Final ID: P1120
Association Between Depression and Movement Behaviors with Risk of Mortality among people with Arthritis: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2007-2016
Abstract Body: Arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by joint pain, swelling and limited range of motion. Depression is prevalent among individuals with arthritis and is associated with increased risks of health conditions and mortality. Physical activity (PA) is a strong predictor of lower mortality and can serve as a protective factor against both depression and arthritis. This study aimed to examine the associations between depression, moderate to vigorous PA (MVPA) and sedentary behavior (SB) with all-cause mortality among individuals with arthritis.
Methods: We included 5129 participant aged ≥ 40 years from NHANES 2007-2016. The death records through 2019 were ascertained. Depression was assessed using Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ9) and categorized into depressed and not depressed groups. MVPA and SB were measured using the Global Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPAQ). Individuals with no leisure time MVPA were classified as inactive and those with ≥ 8 hours of daily sitting were considered sedentary. To investigate joint associations, participants were grouped based on depression status and MVPA or sedentary status. Weighted multivariate Cox regression models adjusted for age (Model 1) and additional covariates (Model 2) were used to examine the associations of depression, MVPA and SB with mortality (Table).
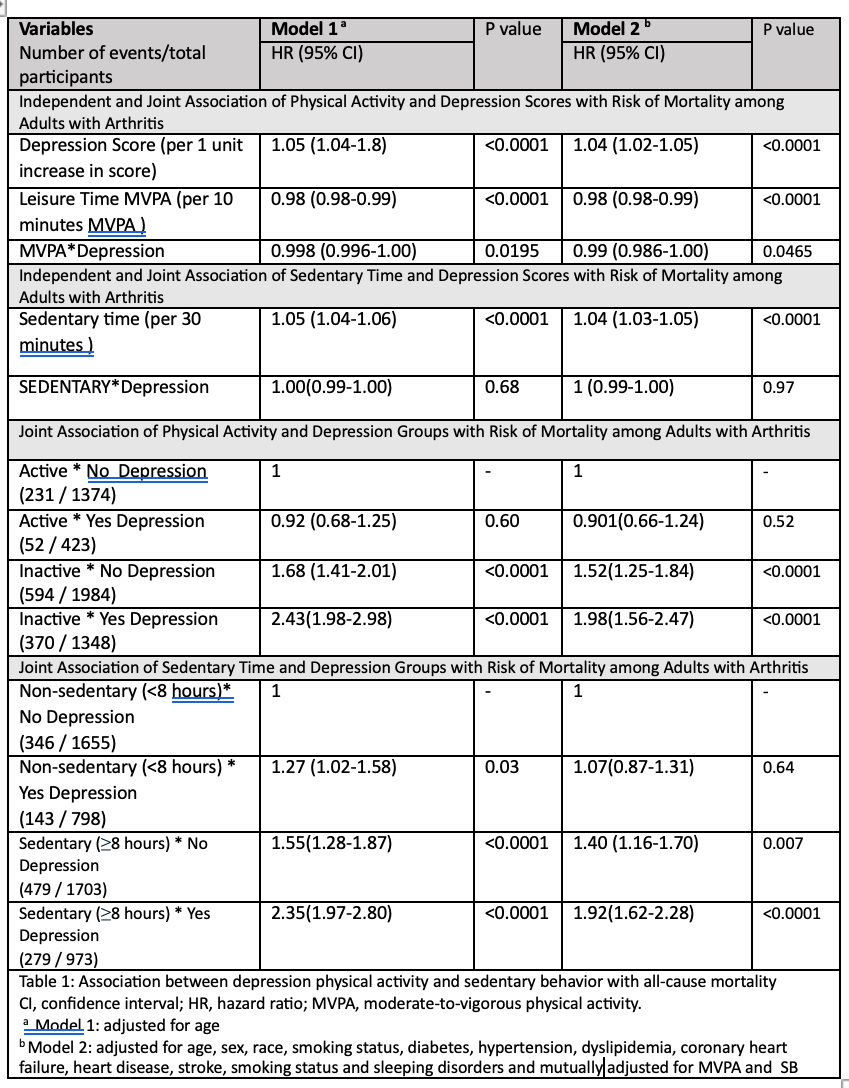
Results: Over 8 ± 3 years of follow-up,1247 (24%) participants died. Compared to active group without depression, inactive groups with and without depression had 1.98 (95% CI: 1.56-2.47) and 1.52 (95% CI: 1.25-1.84) times risk of mortality, respectively (Table). Compared to the non-sedentary group without depression, sedentary groups with and without depression had 1.92 (95% CI: 1.62-2.28) and 1.40 (95% CI: 1.16-1.70) times risk of mortality (Table).
Conclusion: Depression, MVPA and SB, were independently and jointly associated with all-cause mortality among people with arthritis. Being more active and less sedentary may help lower the risk of mortality in this population.
Methods: We included 5129 participant aged ≥ 40 years from NHANES 2007-2016. The death records through 2019 were ascertained. Depression was assessed using Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ9) and categorized into depressed and not depressed groups. MVPA and SB were measured using the Global Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPAQ). Individuals with no leisure time MVPA were classified as inactive and those with ≥ 8 hours of daily sitting were considered sedentary. To investigate joint associations, participants were grouped based on depression status and MVPA or sedentary status. Weighted multivariate Cox regression models adjusted for age (Model 1) and additional covariates (Model 2) were used to examine the associations of depression, MVPA and SB with mortality (Table).
Results: Over 8 ± 3 years of follow-up,1247 (24%) participants died. Compared to active group without depression, inactive groups with and without depression had 1.98 (95% CI: 1.56-2.47) and 1.52 (95% CI: 1.25-1.84) times risk of mortality, respectively (Table). Compared to the non-sedentary group without depression, sedentary groups with and without depression had 1.92 (95% CI: 1.62-2.28) and 1.40 (95% CI: 1.16-1.70) times risk of mortality (Table).
Conclusion: Depression, MVPA and SB, were independently and jointly associated with all-cause mortality among people with arthritis. Being more active and less sedentary may help lower the risk of mortality in this population.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acculturation Class Influences Physical Activity Among African Immigrants Living with Diabetes and/or Hypertension: A Qualitative Analysis
Osokpo Onome, Bracy Danny, Adeniji Dolapo, Bankole Ayomide Okanlawon, Lewis Lisa, Riegel Barbara
A Quarter Century of Cardiovascular Risk: National Mortality Trends in Hypertension and Arrhythmias Among U.S. Adults Aged 55 and OlderAhmad Husnain, Khan Muhammad, Sharif Aleena, Hossain Mohammad, Eltawansy Sherif, Faizan Muhammad, Ali Muhammad Faizan, Ahmed Ashraf, Abdul Malik Mohammad Hamza Bin, Pahwani Ritesh, Patel Rahul, Mehdi Hassan