Final ID: MDP1093
Association of Mitral Regurgitation with Heart Failure Subtypes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: the CRIC Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Data on the association between mitral regurgitation (MR) and heart failure (HF) subtypes in participants with chronic kidney disease (CKD) are scarce.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that the worsening of MR severity is associated with the incidence of both HF with preserved (HFpEF) and reduced (HFrEF) ejection fraction in participants with CKD. Additionally, these associations may differ by sex, race, or the presence of atrial fibrillation (AF).
Methods: We studied participants with CKD who had an echocardiography exam (2013-2015) in the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) study and were free of HF at the time of enrollment in the study. The incidence of HFpEF and HFrEF was determined and classified based on the hospitalization diagnosis and ejection fraction measured by echocardiography during the hospitalization or follow-up visits. The level of MR severity was categorized as absent/trace, mild, and moderate/severe based on visualization and quantification of the effective regurgitant orifice area from an apical-four chamber. Multivariable Cox hazard models were used to examine the association of MR degree with the incidence of overall HF, HFpEF, and HFrEF.
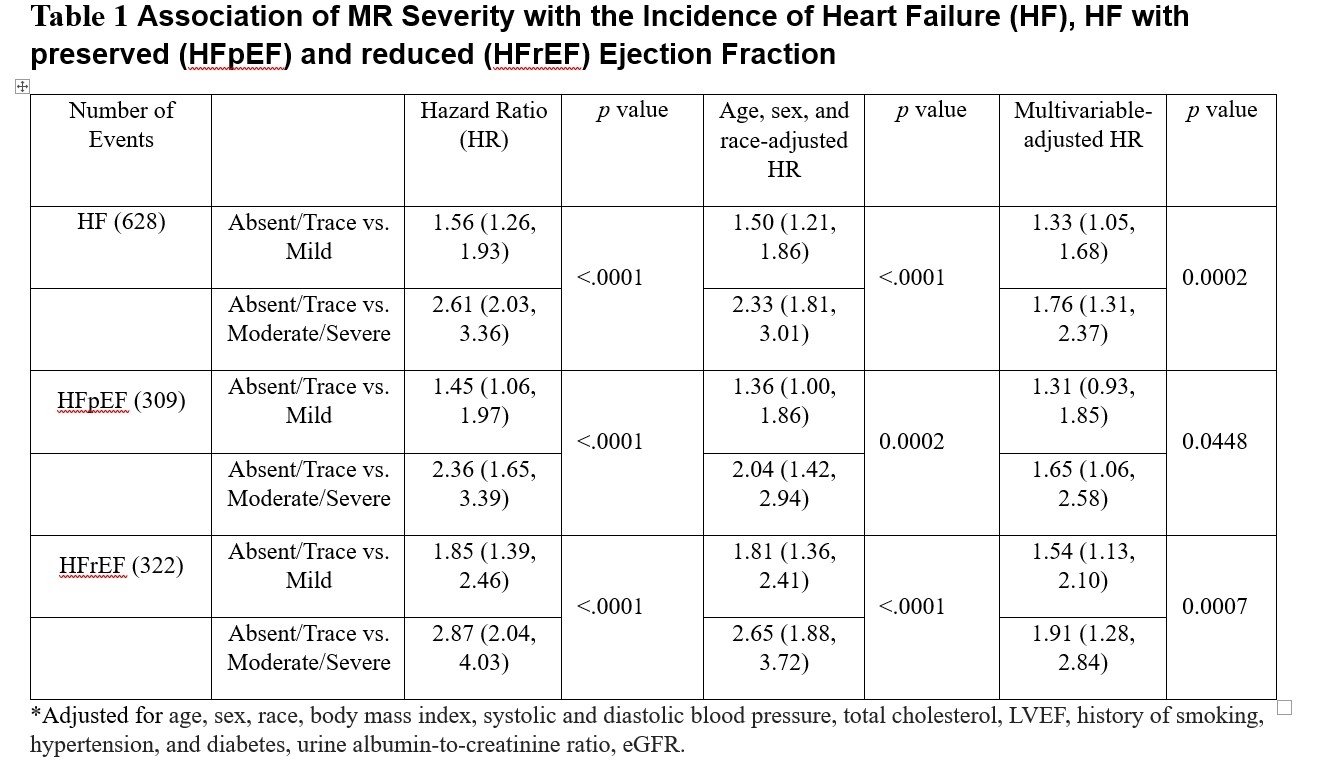
Results: Among 2951 participants with CKD (58.9 years, 46.1% women, and 73.4% with MR), 309 incident HFpEF and 322 incident HFrEF were confirmed during follow-up. Worsening MR severity was associated with the incidence of HFpEF (hazard ratio [HR] 1.65, p=0.04) and HFrEF (hazard ratio 1.91, p<0.001), independent of traditional clinical risk factors, ejection fraction, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (Table 1). In addition, AF accounted for 10.1% and 11.1% of the association of MR severity with HFpEF and HFrEF, respectively. Furthermore, MR severity was associated with HFrEF in women (HR 4.04, p<0.001, psex-interaction =0.0019), but not in men (HR 1.20, p=0.80).
Conclusion: In patients with CKD, worsening MR severity was significantly and independently associated with the risk of HFpEF and HFrEF. These associations are partially explained by the presence of AF.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that the worsening of MR severity is associated with the incidence of both HF with preserved (HFpEF) and reduced (HFrEF) ejection fraction in participants with CKD. Additionally, these associations may differ by sex, race, or the presence of atrial fibrillation (AF).
Methods: We studied participants with CKD who had an echocardiography exam (2013-2015) in the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) study and were free of HF at the time of enrollment in the study. The incidence of HFpEF and HFrEF was determined and classified based on the hospitalization diagnosis and ejection fraction measured by echocardiography during the hospitalization or follow-up visits. The level of MR severity was categorized as absent/trace, mild, and moderate/severe based on visualization and quantification of the effective regurgitant orifice area from an apical-four chamber. Multivariable Cox hazard models were used to examine the association of MR degree with the incidence of overall HF, HFpEF, and HFrEF.
Results: Among 2951 participants with CKD (58.9 years, 46.1% women, and 73.4% with MR), 309 incident HFpEF and 322 incident HFrEF were confirmed during follow-up. Worsening MR severity was associated with the incidence of HFpEF (hazard ratio [HR] 1.65, p=0.04) and HFrEF (hazard ratio 1.91, p<0.001), independent of traditional clinical risk factors, ejection fraction, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (Table 1). In addition, AF accounted for 10.1% and 11.1% of the association of MR severity with HFpEF and HFrEF, respectively. Furthermore, MR severity was associated with HFrEF in women (HR 4.04, p<0.001, psex-interaction =0.0019), but not in men (HR 1.20, p=0.80).
Conclusion: In patients with CKD, worsening MR severity was significantly and independently associated with the risk of HFpEF and HFrEF. These associations are partially explained by the presence of AF.
More abstracts on this topic:
Abrupt cardiac rupture of the patient with ATTR amyloidosis
Tagata Kento, Yutaro Nomoto, Tao Koji, Kataoka Tetsuro, Ohishi Mitsuru
Adjusted Odds of In-Hospital Mortality by Surgical Timing and Procedure Type in Cardiac Transplant Recipients With Intestinal Ischemia: An NIS 2017–2022 AnalysisPopat Apurva, Yerukala Sathipati Srinivasulu, Sharma Param, Nwaedozie Somto, Yadav Sweta, Sethi Aaftab, Modi Karnav, Vempati Roopeessh, Usman Muhammad, Zubair Muhammad Haseeb, Rehman Ateeq