Final ID: P1038
Blood Metabolomic Signatures of Incident Coronary Heart Disease in Racially and Ethnically Diverse Populations
Hypothesis Circulating metabolite alterations are associated with CHD risk, but associations vary across race/ethnicity.
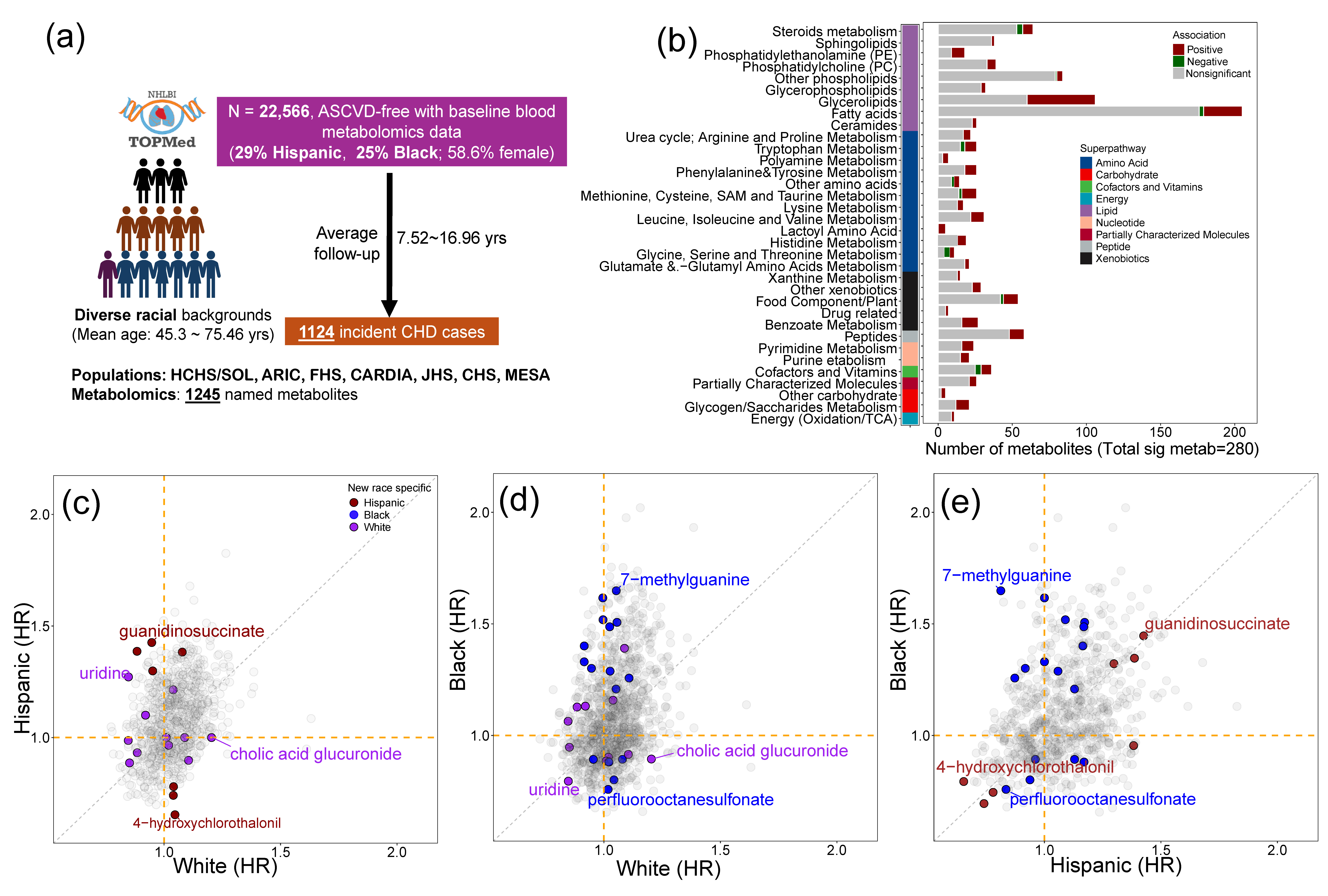
Methods We included 22,566 CHD-free individuals of multi-ethnic groups from 7 studies in the Trans-Omics for Precision Medicine Program (Fig.a). Associations between metabolites (1245 named metabolites) and incident CHD were assessed by study/race-specific Cox proportional hazards regression. Results were pooled via random-effect meta-analyses.
