Final ID: TAC201
Socioeconomic and Clinical Predictors of Heart Disease Risk Knowledge among Older African Americans in the EnGAGE with Heart Study
Abstract Body: Background
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains a leading cause of death among older Black populations in the US, who face disproportionate burdens due to socioeconomic and structural inequities. We aimed to assess knowledge and awareness of heart disease risk factors and identify demographic and socioeconomic correlates of heart disease knowledge.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of baseline data from 181 older Black adult populations in the EnGAGE with Heart Study in Baltimore. Knowledge of risk for heart disease was measured using an abridged version of the Heart Disease Fact Questionnaire (HDFQ). Low Heart disease risk knowledge was defined as a total HDFQ score <9, a moderate level between 10 -13, and a high level of knowledge >14. We conducted a linear regression analysis to predict HDFQ scores from demographic, clinical, and socioeconomic variables.
Results
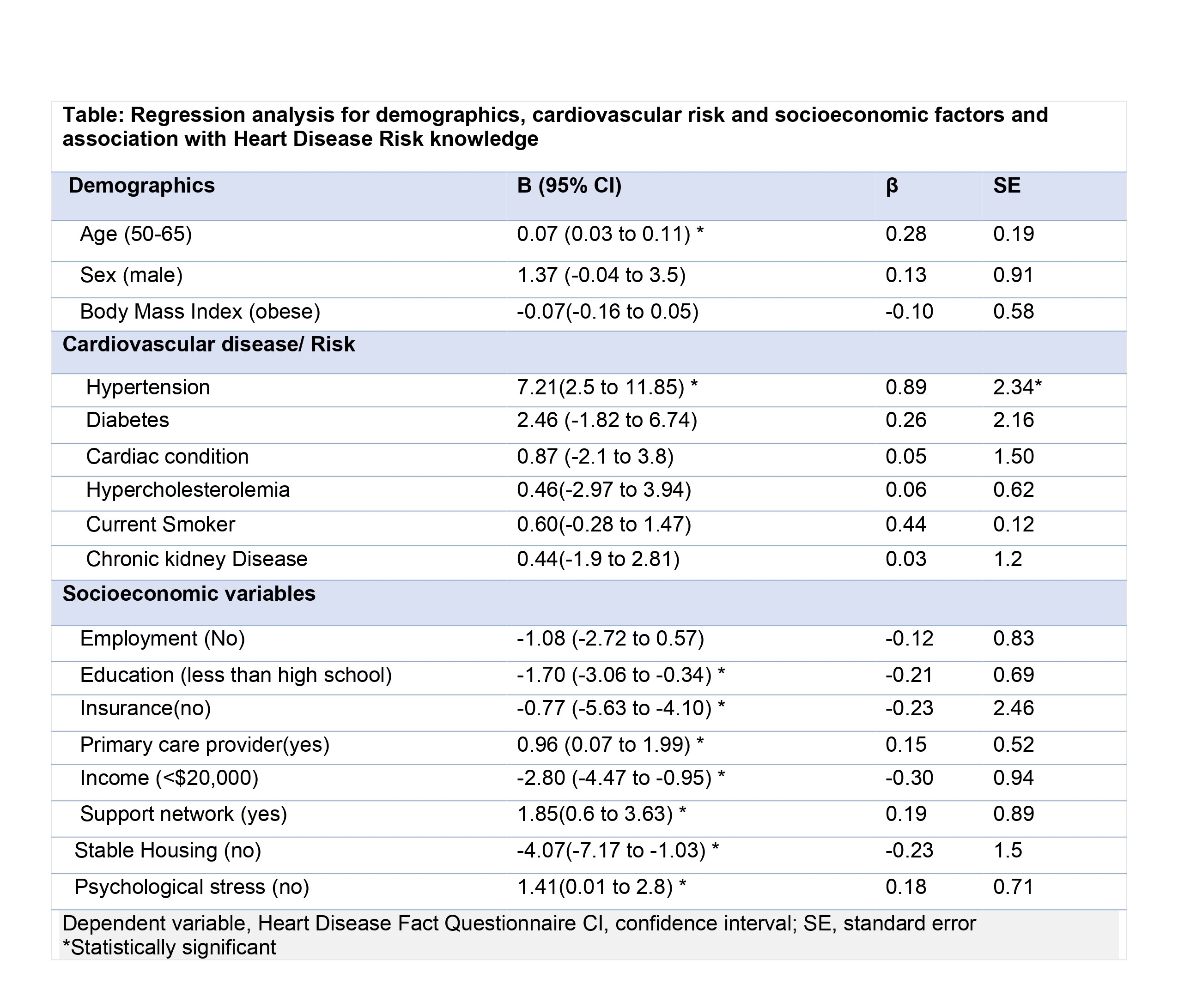
Among 181 participants (mean age 59.0 ± 16.6 years; 79.2% female), the mean HDFQ score was 12.1 (SD = 4.0). Overall knowledge of heart disease risk score was good (mean score 12.1 [out of 16], SD=4.0) with higher scores among men (13.26 ±3.2) than women 11.9± 4.1, p=0.014). Approximately 16% of participants demonstrated low heart disease knowledge, 24.2% had moderate knowledge, and 60.1% exhibited high knowledge levels. Age (β = 0.28; p<0.05), hypertension diagnosis (β = 0.89; p<0.05), having a primary care provider (β = 0.15 p<0.05), and a support network (β = 0.19; p<0.05) were associated with higher knowledge scores. In contrast, education less than high school (β = –0.21; p<0.05), income below $20,000 (β = –0.30; p<0.05), lack of insurance (β = –0.23; p<0.05), and housing instability (β = –0.23 p<0.05) were associated with lower knowledge scores. (Table).
Conclusions
Heart disease risk knowledge among older African Americans in Baltimore is suboptimal. Socioeconomic factors such as income and education significantly influence knowledge levels. Interventions focused on heart health literacy and risk awareness are needed to empower patients and improve cardiovascular outcomes in this high-risk population.