Final ID: P3047
Consumption of Ultra-processed Food and Risk of Major Complications in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study
Abstract Body: Background: The consumption of ultra-processed food may increase the risk of complications by adversely affecting cardiometabolic health. However, in persons with cardiometabolic disease such as type 2 diabetes, it is unclear whether ultra-processed food is associated with adverse outcomes.
Methods: We conducted a prospective cohort analysis in middle-aged adults with type 2 diabetes in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study, with follow-up from 1987-1989 until December 31, 2021. Diabetes was defined as fasting blood glucose ≥126 mg/dL, non-fasting blood glucose ≥200 mg/dL, self-reported physician diagnosed diabetes, or use of diabetes medication. Ultra-processed food was defined according to the NOVA classification from a 66-item food frequency questionnaire. We used Cox models to examine the association between residual-adjusted quartiles of ultra-processed food consumption and incident cardiovascular outcomes (coronary heart disease, stroke, or heart failure), incident chronic kidney disease, and all-cause mortality.
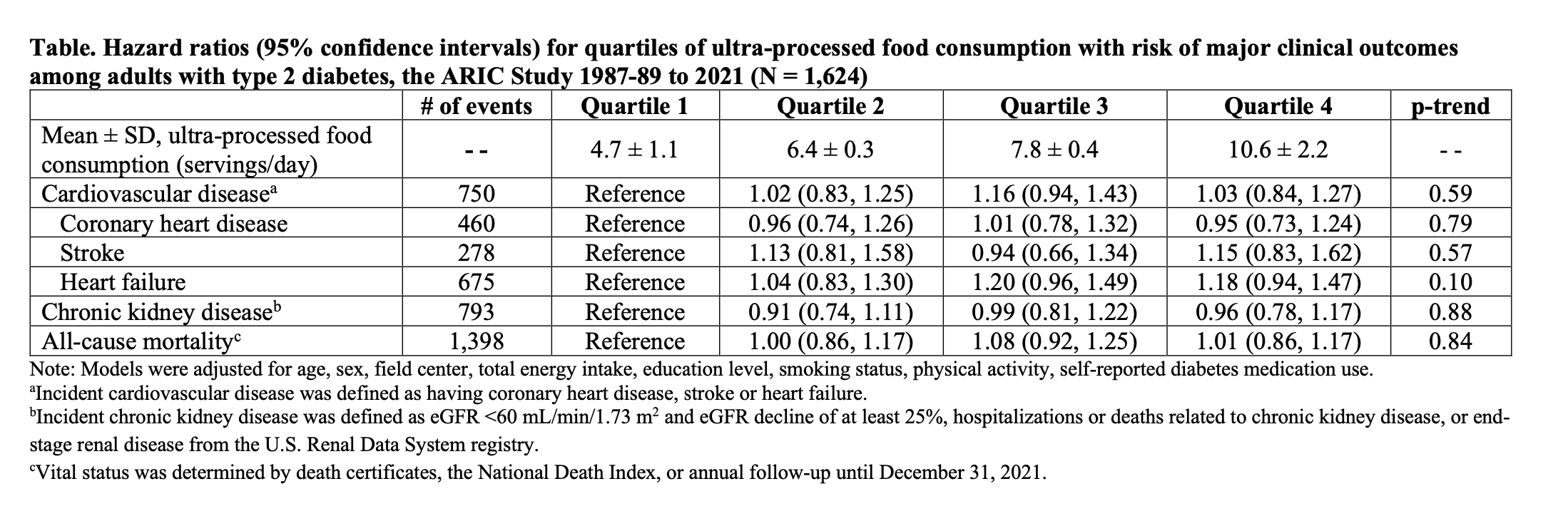
Results: Among 1,624 participants (mean age of 56 years, 42% Black, 55% female), there were 1,398 deaths, 750 incident cardiovascular events, and 793 cases of incident chronic kidney disease over a median follow-up of 20 years. There were no significant differences in the risk of all-cause mortality, cardiovascular disease (overall and across subtypes), or chronic kidney disease across residual-adjusted quartiles of ultra-processed food consumption after adjusting for demographic, socioeconomic, and lifestyle characteristics (Table).
Conclusion: Among middle-aged adults with type 2 diabetes, higher levels of ultra-processed food consumption was not associated with higher risk of incident cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, or mortality. In persons with cardiometabolic disease, consumption of ultra-processed food may not confer additional risk for major complications.
Methods: We conducted a prospective cohort analysis in middle-aged adults with type 2 diabetes in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study, with follow-up from 1987-1989 until December 31, 2021. Diabetes was defined as fasting blood glucose ≥126 mg/dL, non-fasting blood glucose ≥200 mg/dL, self-reported physician diagnosed diabetes, or use of diabetes medication. Ultra-processed food was defined according to the NOVA classification from a 66-item food frequency questionnaire. We used Cox models to examine the association between residual-adjusted quartiles of ultra-processed food consumption and incident cardiovascular outcomes (coronary heart disease, stroke, or heart failure), incident chronic kidney disease, and all-cause mortality.
Results: Among 1,624 participants (mean age of 56 years, 42% Black, 55% female), there were 1,398 deaths, 750 incident cardiovascular events, and 793 cases of incident chronic kidney disease over a median follow-up of 20 years. There were no significant differences in the risk of all-cause mortality, cardiovascular disease (overall and across subtypes), or chronic kidney disease across residual-adjusted quartiles of ultra-processed food consumption after adjusting for demographic, socioeconomic, and lifestyle characteristics (Table).
Conclusion: Among middle-aged adults with type 2 diabetes, higher levels of ultra-processed food consumption was not associated with higher risk of incident cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, or mortality. In persons with cardiometabolic disease, consumption of ultra-processed food may not confer additional risk for major complications.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Clinical Trial of Healthy Food Subsidies and Behavioral Interventions to Increase Fruit and Vegetable Purchasing in an Online Store
Hua Sophia, Klaiman Tamar, Dixon Erica, Volpp Kevin, Putt Mary, Coratti Samantha, White Jenna, Hossain Mohammad, Posner Hannah, Wang Erkuan, Zhu Jingsan, John Aileen
A major effect of aprocitentan on albuminuria in patients with resistant hypertensionSchlaich Markus, Bakris George, Flack John, Gimona Alberto, Narkiewicz Krzysztof, Sassi-sayadi Mouna, Wang Jiguang, Weber Michael