Final ID: FR541
High Fiber Diet Attenuates Established Age-Dependent Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis, Hypertension, and Impaired Renal Sodium Handling
Abstract Body: Introduction: Hypertension is the leading preventable cause of premature death worldwide and its prevalence increases with age. Previously, we reported that aging caused hypertension, sympathoexcitation and increased renal sodium retention in male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats. Aging also leads to gut microbiota dysbiosis, which can drive the development of hypertension. Interestingly, high dietary fiber, which is absent in a Western diet, is essential for gut microbiota homeostasis and is associated with lower blood pressure and improved cardiorenal function.
Hypothesis: High prebiotic fiber (HF) diet attenuates age-dependent gut microbiota dysbiosis and hypertension through improving renal dysfunction in aged male SD rats.
Method: Groups of male SD rats (n=4-6/group) were used in this study: 3 months (mo) old (Young) on normal fiber chow (NC), 16 mo old on NC (Aged), and 16 mo old on NC plus 6 weeks of 20% HF diet (Aged+HF). Mean arterial pressure (MAP; assessed by acute femoral artery cannulation), gut microbiota taxonomy (by WGS), cecal short chain fatty acid (SCFA) content (by GC-MS), paraventricular nucleus (PVN) blood brain barrier (BBB) integrity (by FITC extravasation) and neuroinflammation (by microglial activation), renal sodium handling (by 24-hour Na+ balance & acute 5% body weight volume expansion), renal cortex norepinephrine (NE; by ELISA) and sodium chloride cotransporter (NCC) and phosphorylated NCC (pNCC T53) expression normalized to total protein expression (by immunoblotting) were assessed in all rats.
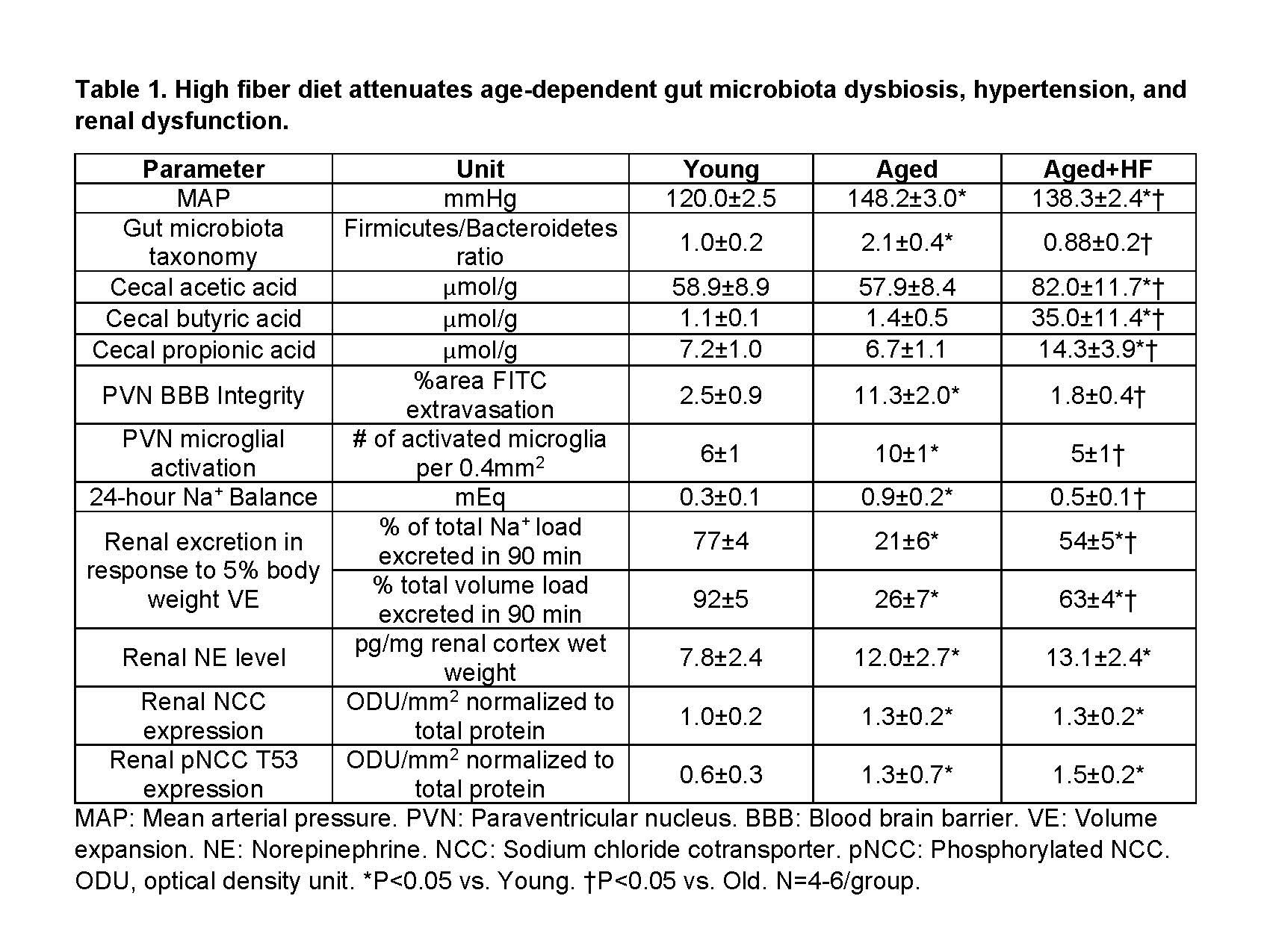
Result: We observed that a HF diet attenuated age-dependent gut microbiota dysbiosis and hypertension in aged+HF compared to aged rats (P<0.05). PVN BBB integrity was impaired and neuroinflammation was increased in aged rats but rescued in aged+HF rats (P<0.05). Renal sodium handling was impaired in aged rats but improved in aged+HF rats (P<0.05). However, renal NE, NCC, and pNCC T53 levels were higher in aged rats (P<0.05), but were not lowered in aged+HF rats (P>0.05). Data are presented in Table 1.
