Final ID: MDP1111
Large-Scale Proteomics Identifies Novel Circulating Markers of Pulmonary Hypertension: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Biomarkers for early-stage pulmonary hypertension (PH) are unavailable in clinical practice.
Aims: We aimed to discover novel plasma biomarkers associated with pulmonary pressure and PH.
Methods: Among participants in the community-based Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) cohort study who underwent protocol echocardiography at the 5th study visit (2011-2013), had assessable pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP), and were free of diagnosed heart failure (HF) or pulmonary disease, we measured 4,955 plasma proteins (SomaScan aptamer-affinity assay). Participants also performed spirometry at the same study visit. We assessed cross sectional associations of individual proteins with PASP using multivariable linear regression adjusted for demographic and clinical covariates. We further assessed the associations of candidate proteins with cardiac and pulmonary function to explore mechanisms of association with PASP. Additionally, we performed two-sample Mendelian Randomization (MR) analyses using cis-pQTLs to identify potential causal associations.
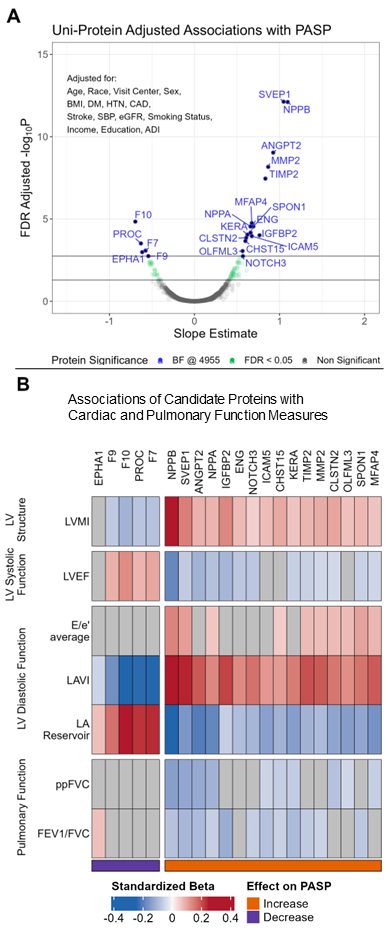
Results: Among 2,015 participants included, mean age was 75±5 years, 64% were female, 17% reported Black race, and LVEF was 66±6%. Mean PASP was 28±6 mmHg. Twenty-five protein aptamers (21 unique proteins) were associated with PASP at Bonferroni significance (Figure A). Of these 21 candidate proteins, the 16 associated with higher PASP were also generally associated with greater LV mass, lower LVEF, and worse LV diastolic function (specially higher LA volume index and lower LA reservoir strain) and worse spirometric measures (Figure B). The 5 proteins associated with lower PASP were generally associated with better LV structure and function. Of these 21 proteins, two-sample MR identified one protein with potential causal effects on pulmonary arterial hypertension (PROC), one with effects on LV size (ENG), and 4 with effects on pulmonary function (ANGPT2, CLSTN2, ICAM5, SPON1).
Conclusion: We identified novel protein markers of pulmonary pressure, with potential causal associations related to the pathological substrate for types 1, 2 and 3 PH.
Aims: We aimed to discover novel plasma biomarkers associated with pulmonary pressure and PH.
Methods: Among participants in the community-based Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) cohort study who underwent protocol echocardiography at the 5th study visit (2011-2013), had assessable pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP), and were free of diagnosed heart failure (HF) or pulmonary disease, we measured 4,955 plasma proteins (SomaScan aptamer-affinity assay). Participants also performed spirometry at the same study visit. We assessed cross sectional associations of individual proteins with PASP using multivariable linear regression adjusted for demographic and clinical covariates. We further assessed the associations of candidate proteins with cardiac and pulmonary function to explore mechanisms of association with PASP. Additionally, we performed two-sample Mendelian Randomization (MR) analyses using cis-pQTLs to identify potential causal associations.
Results: Among 2,015 participants included, mean age was 75±5 years, 64% were female, 17% reported Black race, and LVEF was 66±6%. Mean PASP was 28±6 mmHg. Twenty-five protein aptamers (21 unique proteins) were associated with PASP at Bonferroni significance (Figure A). Of these 21 candidate proteins, the 16 associated with higher PASP were also generally associated with greater LV mass, lower LVEF, and worse LV diastolic function (specially higher LA volume index and lower LA reservoir strain) and worse spirometric measures (Figure B). The 5 proteins associated with lower PASP were generally associated with better LV structure and function. Of these 21 proteins, two-sample MR identified one protein with potential causal effects on pulmonary arterial hypertension (PROC), one with effects on LV size (ENG), and 4 with effects on pulmonary function (ANGPT2, CLSTN2, ICAM5, SPON1).
Conclusion: We identified novel protein markers of pulmonary pressure, with potential causal associations related to the pathological substrate for types 1, 2 and 3 PH.
More abstracts on this topic:
AI-informed Coronary Artery Tortuosity Index (CArTI) from Cardiac CT Angiography Predicts 5-Year Cardiovascular Risk
Lebowitz Mendel, Modanwal Gourav, Dhamdhere Rohan, Mutha Pushkar, De Cecco Carlo, Van Assen Marly, Madabhushi Anant
Age and White Matter Injury due to Cerebral Small Vessel Disease are Synergistically Associated with Impaired Neurovascular Coupling.Yang Sheng, Webb Alastair