Final ID: P-204
Global, National and regional burden and Trend of Chronic Kidney Disease due to Hypertension in 204 Countries and Territories from 1990-2021: A Benchmarking Global Analysis
Abstract Body: Background: Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) ranks as the 11th leading cause of death globally, with over 1.5 million deaths annually. Despite its growing impact, there is a lack of data on the burden of CKD attributable to various risk factors. This study represents the first-ever comprehensive analysis of the global burden of CKD due to Hypertension (HTN) over the past three decades, including the initial two years of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Method: Utilizing the Global Burden of Disease 2021 methodology, we assessed the incidence, prevalence, mortality, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), and years lived with disability (YLDs) attributable to CKD due to HTN across 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2021.
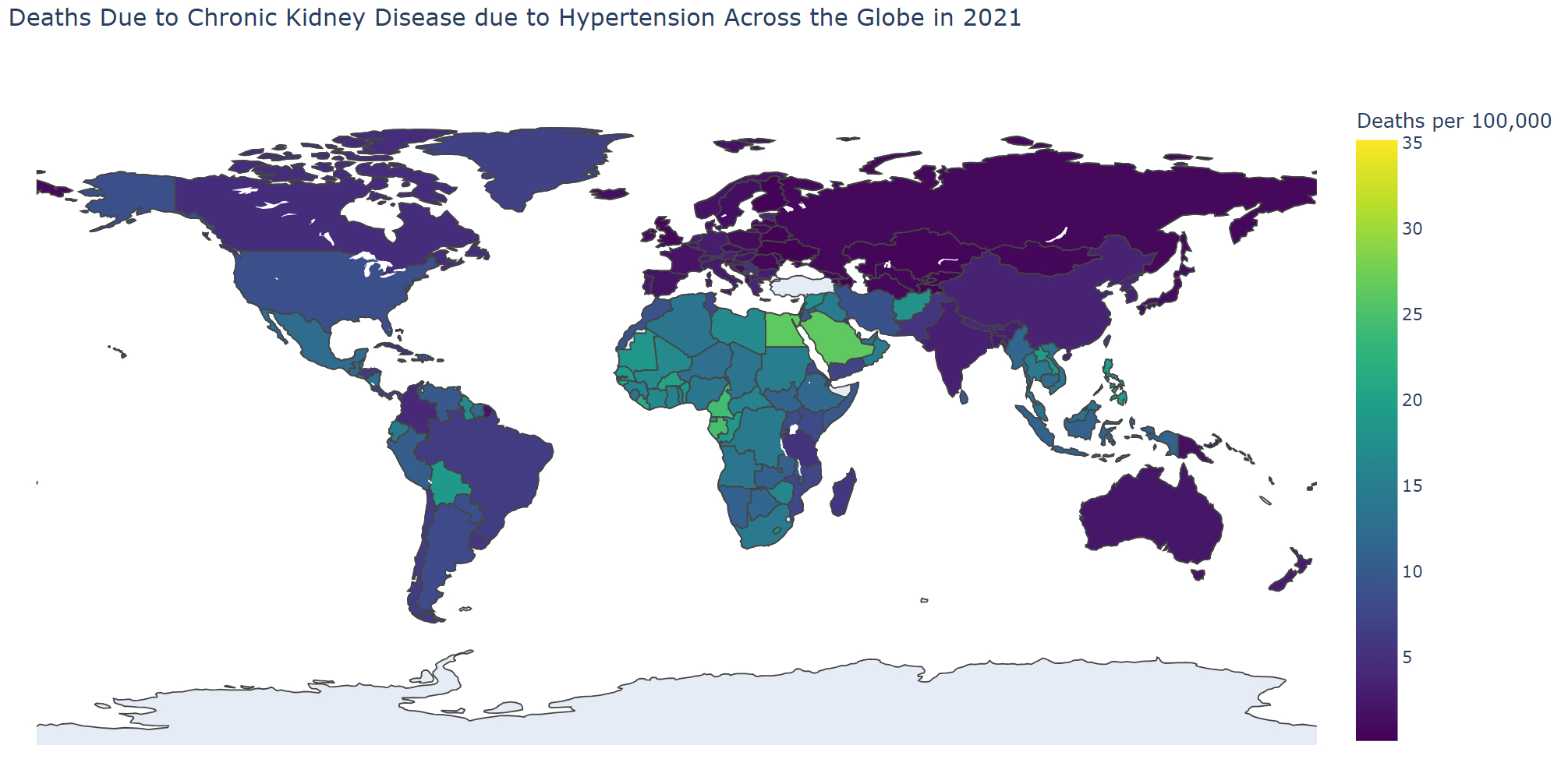
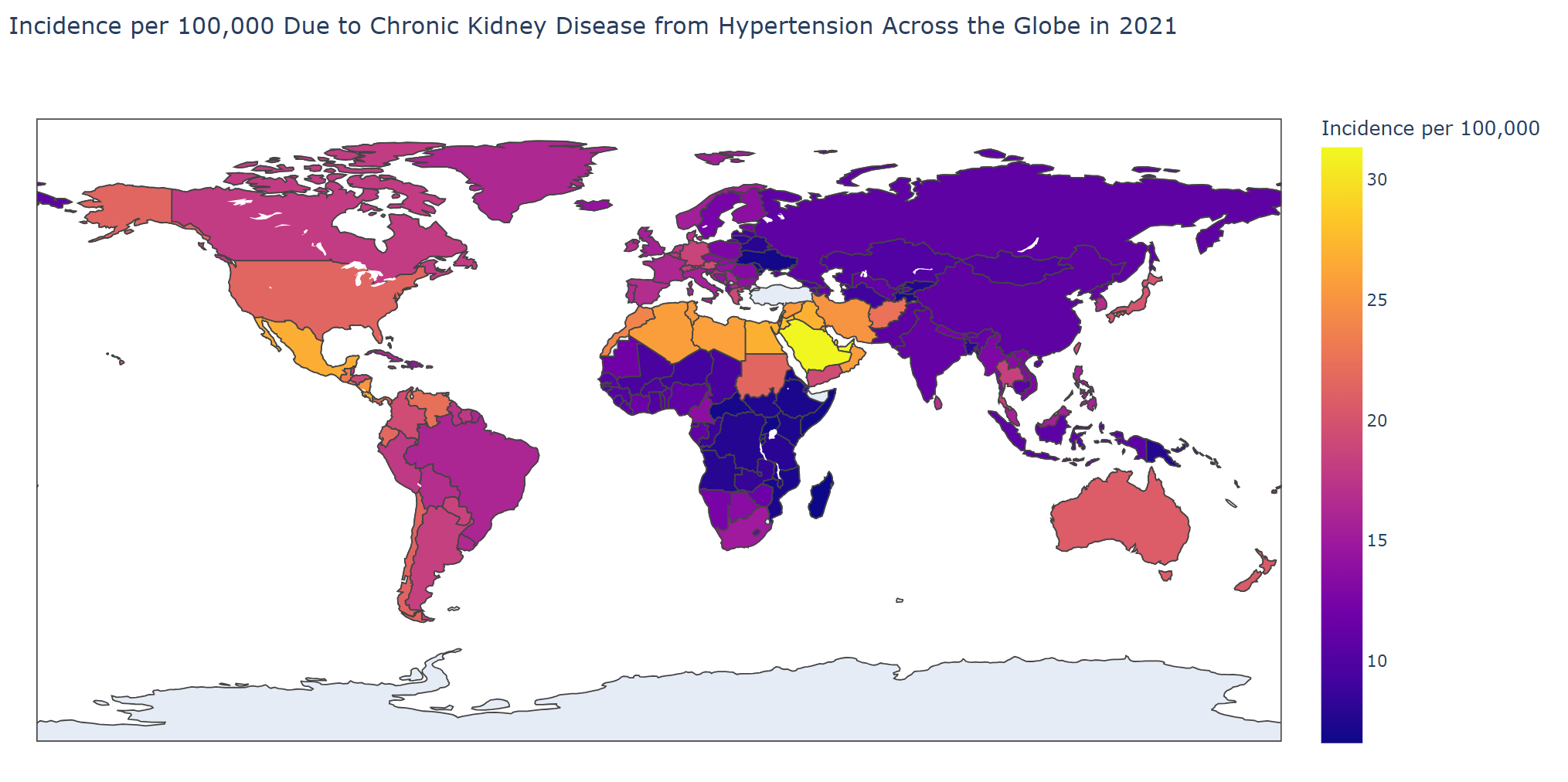
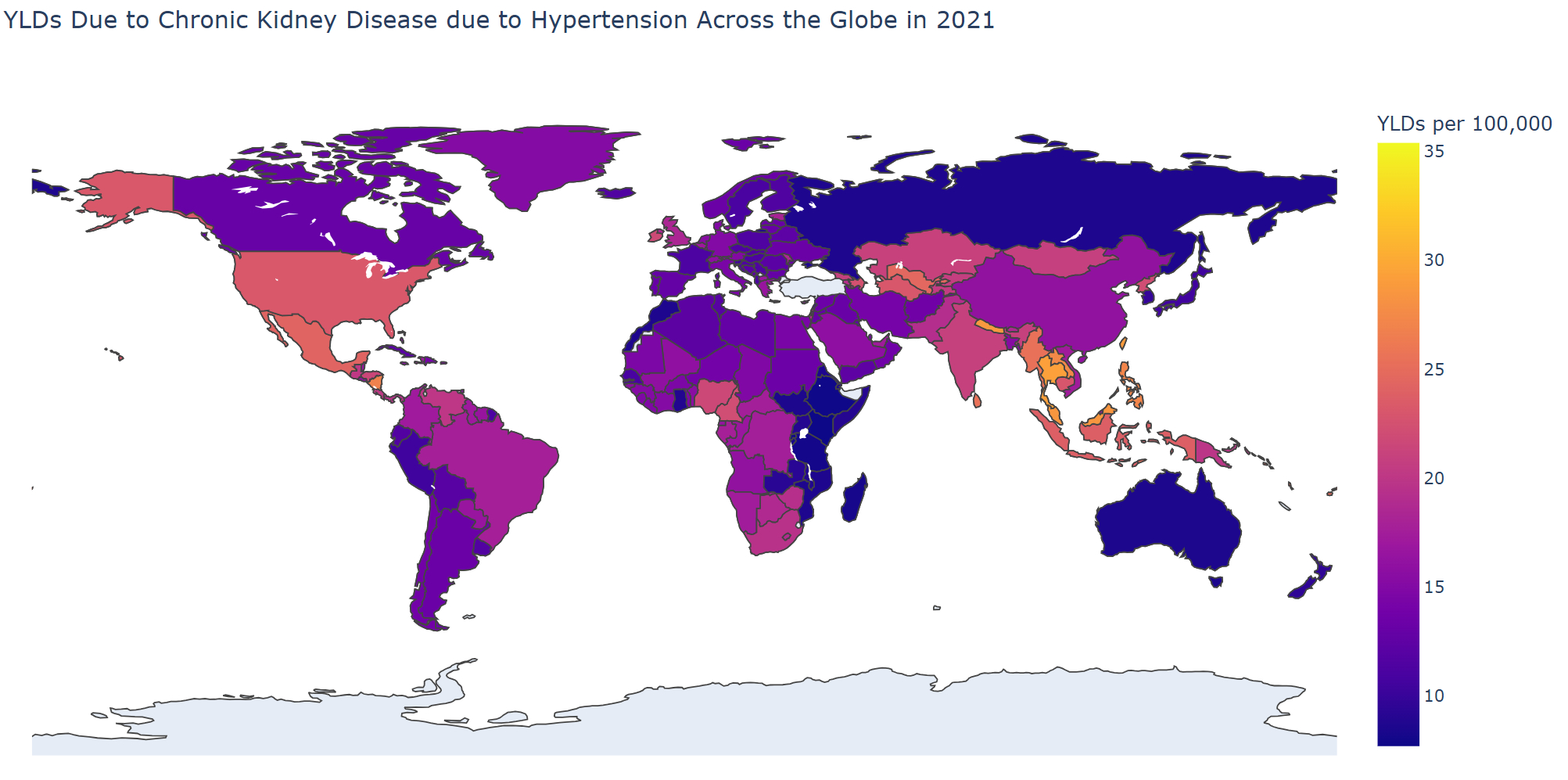