Results Over an average of 7.5~17.0 yrs of follow-up 1124 incident CHD cases were recorded. We found that 280 metabolites were associated with incident CHD after adjusting for sociodemographic, behavioral factors, medications use, physical activity, and diet (FDR < 0.05), with over 64% were independent of other major cardiometabolic traits (Fig.b). Over 90% of these metabolites showed positive associations, with strongest associations in metabolites of glycerolipids, phosphatidylethanolamine, fatty acids, lactoyl amino acid, histidine, aromatic amino acids, and branched amino acids (Fig.b). Race-specific analyses identified 70 metabolites presenting significant race/ethnicity differences (FDR<0.05) in associations with CHD, with 34 being race/ethnicity specific metabolites that were not found in all participants (16 in Blacks, 11 in Whites and 7 in Hispanics; Fig.c-e). For example, guanidinosuccinate, a known uremic toxin, was associated with increased risk of CHD only in US Hispanics, reinforcing the chronic kidney disease (CKD)-cardiovascular diseases continuum, especially for populations at high risk of CKD.
Conclusion Our study characterized the most comprehensive metabolic signatures of incident CHD and revealed substantial racial differences, further emphasizing the need of multi-ethnic resources to uncover metabolic perturbation underlying CHD.
- Luo, Kai ( Albert Einstein College of Medicine , Bronx , New York , United States )
- Hutton, Scott ( Metabolon, Inc , Morrisville , North Carolina , United States )
- Kaplan, Robert ( Albert Einstein College of Medicine , Bronx , New York , United States )
- Lemaitre, Rozenn ( University of Washington , Seattle , Washington , United States )
- Lloyd-jones, Donald ( Northwestern University , Chicago , Illinois , United States )
- Nayor, Matthew ( Boston Unviersity Medical Center , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- North, Kari ( University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill , Chapel Hill , North Carolina , United States )
- Psaty, Bruce ( UNIVERSITY WASHINGTON , Shoreline , Washington , United States )
- Raffield, Laura ( University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill , Chapel Hill , North Carolina , United States )
- Rich, Stephen ( UNIVERSITY VIRGINIA , Charlottesville , Virginia , United States )
- Rotter, Jerome ( The Lundquist Institute , Torrance , California , United States )
- Alkis, Taryn ( University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Tahir, Usman ( Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Wang, Tao ( Albert Einstein College of Medicine , Bronx , New York , United States )
- Wong, Kari ( Metabolon, Inc. , Morrisville , North Carolina , United States )
- Xanthakis, Vanessa ( BU SCHOOL OF MEDICINE , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Qi, Qibin ( Albert Einstein College of Medicine , Bronx , New York , United States )
- Yu, Bing ( University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Moon, Eun Hye ( University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Ballantyne, Christie ( BAYLOR COLLEGE MEDICINE , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Boerwinkle, Eric ( University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Clish, Clary ( Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard , Cambridge , Massachusetts , United States )
- Gerszten, Robert ( Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Grove, Megan ( University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Hou, Lifang ( NORTHWESTERN UNIVERSITY , Chicago , Illinois , United States )
Meeting Info:
Session Info:
PS01.03 Cardiometabolic Health and Disorders 1
Thursday, 03/06/2025 , 05:00PM - 07:00PM
Poster Session
More abstracts on this topic:
Chen Zhuo, Nasir Khurram, Al-kindi Sadeer, Rajagopalan Sanjay, Ponnana Sai Rahul, Dazard Jean-eudes, Zhang Tong, Dong Weichuan, Okyere Robert, Sirasapalli Santosh, Deo Salil, Khraishah Haitham
Assessing Health Literacy and the Role of Race and Social Determinants in Cardiac Patients.Odigwe Celestine, Lakkis Nasser, Mayfield Hanna, Mulyala Rajasekhar, Riad Mariam, Malik Hajira, Ruiz Brent, Mulekar Madhuri, Malozzi Christopher, Omar Bassam
More abstracts from these authors:
Moon Eun Hye, Hutton Scott, Kaplan Robert, Lloyd-jones Donald, Psaty Bruce, Raffield Laura, Rodriguez Carlos, Rotter Jerome, Shah Amil, Shah Sanjiv, Taylor Kent, Alkis Taryn, Wong Kari, Xanthakis Vanessa, Ramachandran Vasan, Yu Bing, Luo Kai, Grove Megan, Boerwinkle Eric, Clish Clary, Gerszten Robert, Hall Michael And Jo Alice, Hou Lifang
Proteomic Profiling of Pulmonary Function Decline and Cardiovascular Disease Risk from Two Cohort StudiesLee Yura, Gharib Sina, London Stephanie, Yu Bing, Austin Thomas, Bartz Traci, Ladd-acosta Christine, Morrison Alanna, North Kari, Boerwinkle Eric, Shah Amil, Psaty Bruce