Final ID: FR480
A Quarter Century of Cardiovascular Risk: National Mortality Trends in Hypertension and Arrhythmias Among U.S. Adults Aged 55 and Older
Abstract Body:
Background
Hypertension (HTN) and arrhythmias are major contributors to cardiovascular mortality in aging populations, yet their long-term combined burden remains underexplored. Tracking these trends is critical for targeted prevention and health system planning.
Aim:
This study investigates mortality trends associated with HTN and arrhythmia in the U.S., examining demographic disparities and regional variations.
Methods
Mortality data from CDC WONDER (1999–2023) were analyzed using Joinpoint regression to assess HTN and arrhythmia-related deaths in U.S. adults aged 55+. Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) and average annual percent change (AAPC) with 95% CIs were calculated.
Results
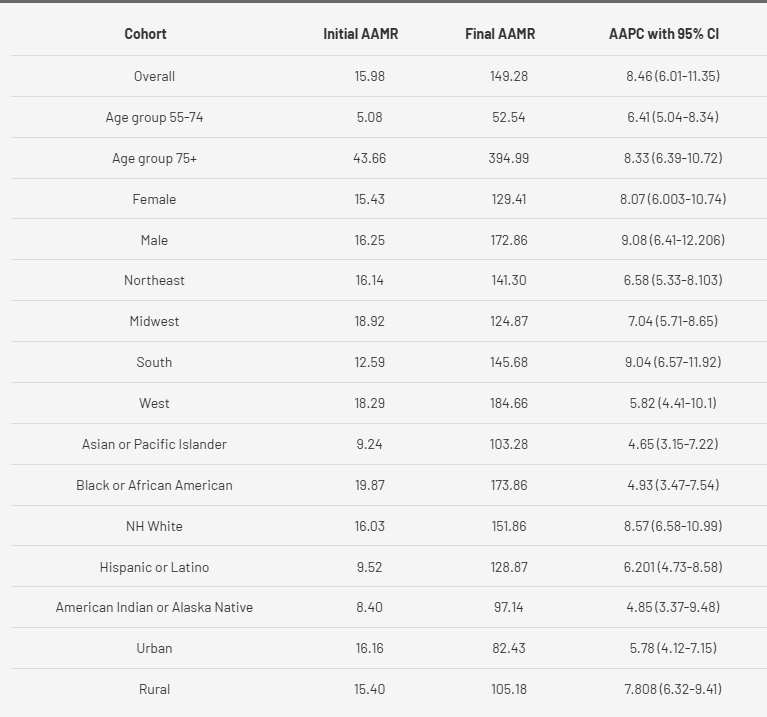
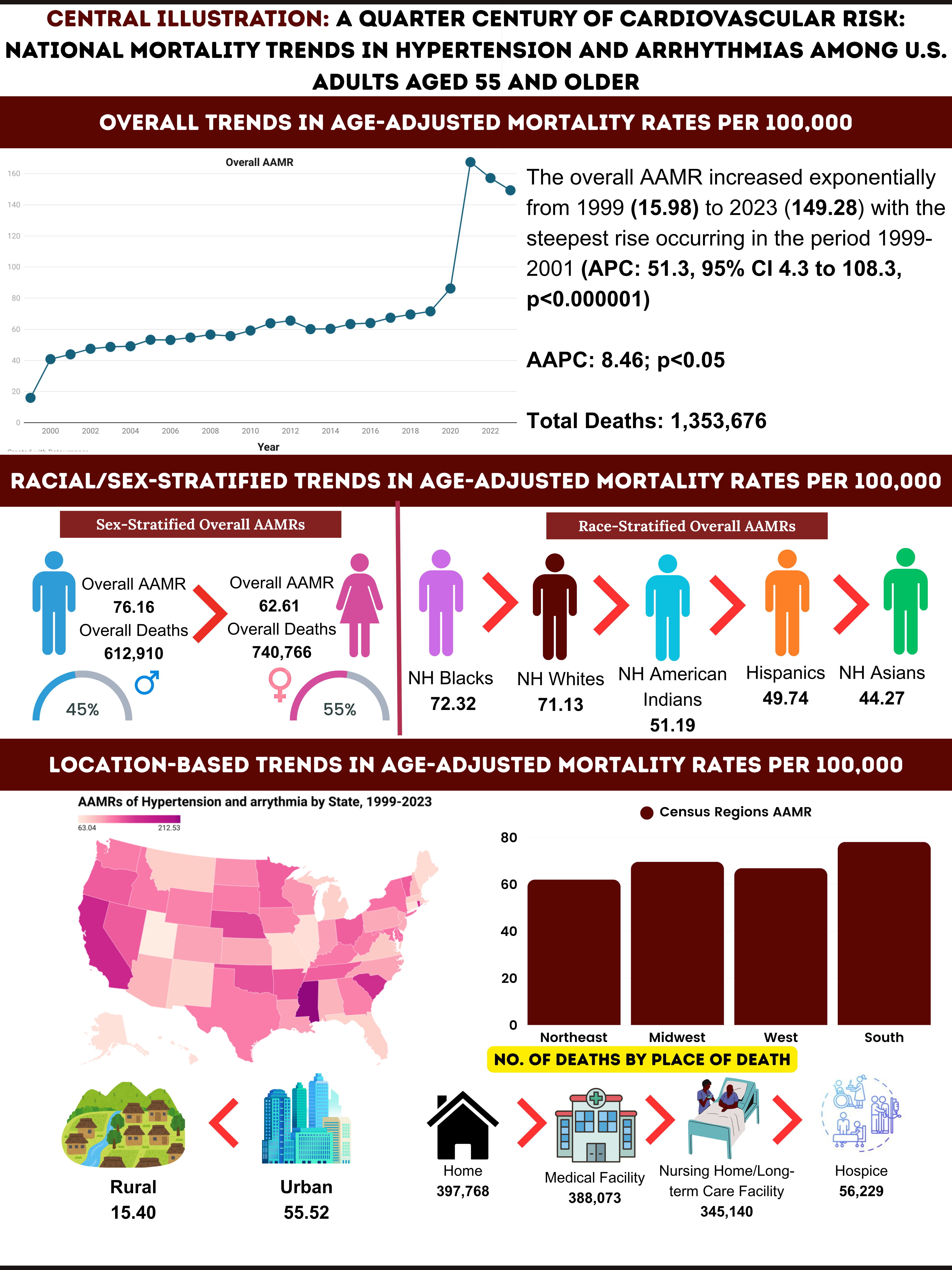
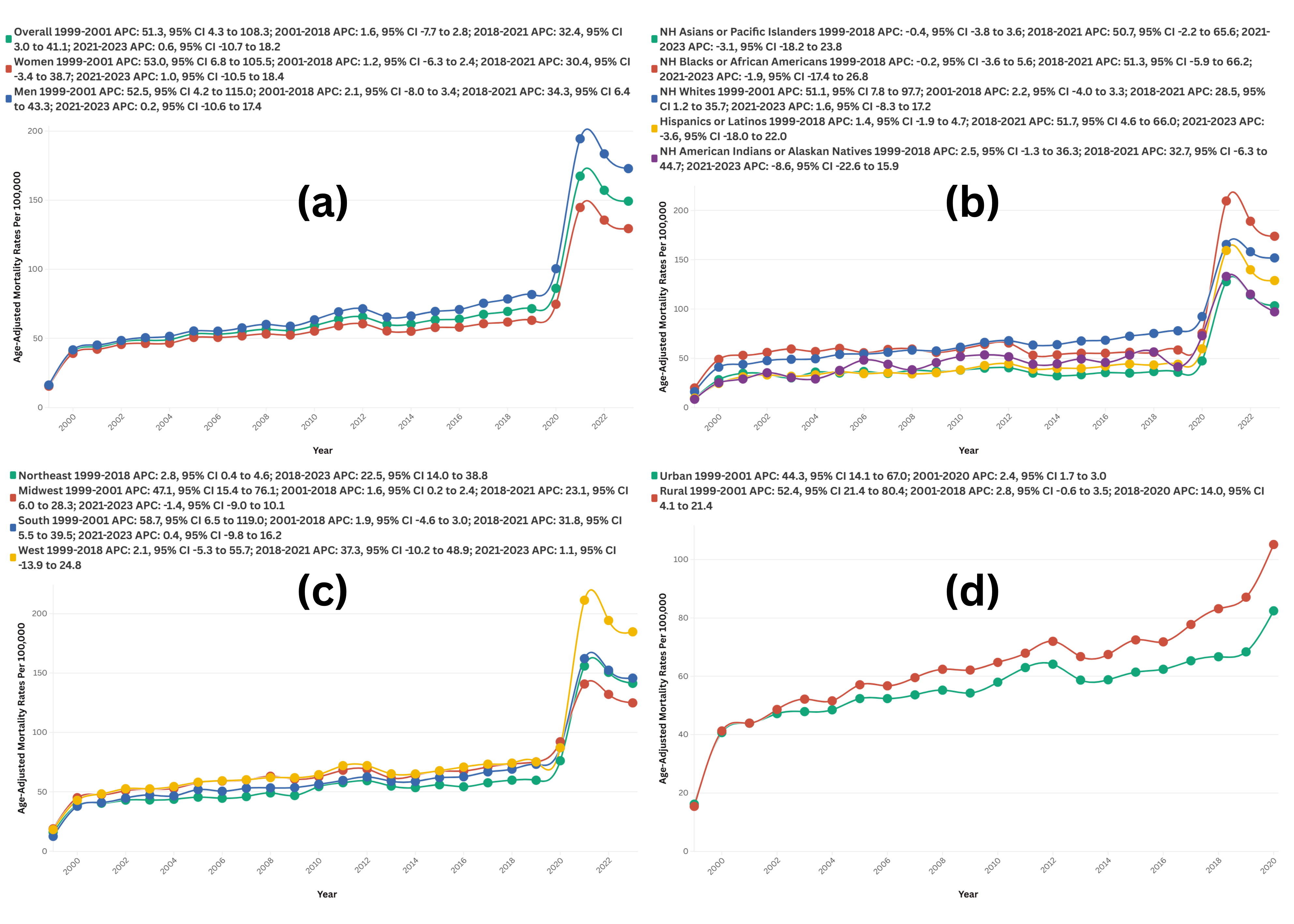
A total of 1,353,676 HTN and arrhythmia-related deaths occurred between 1999 and 2023. The overall AAMR surged from 15.9 to 149.28, with an exponential AAPC of 8.46 (95% CI: 6.01–11.36, p < 0.000001). Gender stratified analysis showed Males had higher mortality rates than females (AAMR: 76.16 vs. 62.62); while also showing a steeper increase in males (AAPC: 9.09, 95% CI: 6.41–12.21) compared to females (AAPC: 8.08, 95% CI: 6.00–10.75), both with p < 0.000001.
Non-Hispanic (NH) Blacks exhibited the highest AAMR (72.32) among racial groups, followed by NH Whites (71.13), Hispanic or Latino (49.74) and Asians (44.27). Sharpest rise was seen in NH Whites (AAPC: 8.58, 95% CI: 6.58–11.00), followed by Hispanic or Latino (AAPC: 6.20, 95% CI: 4.74–8.59).
