Final ID: P-373
Statewide burden and Trend of Cardiovascular Disease attributable to High Systolic Blood Pressure in India from 1990-2021: An insight from the global burden of disease study 2021.
Abstract Body:
Background:Cardiovascular disease(CVD) is the foremost cause of death and disability worldwide,including in India,where high systolic blood pressure(HBP) stands as the principal modifiable risk factor.The escalating burden of hypertension in India is primarily driven by lifestyle changes,population aging,rising stress levels,growing obesity rates,high tobacco & alcohol use,and variable access to healthcare. This critical backdrop underscores the necessity of assessing the CVD burden attributable to HBP,a domain currently lacking robust data. This pioneering study provides the first comprehensive estimation of this burden over the past three decades,incorporating the initial 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Method:Using global burden of disease 2021 tool, we estimated deaths,disability-adjusted life years(DALYs),Years lived with disability(YLDs) due to CVD attributable to HBP by age,sex,year,location across the India from 1990-2021.
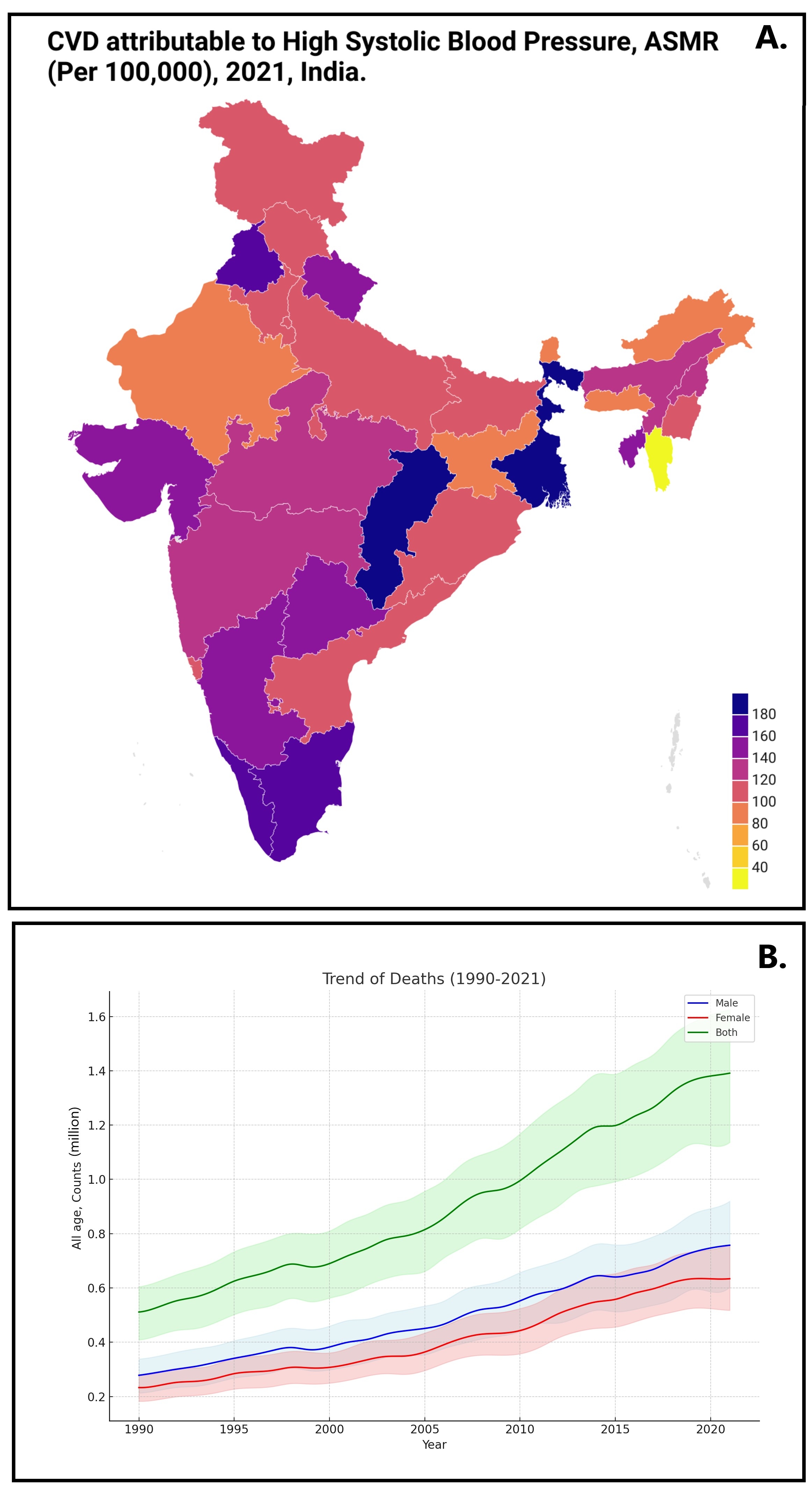
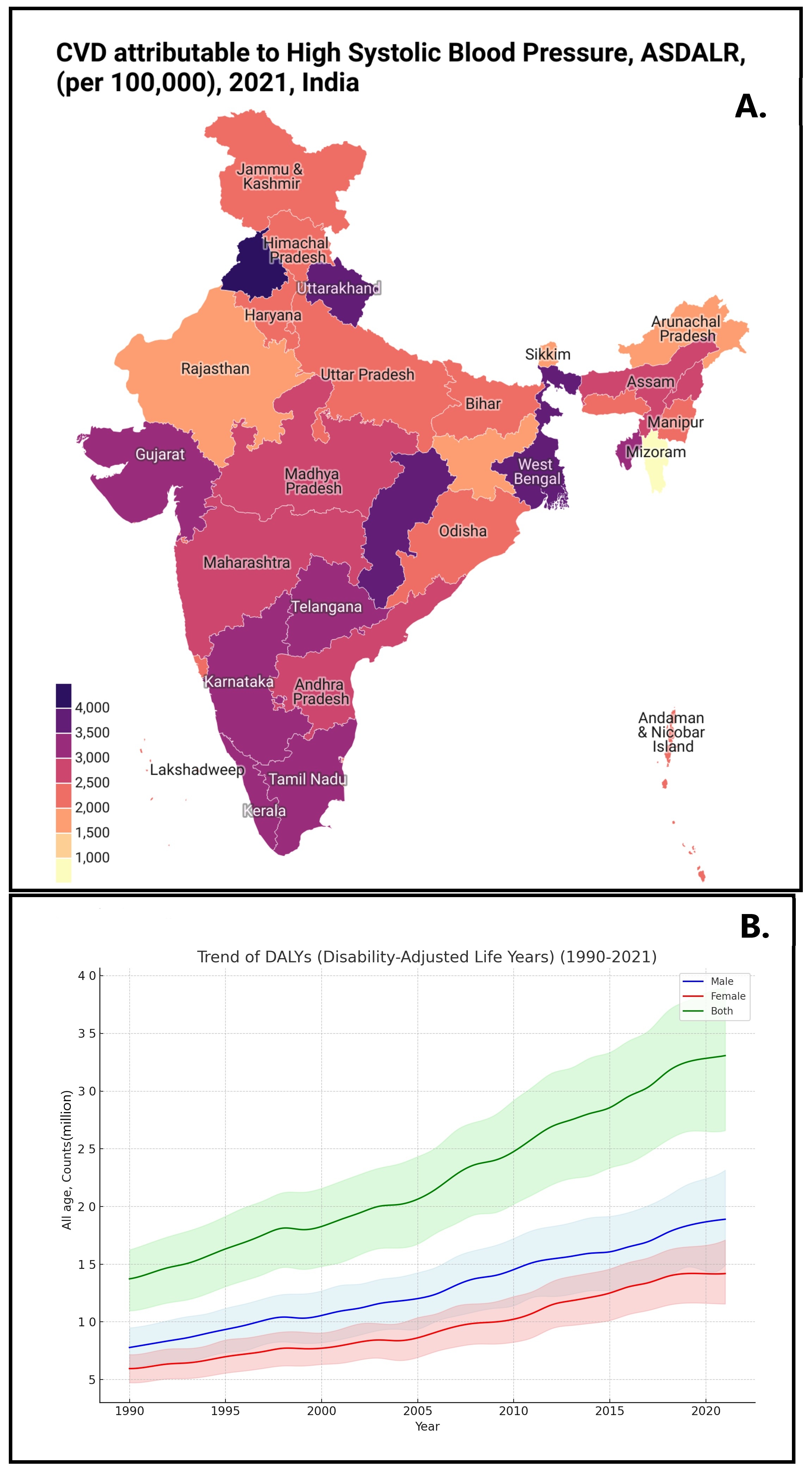
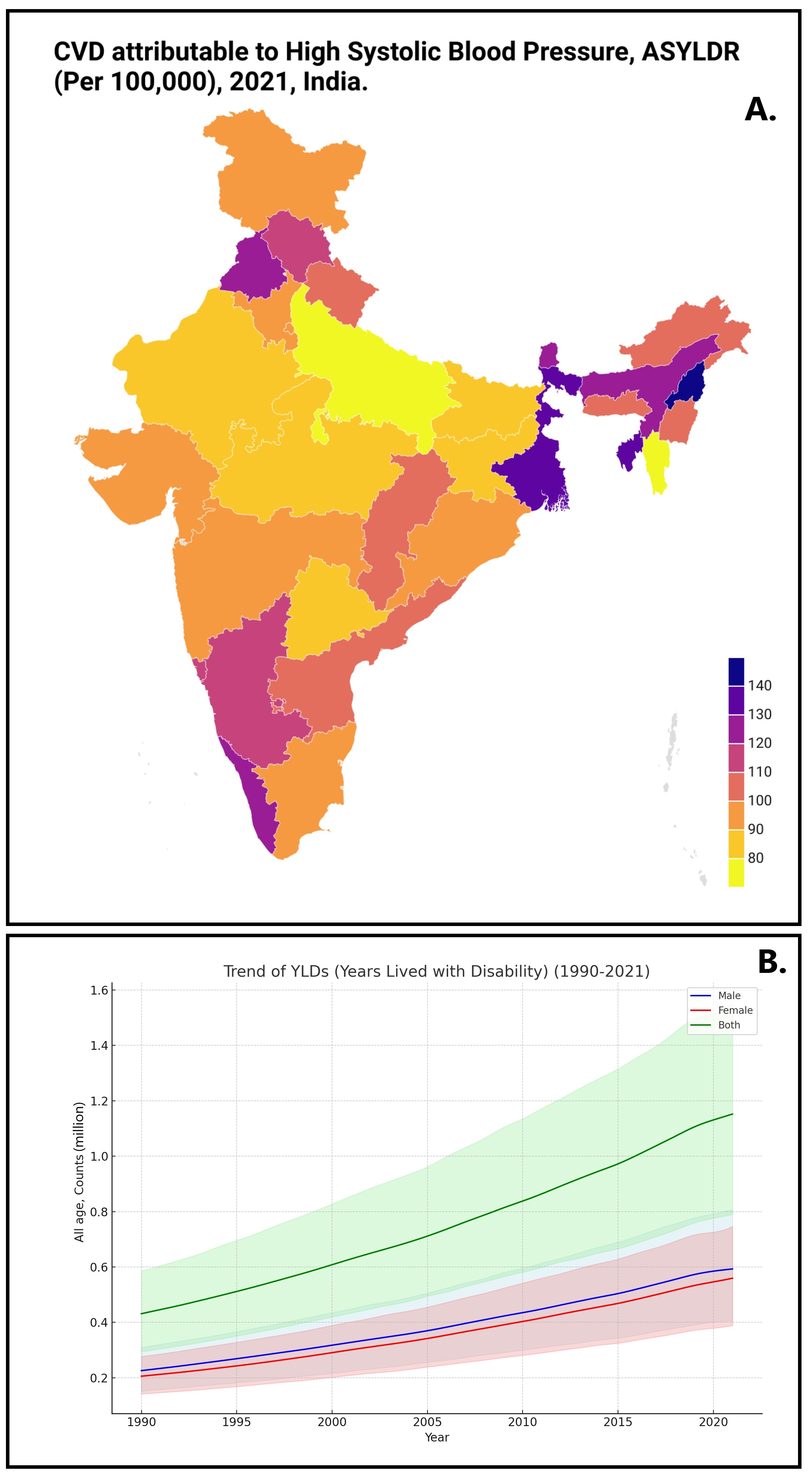
Results:The total number of deaths escalated from 511,200(95%Uncertainty Interval: 408,893-604,527) in 1990to1.3 million(1.1-1.6 million) in 2021.The total percentage of change(TPC) in age-standardized YLDs rate(ASYLDR) increased by 4%(1% - 8%) from 1990-2021.Haryana observed the highest increase in mortality rate(ASMR) by 41%(13% -80%),followed by Uttar Pradesh 31%(6%- 62%).Amongst various CVD attributable to HBP,highest TPC in ASMR observed due to lower extremity peripheral arterial disease by 110%(51% - 196%) followed by Aortic aneurysm at 81%(30% - 159%),Atrial fibrillation and flutter at 67%(19% - 125%),Ischemic heart disease at 16%(2%- 34%),while strokes attributable to HBP saw a decrease of 20%from 1990-2021.The age group of 70-74 years recorded the highest number of deaths at 224,671,with the 65-69 age group showing the most YLDs at 169,175 in 2021.Males demonstrated a higher overall burden than females,with an 11% increase in ASMR for males compared to a 9% decrease for females,and YLD rates increasing by 9% in males versus 1% in females from 1990-2021.
