Final ID: 079
Eplerenone treatment limit electrocardiogram alteration in a non-diabetic chronic kidney disease rat model.
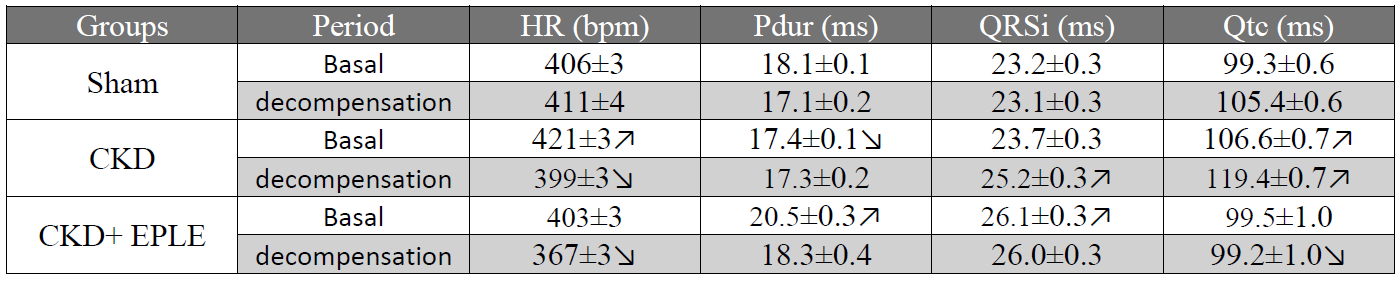
Abstract Body: Background: Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular mortality, particularly due to arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. While the mechanisms underlying CKD-induced sudden cardiac death remain unclear, they may involve electrolyte imbalances, atrial/ventricular extracellular matrix remodeling, and electrophysiological changes. Of interest mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) antagonists have been consistently reported by us and others to be beneficial, partly by reducing atrial fibrillation and sudden cardiac death which is mainly caused by ventricular arrythmia. This study aims to assess the electrocardiogram (ECG) remodeling in a rat model of CKD and evaluate the impact of MR antagonism in preventing arrhythmias. Methods: CKD was induced in Sprague-Dawley rats via 5/6 nephrectomy. A subset of rats was treated with eplerenone (100 mg/kg/day, oral) for 3 months. ECG were recorded non-invasively using a jacket system (DECRO, ETISENSE) for 22 hours, and ECG intervals were averaged hourly. Following these baseline recordings, rats underwent sodium overload (NaCl 1.8g/kg, oral) to induce cardiac decompensation, and the ECG recording was repeated. Results: Twenty-two-hour ECG recordings revealed that CKD significantly impacted several electrophysiological parameters. The untreated CKD group exhibited decreased P wave duration (Pdur) and increased QT interval (QTc) compared to the SHAM group. Eplerenone-treated CKD rats showed a reduction in QTc elongation, with levels similar to SHAM animals. Following sodium overload, inducing a cardiac decompensation, we observed elongation of QTc in both Sham and CKD compared to non-challenged 22h recording which was not observed in the group treated by eplerenone. Conclusion: QT interval prolongation in CKD rats highlights an increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death, which was prevent by eplerenone. Furthermore, upon mimicking decompensated heart failure, a similar protective effect of eplerenone on QTc prolongation was observed. These results underscores eplerenone potential in mitigating arrhythmic risk in CKD.
More abstracts on this topic:
Efficacy and safety of finerenone in patients with heart failure and mildly reduced or preserved ejection fraction: A prespecified sex-specific analysis of the FINEARTS-HF trial
Chimura Misato, Lam Carolyn, Senni Michele, Shah Sanjiv, Voors Adriaan, Zannad Faiez, Pitt Bertram, Vaduganathan Muthiah, Solomon Scott, Mcmurray John, Jhund Pardeep, Henderson Alasdair David, Claggett Brian, Desai Akshay, Mueller Katharina, Glasauer Andrea, Rohwedder Katja, Viswanathan Prabhakar
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Variability, Progression of Kidney Disease, and Cardiovascular Outcomes in the Chronic Renal Insufficiency CohortByfield Rushelle, Cohen Debbie, Townsend Raymond, Zhang Rachel, Hossain Alavi, Shimbo Daichi, Cohen Jordana