Results: Our findings reveal a significant increase in the burden of CKD due to HTN over the study period. The total percentage of change (TPC) in prevalence, deaths, and DALYs increased by 109%, 205%, and 150% respectively from 1990 to 2019. Age-standardized mortality rates and DALYs rates rose by 29% and 19% respectively. Regionally, Central Asia experienced the highest increase in age-standardized mortality rates (180%), while high-income North America saw a 117% rise in DALYs rates, and Andean Latin America observed an 88% increase in incidence rates. Among nations, Ukraine witnessed the highest increase in mortality rates at 1641% from 1990 to 2021. In terms of age, the highest number of deaths occurred in the 85-89 age group (63,706), with 65-69-year-olds experiencing the highest DALYs at 1.1 million in 2021. Males bore a greater burden compared to females, with TPC in deaths (197% vs. 214%) and incidence (184% vs. 169%) from 1990 to 2021.
Conclusion: In conclusion, addressing the escalating burden of CKD due to HTN requires coordinated efforts from public health policymakers, clinicians, and stakeholders. Preventive measures should focus on early detection and management of hypertension, promoting healthy lifestyle choices, enhancing access to quality healthcare services, and implementing evidence-based interventions. Collaboration across sectors is essential for implementing effective policies and interventions to mitigate the impact of CKD due to HTN on global health.