The South saw the most pronounced increase (AAPC: 9.04, 95% CI: 6.58–11.39), followed by the Midwest (AAPC: 7.04, 95% CI: 5.71–8.66,). States with the highest AAMRs were Mississippi (212.53), California (160.77), and South Carolina (151.72). Rural areas exhibited slightly higher AAMRs than urban areas (63.06 vs. 55.52), which was also reflected in the AAPC as the mortality trajectory was steeper in rural populations (AAPC: 7.81, 95% CI: 6.33–9.41) compared to urban areas (AAPC: 5.78, 95% CI: 4.12–7.16). Individuals aged ≥75 years bore the highest mortality burden, with an AAPC of 8.33 (95% CI: 6.40–10.72), significantly outpacing the rise observed in those between the ages of 55-74 years (AAPC: 6.41, 95% CI: 5.05–8.34).
Conclusion
HTN and arrhythmia-related mortality has increased over time, with the sharpest rises among females, elderly, NH Whites, rural populations, and the Southern U.S., highlighting urgent need for targeted interventions in these high-risk groups.
Background
Hypertension (HTN) and arrhythmias are major contributors to cardiovascular mortality in aging populations, yet their long-term combined burden remains underexplored. Tracking these trends is critical for targeted prevention and health system planning.
Aim:
This study investigates mortality trends associated with HTN and arrhythmia in the U.S., examining demographic disparities and regional variations.
Methods
Mortality data from CDC WONDER (1999–2023) were analyzed using Joinpoint regression to assess HTN and arrhythmia-related deaths in U.S. adults aged 55+. Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) and average annual percent change (AAPC) with 95% CIs were calculated.
Results
A total of 1,353,676 HTN and arrhythmia-related deaths occurred between 1999 and 2023. The overall AAMR surged from 15.9 to 149.28, with an exponential AAPC of 8.46 (95% CI: 6.01–11.36, p < 0.000001). Gender stratified analysis showed Males had higher mortality rates than females (AAMR: 76.16 vs. 62.62); while also showing a steeper increase in males (AAPC: 9.09, 95% CI: 6.41–12.21) compared to females (AAPC: 8.08, 95% CI: 6.00–10.75), both with p < 0.000001.
Non-Hispanic (NH) Blacks exhibited the highest AAMR (72.32) among racial groups, followed by NH Whites (71.13), Hispanic or Latino (49.74) and Asians (44.27). Sharpest rise was seen in NH Whites (AAPC: 8.58, 95% CI: 6.58–11.00), followed by Hispanic or Latino (AAPC: 6.20, 95% CI: 4.74–8.59).
The South saw the most pronounced increase (AAPC: 9.04, 95% CI: 6.58–11.39), followed by the Midwest (AAPC: 7.04, 95% CI: 5.71–8.66,). States with the highest AAMRs were Mississippi (212.53), California (160.77), and South Carolina (151.72). Rural areas exhibited slightly higher AAMRs than urban areas (63.06 vs. 55.52), which was also reflected in the AAPC as the mortality trajectory was steeper in rural populations (AAPC: 7.81, 95% CI: 6.33–9.41) compared to urban areas (AAPC: 5.78, 95% CI: 4.12–7.16). Individuals aged ≥75 years bore the highest mortality burden, with an AAPC of 8.33 (95% CI: 6.40–10.72), significantly outpacing the rise observed in those between the ages of 55-74 years (AAPC: 6.41, 95% CI: 5.05–8.34).
Conclusion
HTN and arrhythmia-related mortality has increased over time, with the sharpest rises among females, elderly, NH Whites, rural populations, and the Southern U.S., highlighting urgent need for targeted interventions in these high-risk groups.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Comparison of Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Symptoms of Palpitations Compared to High Risk Arrythmia Patients.
Treuth Mark, Patel Kunnal, Rissmiller Justin, Holdai Veera
A Quarter Century of Cardiovascular Strain: Mortality Trends in Hypertension and Hypertensive Heart Disease Among U.S. Adults Aged 55+Ali Muhammad Faizan, Khan Muhammad, Sharif Aleena, Hossain Mohammad, Ahmad Husnain, Eltawansy Sherif, Faizan Muhammad, Ahmed Ashraf, Abdul Malik Mohammad Hamza Bin, Pahwani Ritesh, Patel Rahul, Mehdi Hassan