Final ID: 064
Fairness Heterogeneity of the PREVENT Equations in US Young Adults
Abstract Body: Background
In 2023, the AHA published Predicting Risk of cardiovascular disease EVENTs (PREVENT), a new set of race-agnostic risk prediction equations that estimate 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in US adults ages 30-79 years. Equations include a base model and a model adding social deprivation index (SDI).
Aim
To evaluate fairness of the base and SDI-enhanced PREVENT equations across race/ethnicity and sex groups in US young adults.
Methods
We included adults aged 20-39 years enrolled between 2008-2009 without a history of CVD from Kaiser Permanente Southern California. From the eligible sample of 266,378, we randomly selected 50,000 young adults for computational efficiency. Primary outcome was incident CVD (defined as myocardial infarction, fatal coronary heart disease, fatal and nonfatal stroke, and heart failure) at 10 years. We estimated 10-year CVD risk using the PREVENT base and SDI-enhanced models. To assess race-sex specific model performance, we used Brier score, Harrell’s C, and mean calibration in each group. Overall algorithmic fairness was evaluated by (1) fair calibration, which measures whether agreement between predicted and observed risk is equally accurate across groups using Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit and pairwise Wilcoxon signed-rank tests, and (2) concordance imparity, which measures the largest deviation of discriminative abilities across racial and ethnic groups by taking the difference between maximum and minimum Harrell’s C across groups.
Results
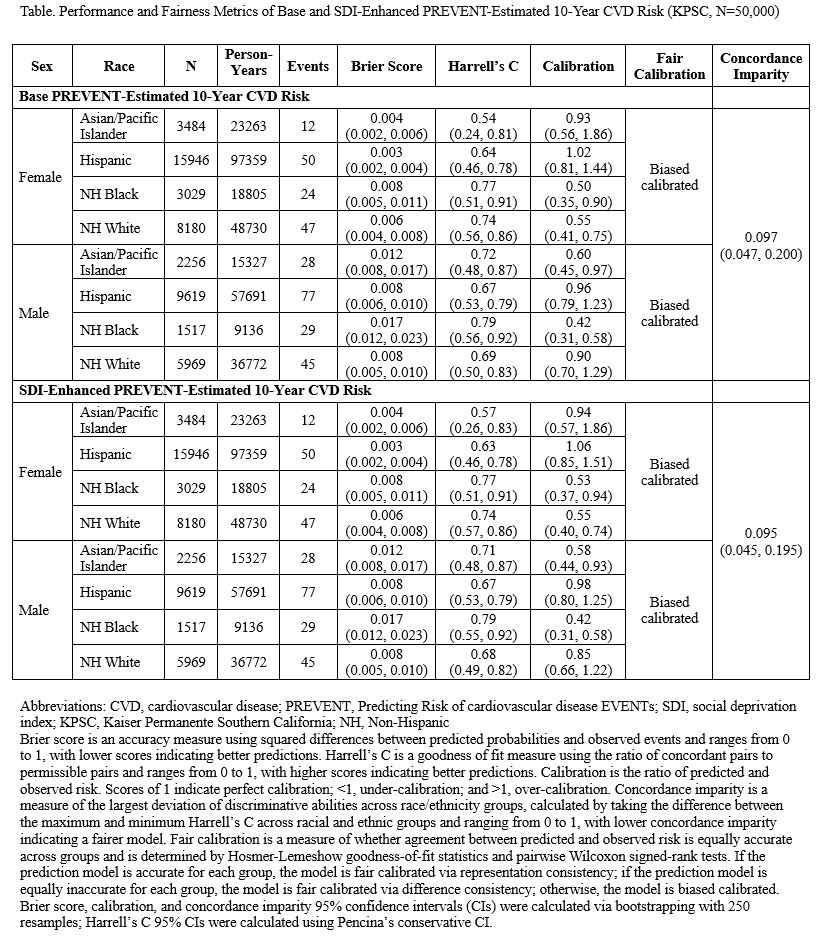
We included 50,000 young adults who were mean (SD) age 31.7 (5.4) years, 61.3% female, and 51.1% Hispanic, who had 312 incident CVD events by 10 years. Performance metrics were similar in the base and SDI-enhanced equations. Models were under-calibrated in Black and White females and Asian and Black males, indicating observed risk was higher than predicted risk. Agreement between predicted and observed risk was not equally accurate across racial and ethnic groups in males or females (biased calibrated). Discriminative abilities also varied across groups, with Harrell’s C highest in Black males and lowest in Asian females. Concordance imparity was similar in the base and SDI-enhanced models (0.097 vs. 0.095).