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains a leading cause of death among older Black populations in the US, who face disproportionate burdens due to socioeconomic and structural inequities. We aimed to assess knowledge and awareness of heart disease risk factors and identify demographic and socioeconomic correlates of heart disease knowledge.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of baseline data from 181 older Black adult populations in the EnGAGE with Heart Study in Baltimore. Knowledge of risk for heart disease was measured using an abridged version of the Heart Disease Fact Questionnaire (HDFQ). Low Heart disease risk knowledge was defined as a total HDFQ score <9, a moderate level between 10 -13, and a high level of knowledge >14. We conducted a linear regression analysis to predict HDFQ scores from demographic, clinical, and socioeconomic variables.
Results
Among 181 participants (mean age 59.0 ± 16.6 years; 79.2% female), the mean HDFQ score was 12.1 (SD = 4.0). Overall knowledge of heart disease risk score was good (mean score 12.1 [out of 16], SD=4.0) with higher scores among men (13.26 ±3.2) than women 11.9± 4.1, p=0.014). Approximately 16% of participants demonstrated low heart disease knowledge, 24.2% had moderate knowledge, and 60.1% exhibited high knowledge levels. Age (β = 0.28; p<0.05), hypertension diagnosis (β = 0.89; p<0.05), having a primary care provider (β = 0.15 p<0.05), and a support network (β = 0.19; p<0.05) were associated with higher knowledge scores. In contrast, education less than high school (β = –0.21; p<0.05), income below $20,000 (β = –0.30; p<0.05), lack of insurance (β = –0.23; p<0.05), and housing instability (β = –0.23 p<0.05) were associated with lower knowledge scores. (Table).
Conclusions
Heart disease risk knowledge among older African Americans in Baltimore is suboptimal. Socioeconomic factors such as income and education significantly influence knowledge levels. Interventions focused on heart health literacy and risk awareness are needed to empower patients and improve cardiovascular outcomes in this high-risk population.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Community-Based Intervention to Improve Cardiovascular Health Understanding in the Dallas-Fort Worth South Asian Community
Deo Parminder, Rohatgi Anand, Sharma Parul, Sathyamoorthy Mohanakrishnan
An Epigenetic Drug, GSK126 Mitigates Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition Attenuating Atherosclerosis in DiabetesAziz Misbah, Jandeleitdahm Karin, Khan Abdul Waheed