Final ID: P3001
Associations of Biomarkers with Epicardial Adipose Tissue Volume and Density in Cardiovascular Risk Assessment: Insights from the PROMISE Trial
Abstract Body: Introduction: Epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) has emerged as a potential biomarker due to its relationship with cardiovascular (CV) events. This study leverages data from the PROMISE trial to investigate relationships between EAT characteristics and biomarkers related to metabolic and CV health.
Hypothesis: We hypothesize that specific biomarkers are significantly associated with CTA-derived EAT volume (EATv) indexed by body surface area (EATv/BSA) and EAT density (EATd), even after adjusting for clinical variables.
Methods: We analyzed 1,544 individuals (mean age: 60.3 + 8.1 years; 52.9% female) with both CTA and blood samples. Biomarkers included alanine transaminase, beta-2 microglobulin, creatinine, cystatin C, galectin-3, high-sensitivity troponin I, glucose, homocysteine, lipoprotein(a), insulin, NT-proBNP, and uric acid. Univariate models assessed the direct relationship between each biomarker and EATv/BSA and EATd. False Discovery Rate (FDR) correction was applied. Significantly associated biomarkers were tested in multivariate models adjusted for age, sex, race, diabetes, hypertension, statin use, and smoking status. For EATv/BSA, models both with and without BMI were considered, due to EATv’s strong association with BMI. For EATd, the multivariate model adjusted for BMI and EATv.
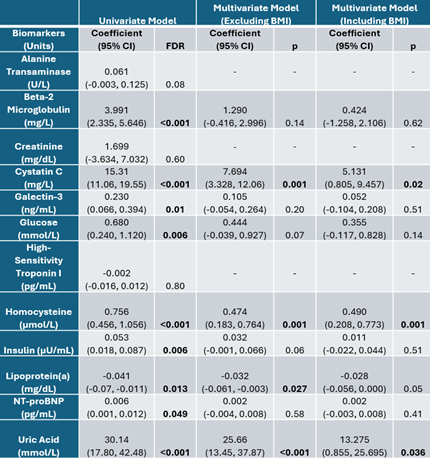
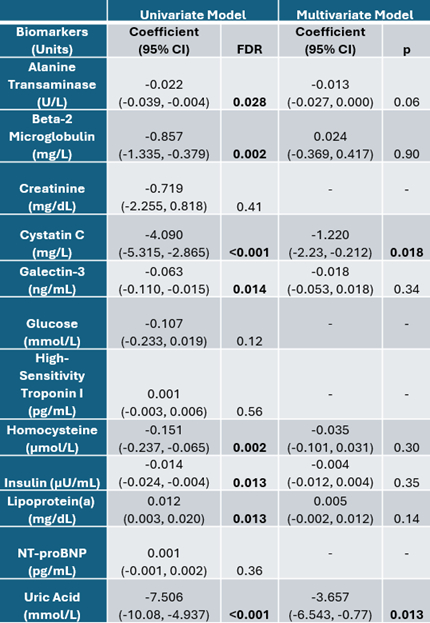
Results: Cystatin C, homocysteine, and uric acid were positively associated with EATv/BSA with statistical significance in both univariate and multivariate models (Table 1). Lipoprotein(a) was significant in both the univariate model and multivariate model excluding BMI, but not in the multivariate model including BMI. Cystatin C and uric acid were negatively associated with EATd, with statistical significance in both univariate and multivariate models (Table 2).
Conclusions: This study identifies cystatin C and uric acid as significant biomarkers associated with both EATv and EATd in individuals with suspected CAD. The relationship between EAT and these biomarkers may reflect underlying metabolic disturbances, with obesity potentially contributing to higher excretion of cystatin C and elevated uric acid levels. Understanding these associations can enhance cardiovascular risk prediction models, leading to more targeted and effective interventions.
Hypothesis: We hypothesize that specific biomarkers are significantly associated with CTA-derived EAT volume (EATv) indexed by body surface area (EATv/BSA) and EAT density (EATd), even after adjusting for clinical variables.
Methods: We analyzed 1,544 individuals (mean age: 60.3 + 8.1 years; 52.9% female) with both CTA and blood samples. Biomarkers included alanine transaminase, beta-2 microglobulin, creatinine, cystatin C, galectin-3, high-sensitivity troponin I, glucose, homocysteine, lipoprotein(a), insulin, NT-proBNP, and uric acid. Univariate models assessed the direct relationship between each biomarker and EATv/BSA and EATd. False Discovery Rate (FDR) correction was applied. Significantly associated biomarkers were tested in multivariate models adjusted for age, sex, race, diabetes, hypertension, statin use, and smoking status. For EATv/BSA, models both with and without BMI were considered, due to EATv’s strong association with BMI. For EATd, the multivariate model adjusted for BMI and EATv.
Results: Cystatin C, homocysteine, and uric acid were positively associated with EATv/BSA with statistical significance in both univariate and multivariate models (Table 1). Lipoprotein(a) was significant in both the univariate model and multivariate model excluding BMI, but not in the multivariate model including BMI. Cystatin C and uric acid were negatively associated with EATd, with statistical significance in both univariate and multivariate models (Table 2).
Conclusions: This study identifies cystatin C and uric acid as significant biomarkers associated with both EATv and EATd in individuals with suspected CAD. The relationship between EAT and these biomarkers may reflect underlying metabolic disturbances, with obesity potentially contributing to higher excretion of cystatin C and elevated uric acid levels. Understanding these associations can enhance cardiovascular risk prediction models, leading to more targeted and effective interventions.
More abstracts on this topic:
AI-Augmented Interpretation of Coronary CT Angiography Reports: A Large Language Model-Based Framework
Liu Zhiyu, Karivelil Mathew, Fennell Adam, Schipper Joslyn, Balaji Sudharshan, Wang Ning, Almeida Shone
Accelerated Coronary Atherosclerosis Following Relugolix Versus Leuprolide Androgen Deprivation Therapy in Men with Prostate Cancer (REVELUTION): An Open-Label Randomized Controlled TrialPatel Sagar, Sebastian Nikhil, Dhere Vishal, Hershatter Bruce, Patel Pretesh, Stillman Arthur, De Cecco Carlo, Sanda Martin, Jani Ashesh, Mandawat Anant, Yadalam Adithya, Van Assen Marly, Cantu Stephanie, Onnis Carlotta, Zheng Bill, Goyal Subir, Liu Yuan, Liu Chang