Conclusion
The PREVENT equations may not provide consistent risk predictions for young adults across race/ethnicity and sex groups, which could lead to unequal CVD prevention efforts. Addition of SDI to the PREVENT equations did not provide improvement in fairness.
In 2023, the AHA published Predicting Risk of cardiovascular disease EVENTs (PREVENT), a new set of race-agnostic risk prediction equations that estimate 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in US adults ages 30-79 years. Equations include a base model and a model adding social deprivation index (SDI).
Aim
To evaluate fairness of the base and SDI-enhanced PREVENT equations across race/ethnicity and sex groups in US young adults.
Methods
We included adults aged 20-39 years enrolled between 2008-2009 without a history of CVD from Kaiser Permanente Southern California. From the eligible sample of 266,378, we randomly selected 50,000 young adults for computational efficiency. Primary outcome was incident CVD (defined as myocardial infarction, fatal coronary heart disease, fatal and nonfatal stroke, and heart failure) at 10 years. We estimated 10-year CVD risk using the PREVENT base and SDI-enhanced models. To assess race-sex specific model performance, we used Brier score, Harrell’s C, and mean calibration in each group. Overall algorithmic fairness was evaluated by (1) fair calibration, which measures whether agreement between predicted and observed risk is equally accurate across groups using Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit and pairwise Wilcoxon signed-rank tests, and (2) concordance imparity, which measures the largest deviation of discriminative abilities across racial and ethnic groups by taking the difference between maximum and minimum Harrell’s C across groups.
Results
We included 50,000 young adults who were mean (SD) age 31.7 (5.4) years, 61.3% female, and 51.1% Hispanic, who had 312 incident CVD events by 10 years. Performance metrics were similar in the base and SDI-enhanced equations. Models were under-calibrated in Black and White females and Asian and Black males, indicating observed risk was higher than predicted risk. Agreement between predicted and observed risk was not equally accurate across racial and ethnic groups in males or females (biased calibrated). Discriminative abilities also varied across groups, with Harrell’s C highest in Black males and lowest in Asian females. Concordance imparity was similar in the base and SDI-enhanced models (0.097 vs. 0.095).
Conclusion
The PREVENT equations may not provide consistent risk predictions for young adults across race/ethnicity and sex groups, which could lead to unequal CVD prevention efforts. Addition of SDI to the PREVENT equations did not provide improvement in fairness.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) and Cardiovascular Health: Future of Families and Child Wellbeing Study (FFCWS)
__PRESENT
__PRESENT
Pedamallu Havisha, Van Horn Linda, Stein James, Korcarz Claudia, Hansen Kristin, Mitchell Colter, Heard-garris Nia, Lloyd-jones Donald, Allen Norrina, Gauen Abigail, Ning Hongyan, Wilkins John, Goldman Noreen, Notterman Daniel, Hou Lifang, Zheng Yinan, Marma Amanda
Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes and Offspring Cardiovascular Health in Early AdulthoodLam Emily, Notterman Daniel, Lloyd-jones Donald, Allen Norrina, Shah Nilay, Gauen Abigail, Khan Sadiya, Freedman Alexa, Stein James, Venkatesh Kartik, Tawa Elisabeth, Savas Hacer, Goldman Noreen