Final ID: P3010
Association of sedentary behavior with cardiovascular risk biomarkers in a population with overweight or obesity: the PREDIMED-Plus trial
Abstract Body: Background
Sedentary behavior is linked to a higher risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Examining its association with CVD-related biomarkers can help understand the underlying mechanisms.
Methods
We studied 98 participants (55-75 years, BMI 27-40 kg/m2, with metabolic syndrome) in PREDIMED-Plus, a multicenter randomized trial in Spain for the primary prevention of CVD. Accelerometer was used to measure physical activity (PA) at baseline and at least once during follow-up at years 3 and 5. Blood samples were collected at each time point to measure CVD-related biomarkers: propeptide of procollagen type I (PICP, cardiac fibrosis), high-sensitivity (hs) troponin T (hsTnT, myocardial damage), hs C-reactive protein (hsCRP, inflammation), 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT, oxidative stress), and N-terminal propeptide of B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP, cardiac overload). Sedentary time was assessed as inactive time (< 1.5 METs in waking time). Using isotemporal substitution, we analyzed the impact of replacing 30-min sedentary time per day with low-intensity PA (LPA, 1.5–3 METs), moderate to vigorous PA (MVPA, > 3 METs) and time in bed (time difference between going to bed and leaving) on log-transformed biomarkers cross-sectionally and longitudinally.
Results
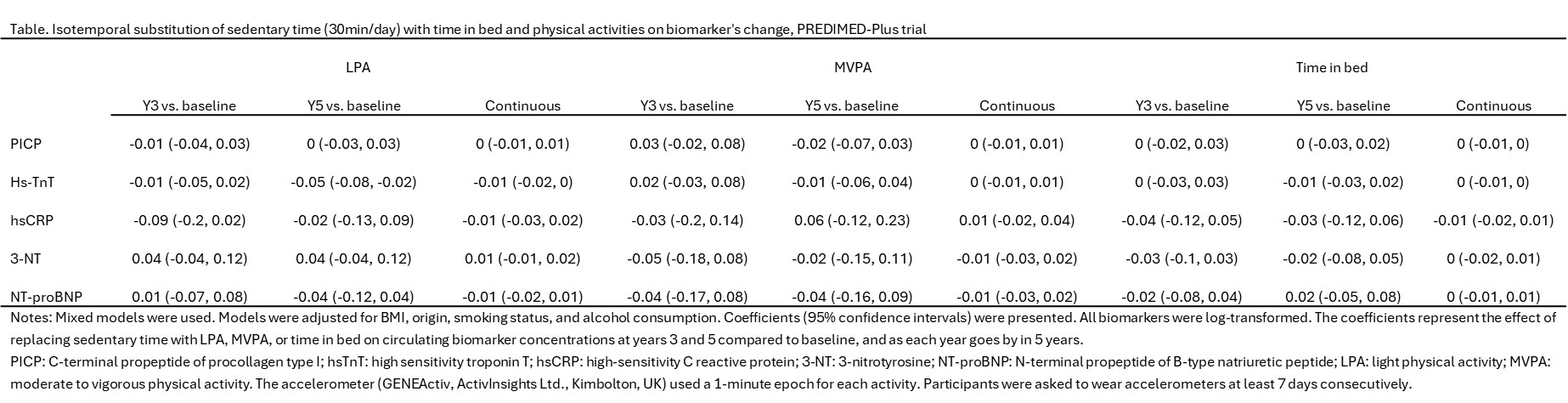
At baseline, year 3 and 5, 98, 72 and 65 participants had valid data. Participants averaged 65 years old (SD 4.9), BMI 32.2 kg/m2 (SD 3.3), and 40% were female. Cross-sectionally, replacing 30-min sedentary time with LPA, MVPA, or time in bed had no significant effect on biomarkers. After 5 years, reallocating baseline 30-min of sedentary time per day with LPA or MVPA was associated with a lower hs-TnT level compared to baseline (-0.05, 95% CI -0.08, -0.02; -0.01, 95% CI -0.06, 0.04, respectively). Substituting 30-min sedentary time with LPA or MVPA showed nonsignificant reductions in NT-proBNP (-0.04, 95% CI -0.12, 0.04; -0.04, 95% CI -0.16, 0.09, respectively), but not a consistent impact on other biomarkers (Table).
Conclusion
In overweight/obese individuals, prolonged sedentary time, when compared to engaging in PA, was associated with unfavorable levels of hs-TnT over 5 years, but not with other CVD risk biomarkers. Further research is warranted to confirm these results in other populations.
Sedentary behavior is linked to a higher risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Examining its association with CVD-related biomarkers can help understand the underlying mechanisms.
Methods
We studied 98 participants (55-75 years, BMI 27-40 kg/m2, with metabolic syndrome) in PREDIMED-Plus, a multicenter randomized trial in Spain for the primary prevention of CVD. Accelerometer was used to measure physical activity (PA) at baseline and at least once during follow-up at years 3 and 5. Blood samples were collected at each time point to measure CVD-related biomarkers: propeptide of procollagen type I (PICP, cardiac fibrosis), high-sensitivity (hs) troponin T (hsTnT, myocardial damage), hs C-reactive protein (hsCRP, inflammation), 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT, oxidative stress), and N-terminal propeptide of B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP, cardiac overload). Sedentary time was assessed as inactive time (< 1.5 METs in waking time). Using isotemporal substitution, we analyzed the impact of replacing 30-min sedentary time per day with low-intensity PA (LPA, 1.5–3 METs), moderate to vigorous PA (MVPA, > 3 METs) and time in bed (time difference between going to bed and leaving) on log-transformed biomarkers cross-sectionally and longitudinally.
Results
At baseline, year 3 and 5, 98, 72 and 65 participants had valid data. Participants averaged 65 years old (SD 4.9), BMI 32.2 kg/m2 (SD 3.3), and 40% were female. Cross-sectionally, replacing 30-min sedentary time with LPA, MVPA, or time in bed had no significant effect on biomarkers. After 5 years, reallocating baseline 30-min of sedentary time per day with LPA or MVPA was associated with a lower hs-TnT level compared to baseline (-0.05, 95% CI -0.08, -0.02; -0.01, 95% CI -0.06, 0.04, respectively). Substituting 30-min sedentary time with LPA or MVPA showed nonsignificant reductions in NT-proBNP (-0.04, 95% CI -0.12, 0.04; -0.04, 95% CI -0.16, 0.09, respectively), but not a consistent impact on other biomarkers (Table).
Conclusion
In overweight/obese individuals, prolonged sedentary time, when compared to engaging in PA, was associated with unfavorable levels of hs-TnT over 5 years, but not with other CVD risk biomarkers. Further research is warranted to confirm these results in other populations.
More abstracts on this topic:
Associations of Accelerometer Measures of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior with Alzheimer’s Disease Related Dementias and Vascular Dementias Classified Using Medicare Claims Data Among Older Black, Hispanic and White Women: The Objective Physical Activity and Cardiovascular Health Study
Nguyen Steve, Di Chongzhi, Hyde Eric, Eaton Charles, Lamonte Michael, Lacroix Andrea
24-hour Movement Behaviors and BMI Among a National, Diverse Sample of AdolescentsAjibewa Tiwaloluwa, Master Lindsay, Booker Robert, Wong Mandy, Reichenberger David, Mathew Gina, Buxton Orfeu, Chang Anne-marie, Hale Lauren