Final ID: P1132
The long-term risk of knee and hip joint replacements attributable to overweight and obesity in the community: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study
Abstract Body: Background: The number of joint replacements due to osteoarthritis has grown recently, likely reflecting the obesity epidemic, demanding substantial medical expenditure (over $20 billion for knee and hip replacements). However, data on joint-specific replacements attributable to overweight/obesity and their lifetime risk are limited.
Methods: In 15,287 ARIC study participants (age 45-64 years) at visit 1 (1987-89), we assessed the association of body mass index (BMI) at mid-life with knee/hip joint replacements due to osteoarthritis based on discharge diagnosis using multivariable Cox models. We calculated a population-attributable fraction for BMI ≥25 kg/m2. We also estimated the residual lifetime risk from age 50 through 95 years, accounting for the competing risk of death.
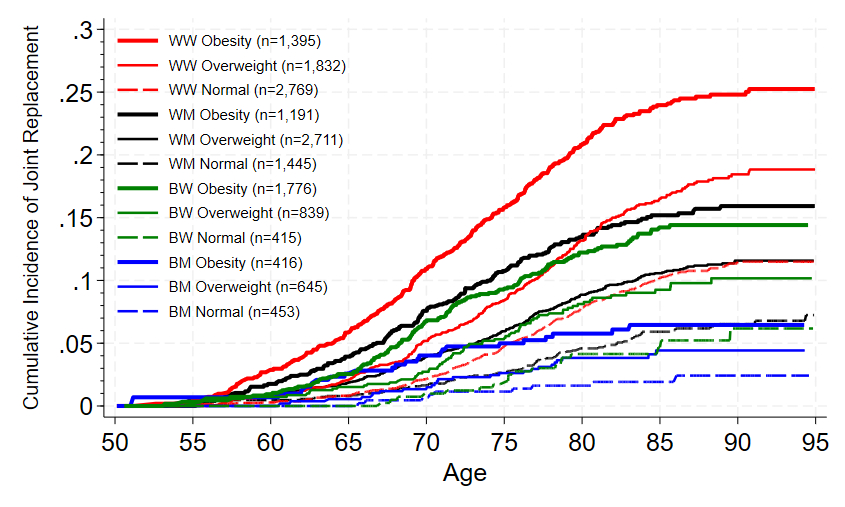
Results: Over a median follow-up of 25.4 years, 1,874 participants (12%) underwent osteoarthritis-related knee or hip replacements (1,380 and 699 cases, respectively). In adjusted Cox models, participants with obesity (BMI ≥30.0 kg/m2) and overweight (25.0-29.9 kg/m2) had a 4- and 2-fold higher risk of joint replacements compared to participants with normal weight (<25.0 kg/m2). The association was stronger for knee vs. hip replacements (hazard ratios 4.58 [95% CI 3.85, 5.44] vs. 2.40 [1.87, 3.07] for BMI 30+ kg/m2 compared to <25 kg/m2). 47% of knee/hip replacements were attributed to overweight and obesity. The residual risk of osteoarthritis-related joint replacements after age of 50 was highest in White women (17%), followed by Black women (12%), White men (11%), and Black men (4%). The residual lifetime risk within the same race and sex varied by ~2-fold according to obesity status (e.g., White women with obesity vs. normal weight: 25% vs. 12%) (Figure).
Conclusions: Obesity and overweight are attributed to half of knee and hip replacements, and one in five to ten Whites and Blacks with obesity/overweight require joint replacements after age 50. Our findings emphasize the importance of weight management, such as increased physical activity.
Methods: In 15,287 ARIC study participants (age 45-64 years) at visit 1 (1987-89), we assessed the association of body mass index (BMI) at mid-life with knee/hip joint replacements due to osteoarthritis based on discharge diagnosis using multivariable Cox models. We calculated a population-attributable fraction for BMI ≥25 kg/m2. We also estimated the residual lifetime risk from age 50 through 95 years, accounting for the competing risk of death.
Results: Over a median follow-up of 25.4 years, 1,874 participants (12%) underwent osteoarthritis-related knee or hip replacements (1,380 and 699 cases, respectively). In adjusted Cox models, participants with obesity (BMI ≥30.0 kg/m2) and overweight (25.0-29.9 kg/m2) had a 4- and 2-fold higher risk of joint replacements compared to participants with normal weight (<25.0 kg/m2). The association was stronger for knee vs. hip replacements (hazard ratios 4.58 [95% CI 3.85, 5.44] vs. 2.40 [1.87, 3.07] for BMI 30+ kg/m2 compared to <25 kg/m2). 47% of knee/hip replacements were attributed to overweight and obesity. The residual risk of osteoarthritis-related joint replacements after age of 50 was highest in White women (17%), followed by Black women (12%), White men (11%), and Black men (4%). The residual lifetime risk within the same race and sex varied by ~2-fold according to obesity status (e.g., White women with obesity vs. normal weight: 25% vs. 12%) (Figure).
Conclusions: Obesity and overweight are attributed to half of knee and hip replacements, and one in five to ten Whites and Blacks with obesity/overweight require joint replacements after age 50. Our findings emphasize the importance of weight management, such as increased physical activity.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Culturally Tailored mHealth Lifestyle Intervention Improves Diet and Physical Activity Self-Regulation Among African Americans
Lalika Mathias, Jenkins Sarah, Hayes Sharonne, Jones Clarence, Burke Lora, Cooper Lisa, Patten Christi, Brewer Laprincess
Adverse Maternal and Offspring Outcomes in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rat Pregnancies: Impact of a Maternal Hypertensive High-Fat DietGomes Viviane, Watts Stephanie, Fink Gregory, Kim Lauren, Lopez Krystal, Gilbert Bryce, Bailey Victoria, Marques Bruno, Garver Hannah, Mckenzie Mckenzie, Lauver Adam