Final ID: FR453
Digital Health Literacy and Patient Activation in Adults at Risk for Stage 2 Hypertension: Insights from the LINKED-BP Program
Abstract Body: Introduction: Digital health literacy (DHL) reflects one's ability to navigate electronic health resources, while patient activation measures an individual's knowledge, skills, and confidence in managing their health. Both are essential for mitigating hypertension. Disparities in DHL across non-rural and rural health systems, as well as social determinants of health (SDoH), may pose barriers to effective patient care.
Objective: To examine the association between DHL and patient activation among adults at risk for stage 2 hypertension, adjusting for health system types and SDoH.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional analysis using baseline survey data from adults at risk for stage 2 hypertension enrolled in the “Home Blood Pressure Telemonitoring LINKED with CHWs to Improve Blood Pressure” (LINKED-BP) Program, a randomized clinical trial in health systems in Maryland and the Washington, DC metro area. Patient activation was assessed using the 13-item Patient Activation Measure (PAM-13, range 0-100). DHL was measured using the 8-item eHealth Literacy Scale (eHEALS, range 8–40; eHEALS < 26: low DHL; eHEALS ≥26: high DHL). Health system rurality was defined by the Federal Office of Rural Health Policy. Covariates included SDoH: age, sex, income, education, insurance, and race/ethnicity. We used descriptive statistics and multivariable linear regression to assess the association between DHL (both continuous and categorical) and patient activation, adjusted for covariates.
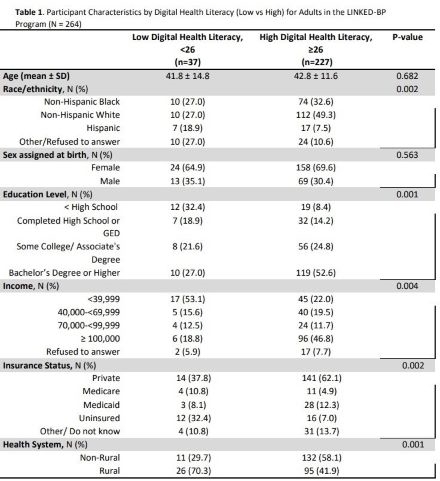
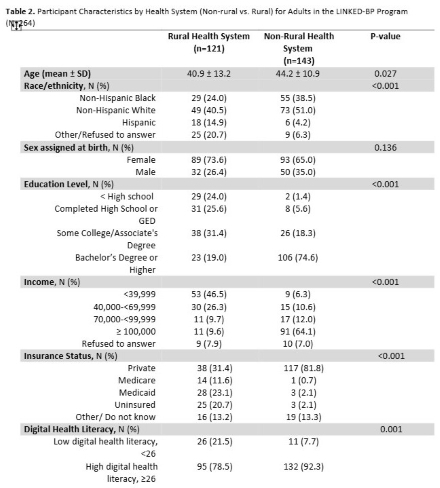
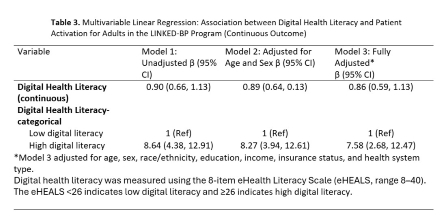
Results: Among 264 participants, 121 received care from a rural and 143 from a non-rural health system. A greater proportion of participants with low DHL vs high DHL were from the rural health system (70.3% vs 41.9%, P=0.001) (Table 1). Rural participants were more likely than non-rural to have a high school education or less (24.0% vs 1.4%, P<0.001) (Table 2). Each one-point increase in eHEALS was associated with a 0.86 higher patient activation score (95% CI: 0.59-1.13) (Table 3) in the fully adjusted model. Participants with high DHL had patient activation scores that were 7.58 points higher (95% CI: 2.68-12.47) compared to those with low DHL (Table 3) in the fully adjusted model.
Conclusions: Higher DHL was associated with greater patient activation among adults at risk for stage 2 hypertension after adjusting for health system type and SDoH. Future studies should explore how tailored digital resources for underserved and rural areas may reduce disparities in chronic disease outcomes.
Objective: To examine the association between DHL and patient activation among adults at risk for stage 2 hypertension, adjusting for health system types and SDoH.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional analysis using baseline survey data from adults at risk for stage 2 hypertension enrolled in the “Home Blood Pressure Telemonitoring LINKED with CHWs to Improve Blood Pressure” (LINKED-BP) Program, a randomized clinical trial in health systems in Maryland and the Washington, DC metro area. Patient activation was assessed using the 13-item Patient Activation Measure (PAM-13, range 0-100). DHL was measured using the 8-item eHealth Literacy Scale (eHEALS, range 8–40; eHEALS < 26: low DHL; eHEALS ≥26: high DHL). Health system rurality was defined by the Federal Office of Rural Health Policy. Covariates included SDoH: age, sex, income, education, insurance, and race/ethnicity. We used descriptive statistics and multivariable linear regression to assess the association between DHL (both continuous and categorical) and patient activation, adjusted for covariates.
Results: Among 264 participants, 121 received care from a rural and 143 from a non-rural health system. A greater proportion of participants with low DHL vs high DHL were from the rural health system (70.3% vs 41.9%, P=0.001) (Table 1). Rural participants were more likely than non-rural to have a high school education or less (24.0% vs 1.4%, P<0.001) (Table 2). Each one-point increase in eHEALS was associated with a 0.86 higher patient activation score (95% CI: 0.59-1.13) (Table 3) in the fully adjusted model. Participants with high DHL had patient activation scores that were 7.58 points higher (95% CI: 2.68-12.47) compared to those with low DHL (Table 3) in the fully adjusted model.
Conclusions: Higher DHL was associated with greater patient activation among adults at risk for stage 2 hypertension after adjusting for health system type and SDoH. Future studies should explore how tailored digital resources for underserved and rural areas may reduce disparities in chronic disease outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association Between Postprandial Hypotension Determined by Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring and Falls Among Older Adults with Hypertension Who Are Taking Antihypertensive Medication: Results from the AMBROSIA Study
Narita Keisuke, Schwartz Joseph, Sim John, Shimbo Daichi, Reynolds Kristi, Wei Rong, Harrison Teresa, Cannavale Kimberly, Qian Lei, Bowling Barrett, Fang Chloe, Muntner Paul
Association of Blood Pressure Control with Distance to Parameters of Social Determinants of HealthZehra Anum, Huang Shuo Jim, Aktay Sinan, Lyalomhe Ozi, Maron Bradley, Mccoy Rozalina