Final ID: P3131
Epic Cosmos Can be Used to Model the Population Impact of Lowering Low-Density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol Goals in Secondary Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract Body: Introduction
Traditionally, access to HIPAA-compliant nationally representative data has been difficult. Cosmos by Epic aims to simplify access to big data for epidemiological research. We used Cosmos to evaluate the population impact of upcoming revised cholesterol guidelines. The upcoming guidelines might lower the LDL-C goal to 55 mg/dL from the current 70 mg/dL goal set by the 2018 ACC/AHA cholesterol guidelines.
Hypothesis
We hypothesized that a democratized business analytic tool like Cosmos can be leveraged to estimate the population-level impact of guideline and policy changes.
Methods
Cosmos was queried using the patient data model to identify adult patients (≥ 18 years) with clinical ASCVD, defined using a combination of ICD-10 codes and SNOMED CT custom groupers. Patients were included if they had at least 1 LDL-C value recorded between September 2022 and September 2024, and only the most recent value was used in our analysis. The population was sliced using the Lab Component à LDL and Medication filters to assess LDL-C levels and lipid lowering therapy (LLT) utilization.
Results
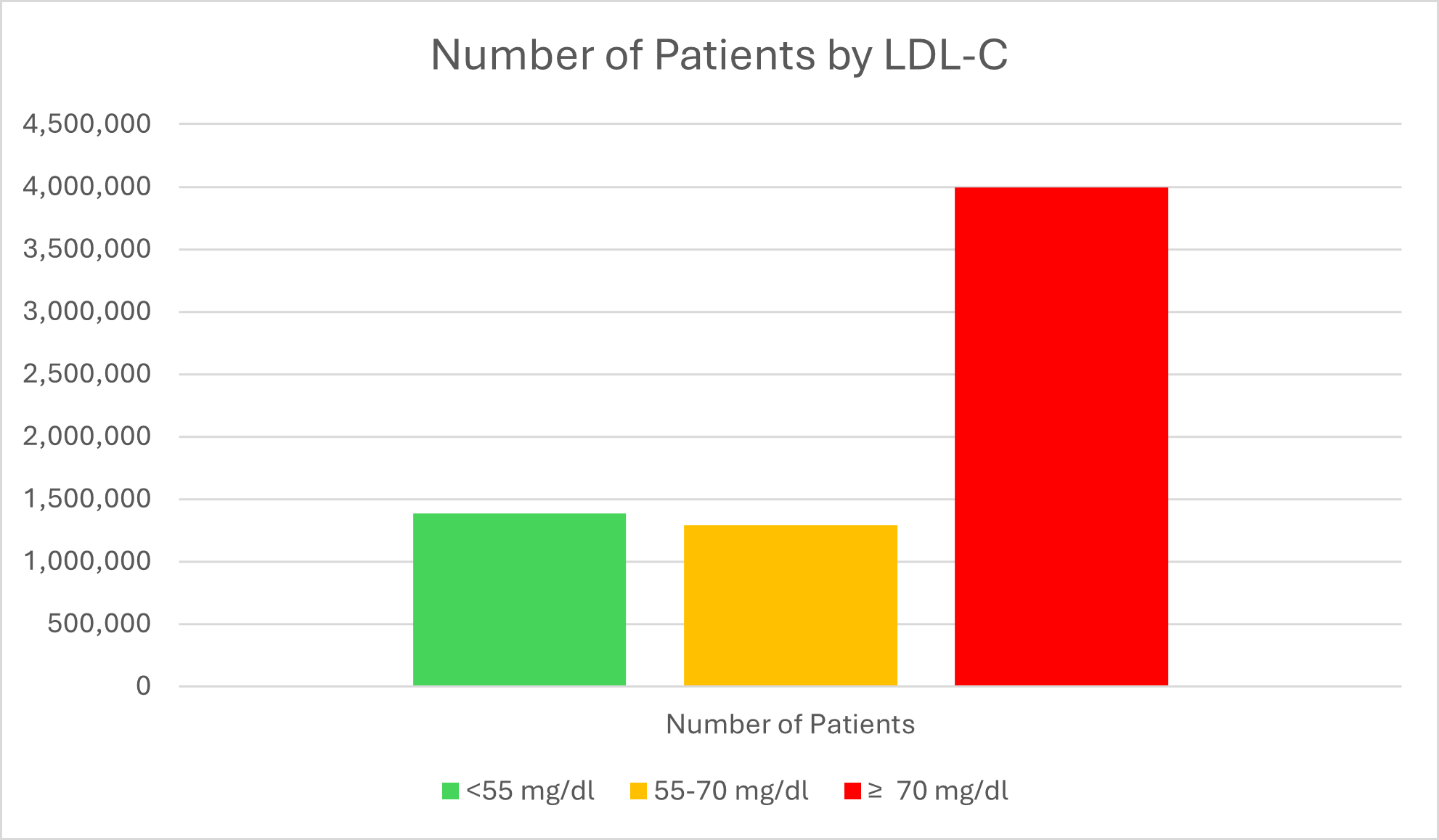
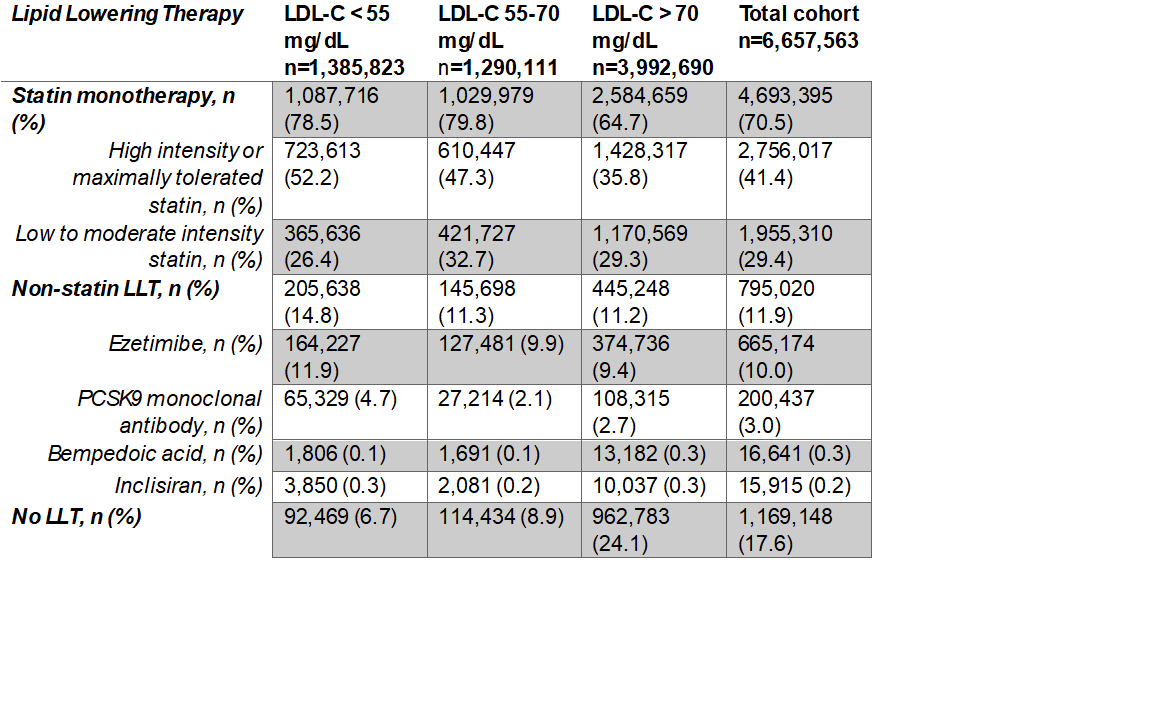
We identified 6,657,563 patients with clinical ASCVD (mean age 69, 53.8% male, 81.7% White). Most of the patients (60.0%) had LDL-C above 70 mg/dL, 19.4% had an LDL-C between 55-70 mg/dL, and 20.8% had an LDL-C below 55 mg/dL (Figure). Among the 1,290,111 patients with an LDL-C between 55-70 mg/dL, 79.8% were on statin monotherapy, 47.3% were on a high intensity or maximally tolerated statin, 11.3% were receiving non-statin LLT, and 8.9% had no record of any LLT (Table).
