitoring and text-message reminders.
A population health-based registry was created to identify patients in large health systems who have uncontrolled BP while on three medications via EMR. A retrospective chart review was conducted to confirm that patients were appropriately identified. Their PCP then received a pended referral to Resistant Hypertension Clinic where patients are screened for secondary causes of hypertension, enrolled in remote BP monitoring and text-messaging for medication adherence, and evaluated for advanced therapies. The mean change in systolic BP and clinical outcomes were assessed longitudinally.
A cohort of 271 patients aged 29-86 years (66 ±15 years) with systolic BP above 160 mmHg while on three or more antihypertensives were screened. Those with suboptimal doses and white-coat hypertension were excluded and a total of 130 clinic referrals were received. Of those identified with resistant hypertension, only 24% had any workup for secondary causes, therefore, screening was initiated in 100% of referred patients. After completing 66 initial clinic visits, medication changes were implemented for 76% of patients, specialty referrals were made to nephrology or endocrinology for 30%, remote BP monitoring was offered to 26%, and advanced renal therapies including denervation, stenting and angioplasty were provided to 26%. Of those screened for secondary causes, elevated aldosterone/renin ratio (36%), documented obstructive sleep apnea (64%), and renal artery stenosis (20%) were detected. To date, 75% of patients have achieved BP control, with 65% experiencing 10 mmHg or more decrease in mean systolic BP.
These results reflect the positive impact of a health systems QI initiative. Here, we show the development and outcomes of a comprehensive program that increases screening for secondary causes, improves access to specialty care and helps patients take active control of their hypertension through remote BP monitoring and text-message reminders.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adherence and Persistence to Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy in Patients with Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Moon Jungyeon, Chiang Erin, Rodriguez Albert, Ozaki Aya, Lee Douglas, Mody Freny, Udell Jacob, Jackevicius Cynthia
Blood Pressure Lowering Effectiveness of Ultrasound Renal Denervation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Guerrero Hernandez Juan Miguel, Nuñez-gil Ivan, Garcia-mena Lissette, Palomino Ojeda Cristian