Conclusion: Deaths due to CVD attributable to HBP accounted for 48.41% of all CVD related deaths in 2021.It is crucial to integrate modern e-health & m-health technologies.These tools can enhance prevention efforts,improve patient engagement,and facilitate remote health monitoring.Leveraging new media for health education can also promote healthier lifestyles and improve public awareness,creating a comprehensive and accessible approach to managing hypertension effectively.
Background:Cardiovascular disease(CVD) is the foremost cause of death and disability worldwide,including in India,where high systolic blood pressure(HBP) stands as the principal modifiable risk factor.The escalating burden of hypertension in India is primarily driven by lifestyle changes,population aging,rising stress levels,growing obesity rates,high tobacco & alcohol use,and variable access to healthcare. This critical backdrop underscores the necessity of assessing the CVD burden attributable to HBP,a domain currently lacking robust data. This pioneering study provides the first comprehensive estimation of this burden over the past three decades,incorporating the initial 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Method:Using global burden of disease 2021 tool, we estimated deaths,disability-adjusted life years(DALYs),Years lived with disability(YLDs) due to CVD attributable to HBP by age,sex,year,location across the India from 1990-2021.
Results:The total number of deaths escalated from 511,200(95%Uncertainty Interval: 408,893-604,527) in 1990to1.3 million(1.1-1.6 million) in 2021.The total percentage of change(TPC) in age-standardized YLDs rate(ASYLDR) increased by 4%(1% - 8%) from 1990-2021.Haryana observed the highest increase in mortality rate(ASMR) by 41%(13% -80%),followed by Uttar Pradesh 31%(6%- 62%).Amongst various CVD attributable to HBP,highest TPC in ASMR observed due to lower extremity peripheral arterial disease by 110%(51% - 196%) followed by Aortic aneurysm at 81%(30% - 159%),Atrial fibrillation and flutter at 67%(19% - 125%),Ischemic heart disease at 16%(2%- 34%),while strokes attributable to HBP saw a decrease of 20%from 1990-2021.The age group of 70-74 years recorded the highest number of deaths at 224,671,with the 65-69 age group showing the most YLDs at 169,175 in 2021.Males demonstrated a higher overall burden than females,with an 11% increase in ASMR for males compared to a 9% decrease for females,and YLD rates increasing by 9% in males versus 1% in females from 1990-2021.
Conclusion: Deaths due to CVD attributable to HBP accounted for 48.41% of all CVD related deaths in 2021.It is crucial to integrate modern e-health & m-health technologies.These tools can enhance prevention efforts,improve patient engagement,and facilitate remote health monitoring.Leveraging new media for health education can also promote healthier lifestyles and improve public awareness,creating a comprehensive and accessible approach to managing hypertension effectively.
More abstracts on this topic:
A machine learning model for individualized risk prediction of ischemic heart disease in people with hypertension in Thailand
Sakboonyarat Boonsub, Poovieng Jaturon, Rangsin Ram
A Key Role of Proximal Tubule Renin-Angiotensin System in The Kidney in The Development of Kidney Ischemia and Reperfusion InjuryLi Xiao, Hassan Rumana, Katsurada Akemi, Sato Ryosuke, Zhuo Jia