Final ID: P-133
Global Burden and Trends of Stroke attributable to High Systolic Blood Pressure in High Income North America countries from 1990-2021: A Secondary analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021
Abstract Body: Background: Stroke is the 5th leading cause of deaths and 8th leading cause of disability amongst all causes in High income north America (HINA) countries. The imperative to evaluate the comprehensive burden of stroke attributable to high systolic blood pressure (HBP) in these countries is heightened by a scarcity of evidence.
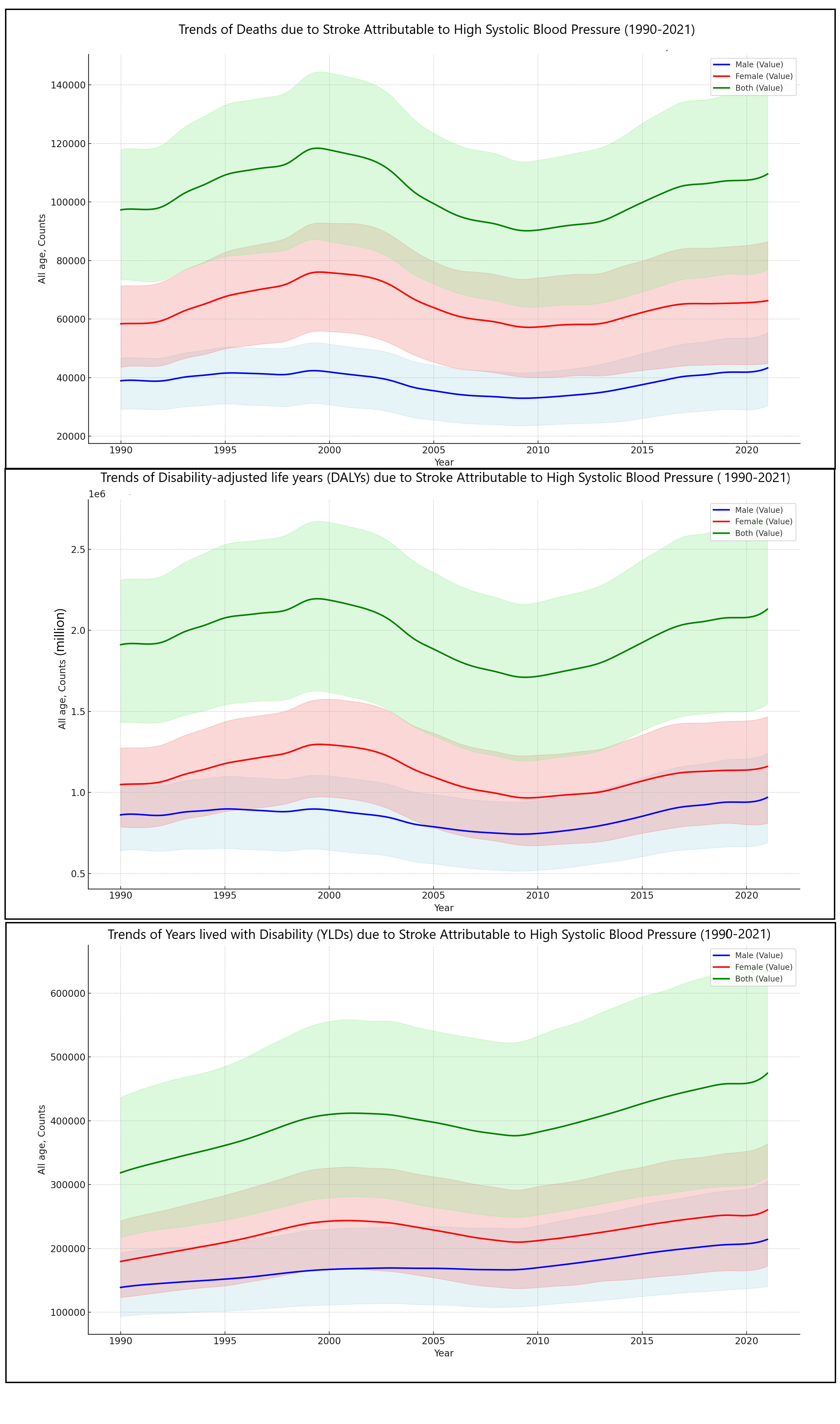
Method: Using GBD standardized methodologies, we estimated Stroke attributable to HBP deaths, DALYs (disability adjusted life years), years lived with disability (YLDs) stratified by Age, Gender, year, location across the HINA countries in the last 3 decades.
