Final ID: 011
Physician-Level Variation in Lipid Management for Secondary Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: Opportunities for Practice Improvement
Abstract Body: Introduction
While prior studies have documented suboptimal lipid therapeutic management and low rates of LDL-C goal achievement in patients with ASCVD, the degree of variability between cardiologists in lipid-lowering therapy (LLT) practice patterns is less well described.
Hypothesis
Significant variability exists between cardiologists in their use of LLT and achievement of LDL-C goals in patients with ASCVD.
Methods
We evaluated the use of LLTs and achievement of LDL-C <70 mg/dL among adults with ASCVD (peripheral arterial disease, coronary artery disease, or ischemic cerebrovascular disease) followed by a cardiologist at a large academic medical center from 1/1/22-6/30/24. LLT utilization and LDL-C goal achievement were modeled using mixed-effects logistic regression with clustering at the cardiologist level, adjusting for patient age, insurance, ASCVD type, and diabetes. From this model, we quantified physician-level variability using the adjusted median odds ratios (aMOR).
Results
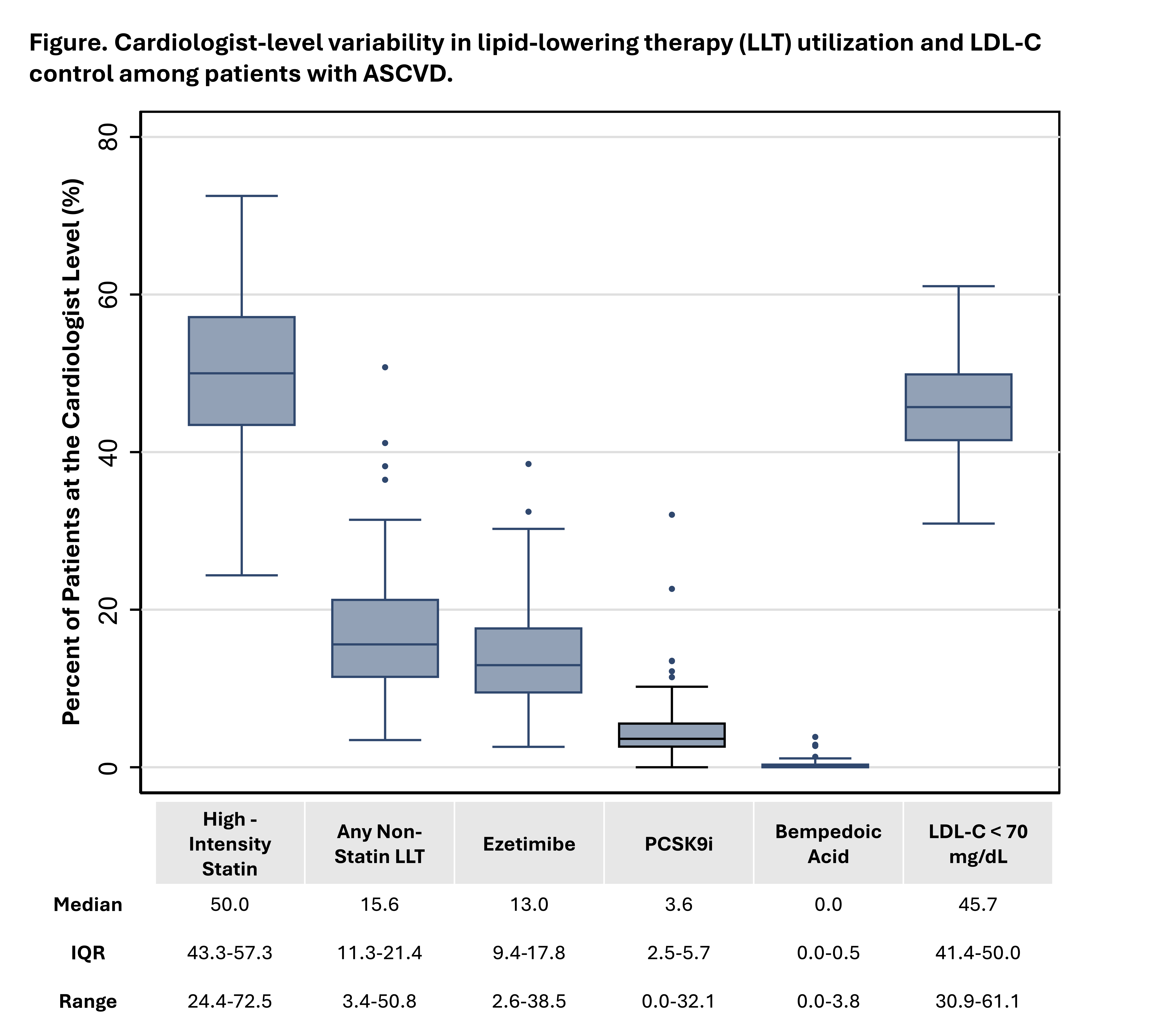
Among 10,531 patients with ASCVD (mean age 68.5 years, 61.1% male, 69.8% White) seen across 55 cardiologists, 80.6% were on any statin, 51.5% were on a high-intensity statin, 14.9% were on ezetimibe, 5.6% were on bempedoic acid or a PCSK9 inhibitor, and 15.1% were not on any LLT. Of those with a lipid panel in the past year (n= 7,555), 45.9% achieved an LDL-C < 70 mg/dL. Lipid management strategies varied substantially across cardiologists (Figure). In mixed-effects models adjusting for patient-level factors, significant physician-level variation was observed in high-intensity statin use (aMOR 1.33, 95% CI 1.25-1.45), ezetimibe use (aMOR 1.62, 95% CI 1.46-1.85), bempedoic acid or PCSK9 inhibitor use (aMOR 2.03, 95% CI 1.75-2.45), and attainment of LDL-C < 70 mg/dL (aMOR 1.27, 95% CI 1.20-1.38).
Conclusion
Even among cardiologists at the same academic medical center, practice patterns varied widely in the use of LLT and achievement of LDL-C goals for secondary prevention. Understanding the reasons for this variability and standardizing lipid management across the specialty may improve quality of care for patients with ASCVD.