Conclusions
Our analysis highlights the potential of Epic Cosmos as a powerful tool for answering epidemiological questions using real-world data. In this cohort of 6.7 million patients with ASCVD, about 1.3 million (19.4%) individuals with an LDL-C between 55-70 mg/dL would be considered to have uncontrolled cholesterol if the LDL-C target is lowered to <55 mg/dL in the future ACC/AHA cholesterol guidelines. Less than half of these patients were on high-intensity or maximally tolerated statins, about 1 in 10 were on non-statin LLTs, and around 9% were not receiving any LLT at all. This presents a substantial opportunity for treatment escalation or initiation to help these individuals achieve lower LDL-C targets.
Traditionally, access to HIPAA-compliant nationally representative data has been difficult. Cosmos by Epic aims to simplify access to big data for epidemiological research. We used Cosmos to evaluate the population impact of upcoming revised cholesterol guidelines. The upcoming guidelines might lower the LDL-C goal to 55 mg/dL from the current 70 mg/dL goal set by the 2018 ACC/AHA cholesterol guidelines.
Hypothesis
We hypothesized that a democratized business analytic tool like Cosmos can be leveraged to estimate the population-level impact of guideline and policy changes.
Methods
Cosmos was queried using the patient data model to identify adult patients (≥ 18 years) with clinical ASCVD, defined using a combination of ICD-10 codes and SNOMED CT custom groupers. Patients were included if they had at least 1 LDL-C value recorded between September 2022 and September 2024, and only the most recent value was used in our analysis. The population was sliced using the Lab Component à LDL and Medication filters to assess LDL-C levels and lipid lowering therapy (LLT) utilization.
Results
We identified 6,657,563 patients with clinical ASCVD (mean age 69, 53.8% male, 81.7% White). Most of the patients (60.0%) had LDL-C above 70 mg/dL, 19.4% had an LDL-C between 55-70 mg/dL, and 20.8% had an LDL-C below 55 mg/dL (Figure). Among the 1,290,111 patients with an LDL-C between 55-70 mg/dL, 79.8% were on statin monotherapy, 47.3% were on a high intensity or maximally tolerated statin, 11.3% were receiving non-statin LLT, and 8.9% had no record of any LLT (Table).
Conclusions
Our analysis highlights the potential of Epic Cosmos as a powerful tool for answering epidemiological questions using real-world data. In this cohort of 6.7 million patients with ASCVD, about 1.3 million (19.4%) individuals with an LDL-C between 55-70 mg/dL would be considered to have uncontrolled cholesterol if the LDL-C target is lowered to <55 mg/dL in the future ACC/AHA cholesterol guidelines. Less than half of these patients were on high-intensity or maximally tolerated statins, about 1 in 10 were on non-statin LLTs, and around 9% were not receiving any LLT at all. This presents a substantial opportunity for treatment escalation or initiation to help these individuals achieve lower LDL-C targets.
More abstracts on this topic:
Assessing Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with New Onset Diabetes After Statin Initiation
Schaaf Lucas, Nadar Priyanka, Gebrehiwot Ledya, Jean-marie Elizabeth, Simon Steven, Rosenberg Michael
A Health Coach-Based Multi-Level Personalized Strategy Lowers LDL-Cholesterol and Enhances Lipid Control in Veterans with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease – The VA Lipid Optimization Reimagined Quality Improvement Project at VA New York Harbor Healthcare SystemChen Tina, Ingerman Diana, Haley Leah, Salovaara Priscilla, Nicholson Andrew, Illenberger Nicholas, Natarajan Sundar