Final ID: MP-32
Megalin and lysosomal disruption in the kidney epithelial cells of high salt diet fed rats: protective role of angiotensin II type 2 receptor
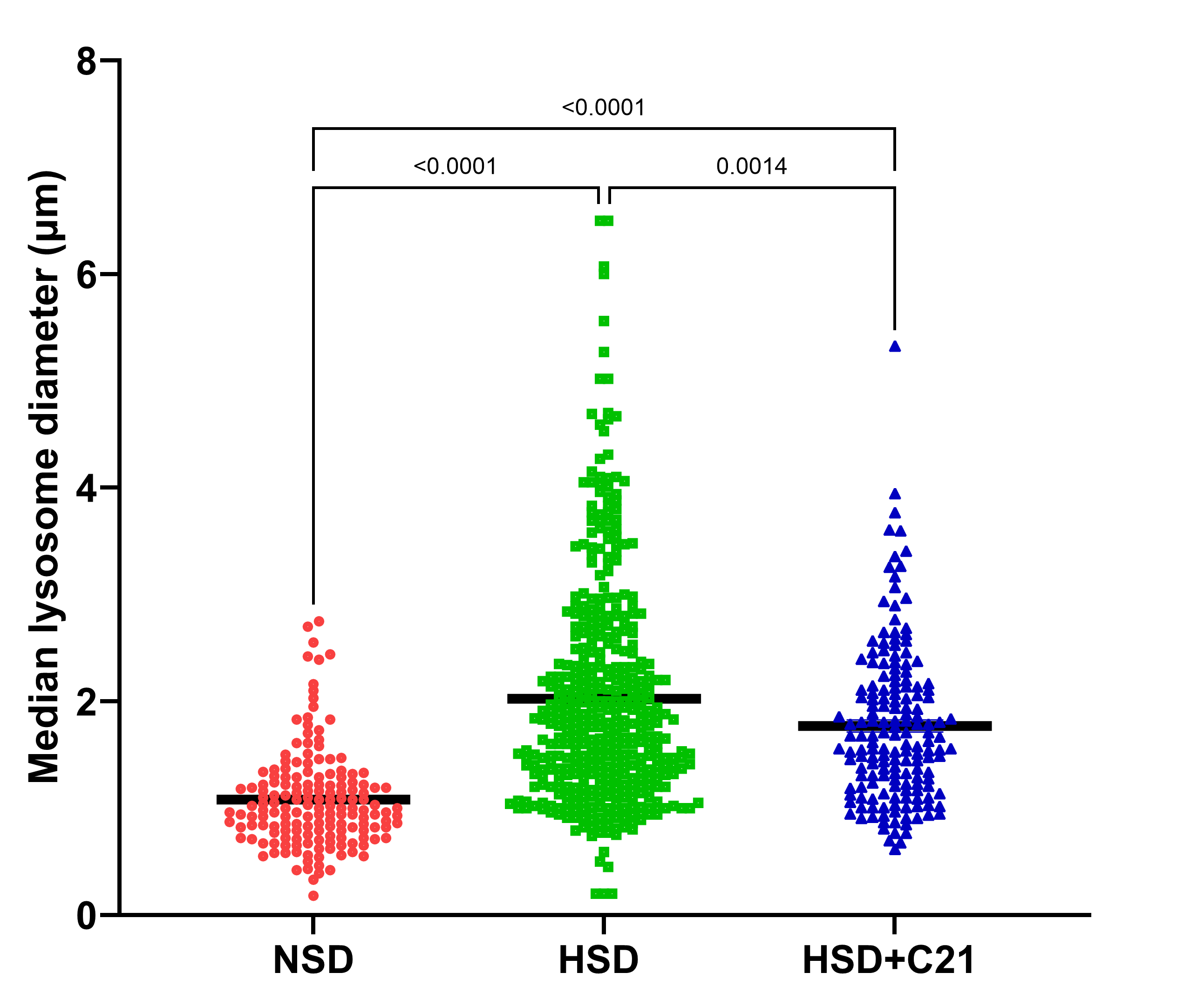
Abstract Body: Earlier we have reported that 2-days high salt diet (HSD) feeding caused proteinuria in obese rats and the AT2R agonist treatment prevented proteinuria. Since HSD feeding for 2 days and the AT2R activation did not affect blood pressure, GFR, glomerular structure, and inflammation, the mechanism responsible for proteinuria remains unknown. Megalin is a proximal tubule epithelial cells endocytic receptor responsible for filtered protein reabsorption. The absorbed proteins are directed to lysosomes for degradation. Lysosomes is a nutrient sensing subcellular compartment and a critical part of the endocytic machinery and cellular trafficking. We hypothesized that high salt intake caused lysosomal stress, which negatively impacted megalin-protein cellular trafficking and thus caused proteinuria. Therefore, we evaluated the markers of lysosomal stress and megalin expression in the proximal tubules of HSD fed obese Zucker rats. Urinary excretion of N-acetyl-glucosaminidase (NAG), which is a marker of lysosomal injury and oxidative stress, was significantly increased in HSD fed rats compared with normal salt diet (NSD: 16.6 vs HSD: 40.5 RFU/hr/µg Cr). This increase was associated with an increase in another oxidative stress marker H2O2 in the urine (NSD: 0.37 vs HSD: 1.72 ΔRFU/min). Confocal analysis revealed that megalin was localized in the lysosomes in HSD fed rats, as megalin was co-localized with the lysosomal marker LAMP-1 in the proximal tubules. Moreover, in HSD fed rats there was a remarkable increase (2-fold) in the lysosomal size (fig) and number per tubule (NSD: 18 vs HSD: 48). The AT2R agonist C21 (0.3 mg/Kg/day, i.p.) treatment of HSD-fed rats restored surface megalin expression, reduced urinary NAG and H2O2 and the lysosomal number and size. Our in vitro studies performed in OK cells (proximal tubule epithelial cells) treated with high NaCl (100 mM) without/with the AT2R agonist C21 (1µM) also revealed that compared to NSD, high NaCl reduced megalin surface expression and C21 treatment prevented it. We conclude that high salt intake causes lysosomal stress. Particularly, large lysosomal size potentially is affecting endocytic machinery, including impairing megalin-protein dissociation and megalin recycling, thus causing proteinuria.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Loss-of-Function Missense Variant in ANGPTL3 Exerts Protective Effects Against Kidney Disease Risk
Zhang David, Ritchie Marylyn, Rader Daniel, Cuchel Marina
Adoptive Transfer of Lupus Patient PBMCs Promotes Salt-Sensitive Hypertension and Kidney Injury in Immunodeficient MiceSaleem Mohammad, Ormseth Michelle, Kirabo Annet, Ahmad Taseer, Haynes Alexandria, Albritton Claude, Arshad Suha, Kulapatana Phicharmon, Posey Olivia, Major Amy, Stein Charles