Conclusion: A HF diet attenuated age-dependent gut microbiota dysbiosis and hypertension in aged SD rats. We speculate that blood pressure reductions are driven by reductions in PVN neuroinflammation-evoked, sympathetically mediated renal sodium retention, which occurs independently from the activity of the NCC, and a HF diet can lower blood pressure, improve cardiorenal function, and evoke healthy aging.
Hypothesis: High prebiotic fiber (HF) diet attenuates age-dependent gut microbiota dysbiosis and hypertension through improving renal dysfunction in aged male SD rats.
Method: Groups of male SD rats (n=4-6/group) were used in this study: 3 months (mo) old (Young) on normal fiber chow (NC), 16 mo old on NC (Aged), and 16 mo old on NC plus 6 weeks of 20% HF diet (Aged+HF). Mean arterial pressure (MAP; assessed by acute femoral artery cannulation), gut microbiota taxonomy (by WGS), cecal short chain fatty acid (SCFA) content (by GC-MS), paraventricular nucleus (PVN) blood brain barrier (BBB) integrity (by FITC extravasation) and neuroinflammation (by microglial activation), renal sodium handling (by 24-hour Na+ balance & acute 5% body weight volume expansion), renal cortex norepinephrine (NE; by ELISA) and sodium chloride cotransporter (NCC) and phosphorylated NCC (pNCC T53) expression normalized to total protein expression (by immunoblotting) were assessed in all rats.
Result: We observed that a HF diet attenuated age-dependent gut microbiota dysbiosis and hypertension in aged+HF compared to aged rats (P<0.05). PVN BBB integrity was impaired and neuroinflammation was increased in aged rats but rescued in aged+HF rats (P<0.05). Renal sodium handling was impaired in aged rats but improved in aged+HF rats (P<0.05). However, renal NE, NCC, and pNCC T53 levels were higher in aged rats (P<0.05), but were not lowered in aged+HF rats (P>0.05). Data are presented in Table 1.
Conclusion: A HF diet attenuated age-dependent gut microbiota dysbiosis and hypertension in aged SD rats. We speculate that blood pressure reductions are driven by reductions in PVN neuroinflammation-evoked, sympathetically mediated renal sodium retention, which occurs independently from the activity of the NCC, and a HF diet can lower blood pressure, improve cardiorenal function, and evoke healthy aging.
More abstracts on this topic:
Activation of TRPA1 with allyl isothiocyanate prevents age-related cardiac diastolic dysfunction
Qian Chunqi, Fernandez Zachary, Wang Donna, Ma Shuangtao
Accelerated Biological Aging, Early-Life Exposure to Tobacco, and Incident Aortic Aneurysm: A Large-Scale Prospective Cohort Study in UK BiobankYang Miaomiao, Feng Weijing, Dang Aimin, Gu Yingzhen