Final ID: MP32
Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Predicted Risks Across Asian American, Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander Subgroups: The PANACHE Study
Abstract Body: Introduction: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk varies substantially across racial and ethnic groups, especially among disaggregated Asian American, Native Hawaiian, and other Pacific Islander (AANHPI) subpopulations. We describe differences in the prevalence of CVD risk factors and predicted CVD risk among a large, diverse population of AANHPI adults living in California and Hawai’i.
Methods: We identified 2,653,007 adults within Kaiser Permanente Northern California and Hawaii from 2012-2022 aged ≥30 years with no prior myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure or atrial fibrillation. CVD risk factors were ascertained using validated diagnosis codes, ambulatory measurements, and dispensed medications in the electronic health record. We calculated the 10-year predicted risk of CVD events using the American Heart Association base PREVENT-CVD equations. Prevalence estimates and means were standardized to the overall age and sex distribution using parametric g-computation.
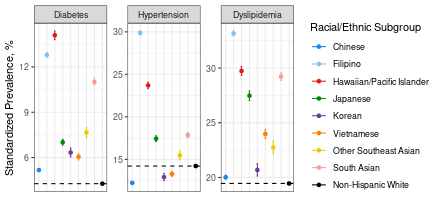
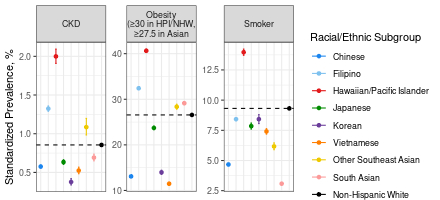
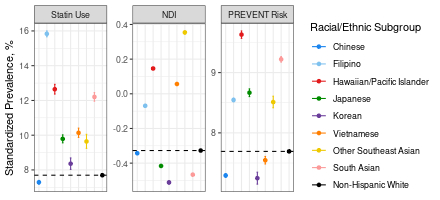
Results: Mean (SD) age was 49 (15) years and ranged from 41 (12) years in South Asian to 55 (16) years in Japanese adults. 53% were women overall, ranging from 48% in Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander to 64% in Korean adults. Compared to non-Hispanic White adults, all AANHPI subgroups had higher prevalences of diabetes and dyslipidemia and lower prevalence of smoking, the latter except Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander adults (Figure). There were notable differences across AANHPI subgroups in the prevalence of hypertension (12% in Chinese to 30% in Filipino adults), obesity (11% in Vietnamese to 41% in Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander adults), and diabetes (5% in Chinese to 14% in Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander adults. Filipino, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, Vietnamese, and other Southeast Asian adults lived in neighborhoods with higher deprivation indices. Based on PREVENT-CVD risk estimates, Filipino, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, South Asian and other Southeast Asian populations had higher standardized 10-year CVD risks.
Conclusions: We found considerable variation in traditional CVD risk factors and predicted CVD risk across disaggregated AANHPI subgroups in a contemporary population with no prior CVD. Further research is needed to investigate potential differences in mediating pathways to the development of CVD across AANHPI subgroups. There is also a need to examine non-traditional structural and social factors that may uniquely affect AANHPI populations.
Methods: We identified 2,653,007 adults within Kaiser Permanente Northern California and Hawaii from 2012-2022 aged ≥30 years with no prior myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure or atrial fibrillation. CVD risk factors were ascertained using validated diagnosis codes, ambulatory measurements, and dispensed medications in the electronic health record. We calculated the 10-year predicted risk of CVD events using the American Heart Association base PREVENT-CVD equations. Prevalence estimates and means were standardized to the overall age and sex distribution using parametric g-computation.
Results: Mean (SD) age was 49 (15) years and ranged from 41 (12) years in South Asian to 55 (16) years in Japanese adults. 53% were women overall, ranging from 48% in Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander to 64% in Korean adults. Compared to non-Hispanic White adults, all AANHPI subgroups had higher prevalences of diabetes and dyslipidemia and lower prevalence of smoking, the latter except Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander adults (Figure). There were notable differences across AANHPI subgroups in the prevalence of hypertension (12% in Chinese to 30% in Filipino adults), obesity (11% in Vietnamese to 41% in Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander adults), and diabetes (5% in Chinese to 14% in Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander adults. Filipino, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, Vietnamese, and other Southeast Asian adults lived in neighborhoods with higher deprivation indices. Based on PREVENT-CVD risk estimates, Filipino, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, South Asian and other Southeast Asian populations had higher standardized 10-year CVD risks.
Conclusions: We found considerable variation in traditional CVD risk factors and predicted CVD risk across disaggregated AANHPI subgroups in a contemporary population with no prior CVD. Further research is needed to investigate potential differences in mediating pathways to the development of CVD across AANHPI subgroups. There is also a need to examine non-traditional structural and social factors that may uniquely affect AANHPI populations.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Randomized Clinical Trial for Asymptomatic Elevated Blood Pressure in Patients Discharged from Emergency Department
Prendergast Heather, Khosla Shaveta, Kitsiou Spyros, Petzel Gimbar Renee, Freels Sally, Sanders Anissa, Daviglus Martha, Carter Barry, Del Rios Marina, Heinert Sara
A Scoping Review Exploring Cardiovascular Risk and Health Metrics and Cancer PredictionKim Ji-eun, Henriquez Santos Gretell, Kumar Sant, Livinski Alicia, Vo Jacqueline, Joo Jungnam, Shearer Joe, Hashemian Maryam, Roger Veronique