Final ID: P1088
The Association of Kidney Function Trajectories with Atrial Fibrillation, Heart Failure, and Mortality over a 19-Year Follow-up: Results from CRIC study
Abstract Body: Background: The long-term trajectories of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) have not yet been well investigated.
Objectives: The current study aims to compare eGFR trajectory patterns over 19-years follow-up, and their association of atrial fibrillation (AF), heart failure (HF), and all-cause mortality.
Methods: Using data from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) where eGFR (creatine-based: CKD-Epi equation) was measured annually, group-base trajectory models were used to identify latent groups. Multivariable Cox proportional hazard models were used to examine the association of eGFR trajectory groups with the incident events of HF and AF based on records of hospitalization, and death from any cause.
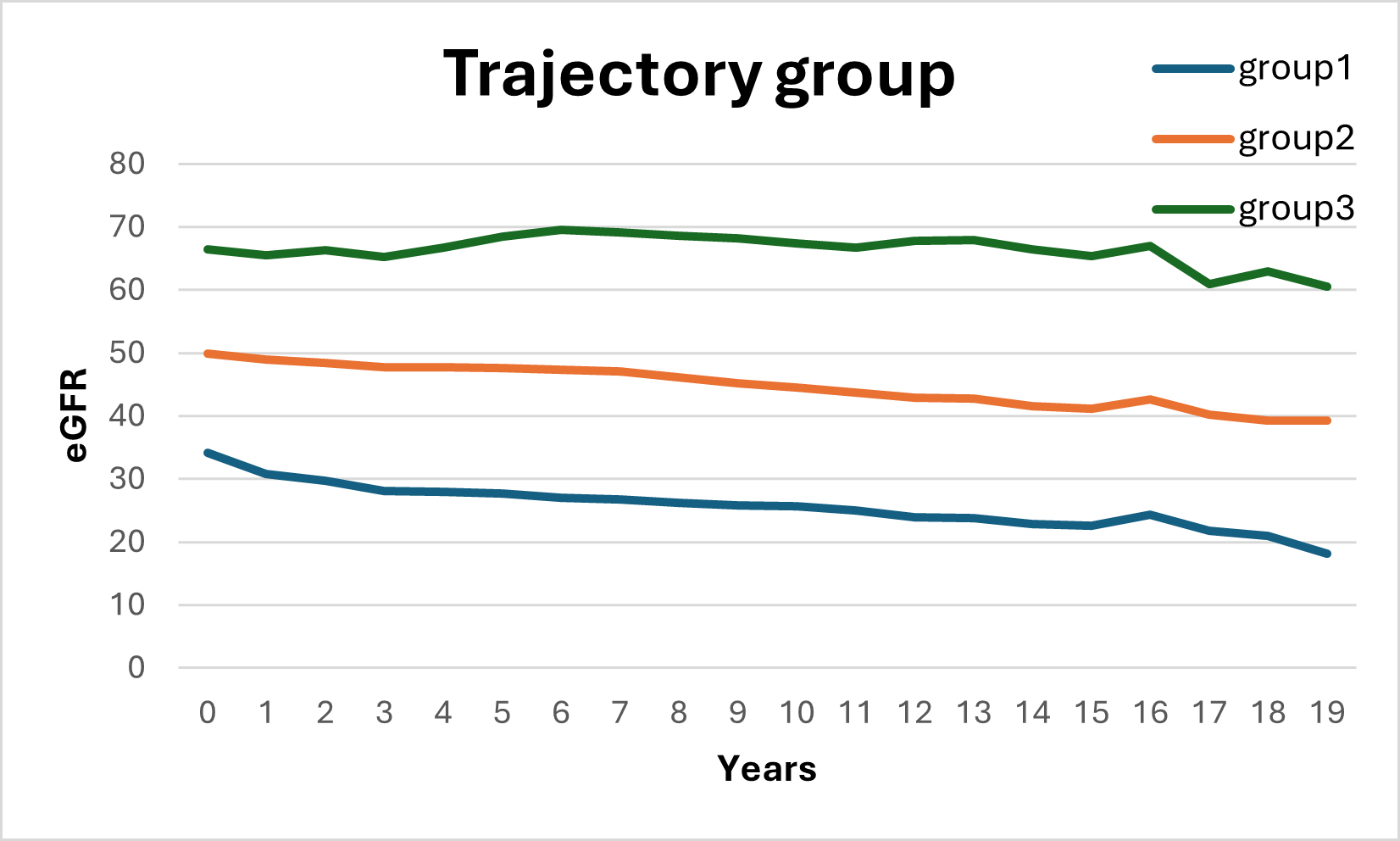
Results: Three eGFR trajectories were identified among 3,939 subjects (Figure 1). The largest was Group 1 (52.0%) with steeper declines both early and late in follow-up. Group 2 (32.7%) displayed a stable declining pattern, and Group 3 (15.3%) was predominantly stable with minimal decline. Group 1 were more likely to be the black (50.6%,) and have a higher BMI (32.3±7.8), hypertension (95%), diabetes (58.4%), and elevated NTproBNP (median 245.2pg/ml), at the baseline (all p<0.0001). Group 3 were younger (54.1 year) compared to Groups 1 and 2 (59.3 and 60.5 years). Compared to Groups 2 and 3, Group 1 had greater hazard ratio (HR) of incident AF (HR, 3.14 [95% CI: 2.40, 4.11]), HF (HR, 9.13 [95% CI: 6.15, 13.6]), and mortality (HR, 3.95[95% CI: 3.29, 4.74]), adjusted for age, sex, race, BMI, hypertension, diabetes, eGFR, and NTproBNP.
Conclusion: This study identified a group of CKD patients with steeper decline in eGFR data over 19-years of follow-up and a significantly higher risk of AF, HF, and all-cause mortality.