While prior studies have documented suboptimal lipid therapeutic management and low rates of LDL-C goal achievement in patients with ASCVD, the degree of variability between cardiologists in lipid-lowering therapy (LLT) practice patterns is less well described.
Hypothesis
Significant variability exists between cardiologists in their use of LLT and achievement of LDL-C goals in patients with ASCVD.
Methods
We evaluated the use of LLTs and achievement of LDL-C <70 mg/dL among adults with ASCVD (peripheral arterial disease, coronary artery disease, or ischemic cerebrovascular disease) followed by a cardiologist at a large academic medical center from 1/1/22-6/30/24. LLT utilization and LDL-C goal achievement were modeled using mixed-effects logistic regression with clustering at the cardiologist level, adjusting for patient age, insurance, ASCVD type, and diabetes. From this model, we quantified physician-level variability using the adjusted median odds ratios (aMOR).
Results
Among 10,531 patients with ASCVD (mean age 68.5 years, 61.1% male, 69.8% White) seen across 55 cardiologists, 80.6% were on any statin, 51.5% were on a high-intensity statin, 14.9% were on ezetimibe, 5.6% were on bempedoic acid or a PCSK9 inhibitor, and 15.1% were not on any LLT. Of those with a lipid panel in the past year (n= 7,555), 45.9% achieved an LDL-C < 70 mg/dL. Lipid management strategies varied substantially across cardiologists (Figure). In mixed-effects models adjusting for patient-level factors, significant physician-level variation was observed in high-intensity statin use (aMOR 1.33, 95% CI 1.25-1.45), ezetimibe use (aMOR 1.62, 95% CI 1.46-1.85), bempedoic acid or PCSK9 inhibitor use (aMOR 2.03, 95% CI 1.75-2.45), and attainment of LDL-C < 70 mg/dL (aMOR 1.27, 95% CI 1.20-1.38).
Conclusion
Even among cardiologists at the same academic medical center, practice patterns varied widely in the use of LLT and achievement of LDL-C goals for secondary prevention. Understanding the reasons for this variability and standardizing lipid management across the specialty may improve quality of care for patients with ASCVD.
More abstracts on this topic:
A drug target Mendelian randomization study of triglyceride lowering therapies for aortic stenosis
Ciofani Jonathan, Han Daniel, Gill Dipender, Rao Karan, Allahwala Usaid, Bhindi Ravinay
A 10-year longitudinal cohort study of lipid variability, cognitive decline, and dementia in 9846 community-dwelling older adultsZhou Zhen, Moran Chris, Murray Anne, Zoungas Sophia, Nelson Mark, Talic Stella, Wolfe Rory, Ryan Joanne