Final ID: TAC279
Chronic Suppression of the Renin-Angiotensin System Induces Renal Vascular Remodeling, Hypoxia, and Metabolic Reprogramming
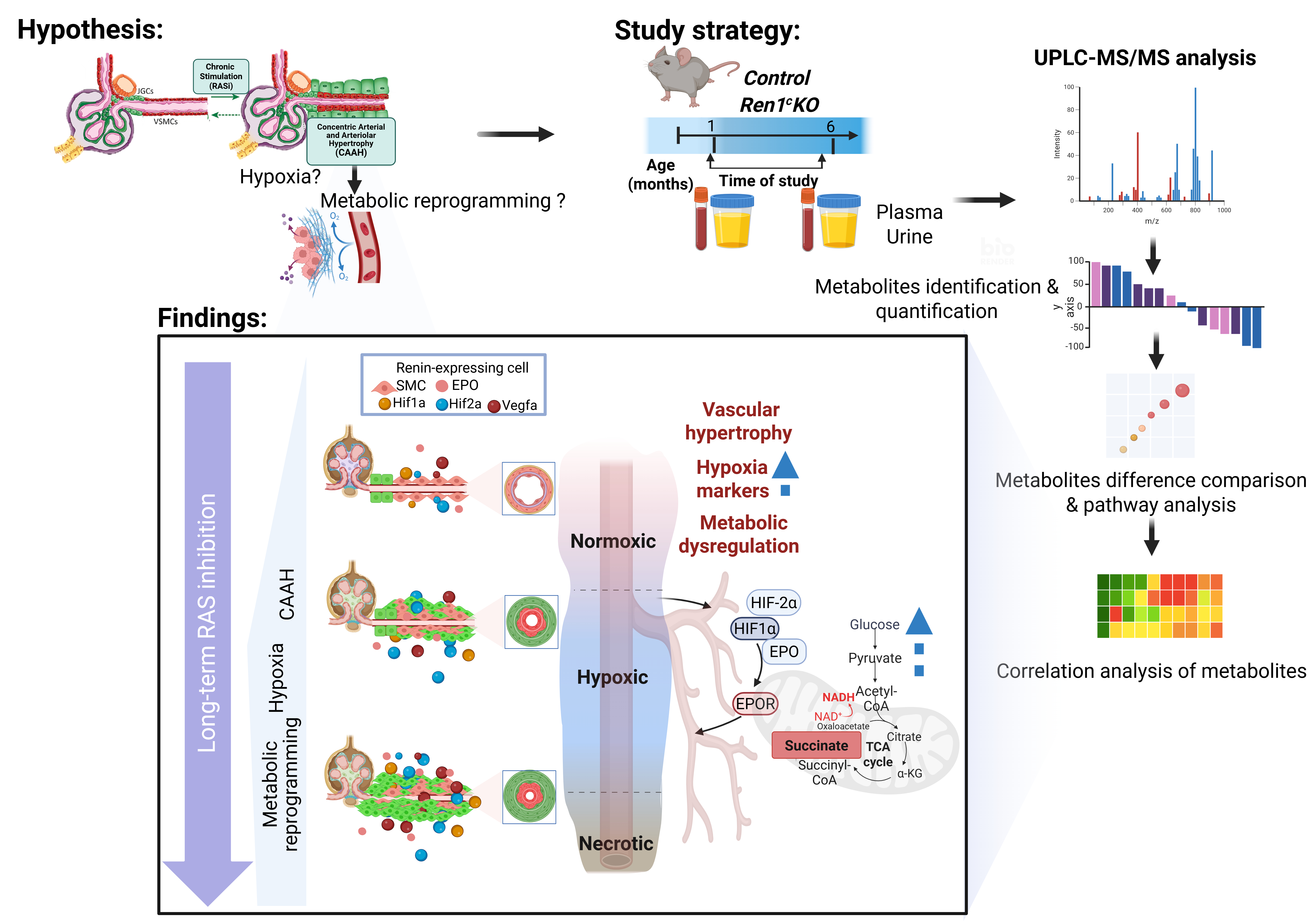
Abstract Body: Introduction: Hypertension is a global health burden and a major cause of cardiovascular, renal disease, and stroke. While renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors are effective antihypertensives, prolonged RAS suppression can induce renal vascular remodeling, characterized by concentric arteriolar and arterial hypertrophy. The metabolic consequences of this remodeling—particularly its role in promoting hypoxia and dysfunction—remain poorly defined. This study investigates whether chronic RAS inhibition drives hypoxia, metabolic reprogramming, and identifies potential biomarker of vascular injury.