Objectives: The current study aims to compare eGFR trajectory patterns over 19-years follow-up, and their association of atrial fibrillation (AF), heart failure (HF), and all-cause mortality.
Methods: Using data from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) where eGFR (creatine-based: CKD-Epi equation) was measured annually, group-base trajectory models were used to identify latent groups. Multivariable Cox proportional hazard models were used to examine the association of eGFR trajectory groups with the incident events of HF and AF based on records of hospitalization, and death from any cause.
Results: Three eGFR trajectories were identified among 3,939 subjects (Figure 1). The largest was Group 1 (52.0%) with steeper declines both early and late in follow-up. Group 2 (32.7%) displayed a stable declining pattern, and Group 3 (15.3%) was predominantly stable with minimal decline. Group 1 were more likely to be the black (50.6%,) and have a higher BMI (32.3±7.8), hypertension (95%), diabetes (58.4%), and elevated NTproBNP (median 245.2pg/ml), at the baseline (all p<0.0001). Group 3 were younger (54.1 year) compared to Groups 1 and 2 (59.3 and 60.5 years). Compared to Groups 2 and 3, Group 1 had greater hazard ratio (HR) of incident AF (HR, 3.14 [95% CI: 2.40, 4.11]), HF (HR, 9.13 [95% CI: 6.15, 13.6]), and mortality (HR, 3.95[95% CI: 3.29, 4.74]), adjusted for age, sex, race, BMI, hypertension, diabetes, eGFR, and NTproBNP.
Conclusion: This study identified a group of CKD patients with steeper decline in eGFR data over 19-years of follow-up and a significantly higher risk of AF, HF, and all-cause mortality.
More abstracts on this topic:
4-5 Years Outcomes of Left Atrial Appendage Closure vs. Oral Anticoagulants in Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis:
Khan Muhammad Aslam, Haider Taimoor, Bhattarai Shraddha, Afzal Hafsa, Khan Bilal, Muhammad Anza, Shafique Nouman, Bhatia Hitesh, Aafreen Asna, Adil Abid Nawaz Khan, Akbar Usman, Khan Alamzaib, Haider Muhammad Adnan
Anticoagulation For Patients On Hemodialysis And Atrial FibrillationEbrahimi Ramin, Alvarez Carlos, Dennis Paul