Method: Utilizing the Global Burden of Disease 2021 methodology, we assessed the incidence, prevalence, mortality, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), and years lived with disability (YLDs) attributable to CKD due to HTN across 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2021.
Results: Our findings reveal a significant increase in the burden of CKD due to HTN over the study period. The total percentage of change (TPC) in prevalence, deaths, and DALYs increased by 109%, 205%, and 150% respectively from 1990 to 2019. Age-standardized mortality rates and DALYs rates rose by 29% and 19% respectively. Regionally, Central Asia experienced the highest increase in age-standardized mortality rates (180%), while high-income North America saw a 117% rise in DALYs rates, and Andean Latin America observed an 88% increase in incidence rates. Among nations, Ukraine witnessed the highest increase in mortality rates at 1641% from 1990 to 2021. In terms of age, the highest number of deaths occurred in the 85-89 age group (63,706), with 65-69-year-olds experiencing the highest DALYs at 1.1 million in 2021. Males bore a greater burden compared to females, with TPC in deaths (197% vs. 214%) and incidence (184% vs. 169%) from 1990 to 2021.
Conclusion: In conclusion, addressing the escalating burden of CKD due to HTN requires coordinated efforts from public health policymakers, clinicians, and stakeholders. Preventive measures should focus on early detection and management of hypertension, promoting healthy lifestyle choices, enhancing access to quality healthcare services, and implementing evidence-based interventions. Collaboration across sectors is essential for implementing effective policies and interventions to mitigate the impact of CKD due to HTN on global health.
More abstracts on this topic:
Cardiology Medications and Medicare Spending: Opportunities for Savings Using Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company and Costco Member Prescription Program Pricing
Schoeffler Katherine, Day Stephanie, Sanjamala Hemanth, Danesh Alireza, Rosales Isaac, Fennell Zachary, Aguilar Atticus, Parikh Suparshva, Nipp Ryan
A Quarter Century of Cardiovascular Strain: Mortality Trends in Hypertension and Hypertensive Heart Disease Among U.S. Adults Aged 55+Ali Muhammad Faizan, Khan Muhammad, Sharif Aleena, Hossain Mohammad, Ahmad Husnain, Eltawansy Sherif, Faizan Muhammad, Ahmed Ashraf, Abdul Malik Mohammad Hamza Bin, Pahwani Ritesh, Patel Rahul, Mehdi Hassan