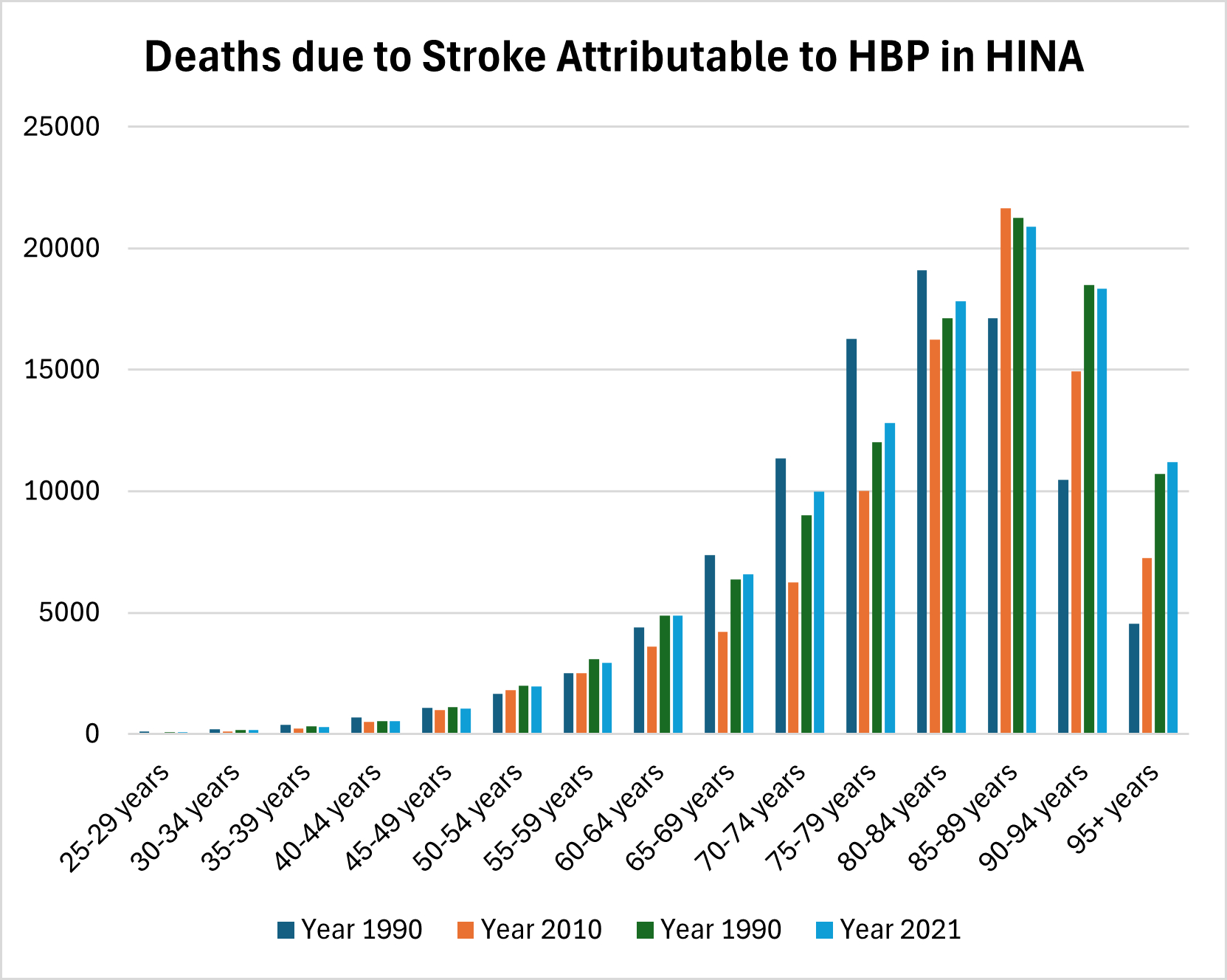
Results: From 1990 to 2021, the total percentage change (TPC) in death counts rose by 13%, with DALYs increasing by 11% and YLDs by 49%. Greenland had the highest age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) for the observed period at 34.86 cases per 100,000, followed by the United States at 15.77 cases per 100,000 and Canada at 10.42 cases per 100,000 in 2021. Greenland also recorded the highest YLD rate at 78.92 cases per 100,000, with the U.S. following at 75.6 cases per 100,000. Among age groups, the highest death rates were in those aged 85-89, while the highest DALYs were in the 80-84 age group, and YLDs peaked in the 70-74 age group. Regarding gender differences from 1990-2021, the TPC showed a 11% increase in male deaths versus a 13% increase in female deaths, with DALYs at 12% for males and 11% for females, and YLDs at 54% for males versus 45% for females.
Conclusion: In 2021, deaths from stroke attributable to HBP made up 52.46% of all stroke-related deaths in HINA, underscoring the urgent need for enhanced public health strategies, targeted campaigns, and policy interventions to facilitate early access to stroke treatments. This calls for a decisive action by clinicians and health policymakers to mitigate this significant health burden.
Method: Using GBD standardized methodologies, we estimated Stroke attributable to HBP deaths, DALYs (disability adjusted life years), years lived with disability (YLDs) stratified by Age, Gender, year, location across the HINA countries in the last 3 decades.
Results: From 1990 to 2021, the total percentage change (TPC) in death counts rose by 13%, with DALYs increasing by 11% and YLDs by 49%. Greenland had the highest age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) for the observed period at 34.86 cases per 100,000, followed by the United States at 15.77 cases per 100,000 and Canada at 10.42 cases per 100,000 in 2021. Greenland also recorded the highest YLD rate at 78.92 cases per 100,000, with the U.S. following at 75.6 cases per 100,000. Among age groups, the highest death rates were in those aged 85-89, while the highest DALYs were in the 80-84 age group, and YLDs peaked in the 70-74 age group. Regarding gender differences from 1990-2021, the TPC showed a 11% increase in male deaths versus a 13% increase in female deaths, with DALYs at 12% for males and 11% for females, and YLDs at 54% for males versus 45% for females.
Conclusion: In 2021, deaths from stroke attributable to HBP made up 52.46% of all stroke-related deaths in HINA, underscoring the urgent need for enhanced public health strategies, targeted campaigns, and policy interventions to facilitate early access to stroke treatments. This calls for a decisive action by clinicians and health policymakers to mitigate this significant health burden.
More abstracts on this topic:
A durable reduction in blood pressure by ultrasound renal denervation: A real-world, single center experience
King Jordan, Gharib Wissam
Acute Myocardial Infarction and Stroke Outcomes Vary Substantially Across Private Equity FirmsBartlett Victoria, Johnson Daniel, Liu Michael, Zheng Zhaonian, Wadhera Rishi