Methods: we used two murine models of chronic RAS inhibition. In a genetic model, renin gene deletion (Ren1cKO, n=6–8) was compared to wild-type (WT) controls (n=6–8). In a pharmacologic model, WT mice were treated long-term with captopril (n=6–7) or left untreated (n=6–7). Plasma, urine, and kidney samples were collected at 1 and 6 months. Untargeted metabolomic profiling was performed by LC-MS. Renal hypoxia was assessed using Hypoxyprobe staining and qPCR for HIF-1α, HIF-2α, erythropoietin (Epo), and its receptor (EpoR). Glycolytic reprogramming was evaluated by qPCR and immunohistochemistry.
Results: Ren1cKO mice exhibited marked vascular thickening (4.54 ± 0.17 μm vs. 11.57 ± 0.91 μm, p<0.0001) and renin-lineage cell accumulation. Hypoxia was confirmed by increased Hypoxyprobe signal and upregulation of HIF-1α (p<0.0001), HIF-2α (p<0.002), Epo (p<0.0001), and EpoR (p<0.0001) (n=6-7). Metabolomic analysis revealed disruptions in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle (FDR=0.004, impact=0.3) and NAD metabolism (FDR=0.008, impact=0.3). Urinary succinate was elevated (log2 fold change= 2.5, p<0.0001), while nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolites were decreased (log2 fold change= –1.6, p<0.001). qPCR showed a 70-fold increase in hexokinase (HK) (p<0.0001) and a 4-fold increase in pyruvate kinase 2 (p<0.0001). Immunohistochemistry confirmed elevated HK and pyruvate kinase 2, supporting a hypoxia-driven glycolytic shift.
Conclusion: Chronic RAS suppression induces vascular remodeling and hypoxia, driving a metabolic shift marked by enhanced glycolysis, NAD depletion, and succinate accumulation. This cascade amplifies HIF signaling and contributes to renal injury, uncovering mechanistic links and potential biomarkers of RAS-driven vascular disease.
Methods: we used two murine models of chronic RAS inhibition. In a genetic model, renin gene deletion (Ren1cKO, n=6–8) was compared to wild-type (WT) controls (n=6–8). In a pharmacologic model, WT mice were treated long-term with captopril (n=6–7) or left untreated (n=6–7). Plasma, urine, and kidney samples were collected at 1 and 6 months. Untargeted metabolomic profiling was performed by LC-MS. Renal hypoxia was assessed using Hypoxyprobe staining and qPCR for HIF-1α, HIF-2α, erythropoietin (Epo), and its receptor (EpoR). Glycolytic reprogramming was evaluated by qPCR and immunohistochemistry.
Results: Ren1cKO mice exhibited marked vascular thickening (4.54 ± 0.17 μm vs. 11.57 ± 0.91 μm, p<0.0001) and renin-lineage cell accumulation. Hypoxia was confirmed by increased Hypoxyprobe signal and upregulation of HIF-1α (p<0.0001), HIF-2α (p<0.002), Epo (p<0.0001), and EpoR (p<0.0001) (n=6-7). Metabolomic analysis revealed disruptions in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle (FDR=0.004, impact=0.3) and NAD metabolism (FDR=0.008, impact=0.3). Urinary succinate was elevated (log2 fold change= 2.5, p<0.0001), while nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolites were decreased (log2 fold change= –1.6, p<0.001). qPCR showed a 70-fold increase in hexokinase (HK) (p<0.0001) and a 4-fold increase in pyruvate kinase 2 (p<0.0001). Immunohistochemistry confirmed elevated HK and pyruvate kinase 2, supporting a hypoxia-driven glycolytic shift.
Conclusion: Chronic RAS suppression induces vascular remodeling and hypoxia, driving a metabolic shift marked by enhanced glycolysis, NAD depletion, and succinate accumulation. This cascade amplifies HIF signaling and contributes to renal injury, uncovering mechanistic links and potential biomarkers of RAS-driven vascular disease.
More abstracts on this topic:
ACS-Specific Gut Microbial and Metabolic Profiles Reveal Diagnostic and Recovery Markers
Xu Jing, Fu Jingyuan, Dai Die, Yang Yanan, Yang Jingang, Gao Shanshan, Wu Chongming, He Jiumin, Chen Weihua, Yang Yue-jin
ADC-based Infarct Density – Validating a Novel Imaging Biomarker of Functional Outcome after Endovascular ThrombectomyFavilla Christopher, Bonkhoff Anna, Rost Natalia, Messe Steven, Regenhardt Robert, Denny Braden, Simonsen Claus, Shakibajahromi Banafsheh, Patel Aman, Leslie-mazwi Thabele, Dmytriw Adam, Schirmer Markus