Final ID: MP37
Proteomics Of Prediabetes Progression And Remission: The Atherosclerosis Risk In Communities (ARIC) Study
Abstract Body: Introduction: Proteomics could improve our understanding of the mechanisms underlying short-term prediabetes progression and remission, i.e., reverting to normoglycemia.
Objective: To identify proteomic predictors of 3-year progression from prediabetes to diabetes and remission.
Method: We used data from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study visit 2 (1990-2) and visit 3 (1993-5). We examined associations of 4,955 plasma proteins (SOMAScan v4.0) in participants with baseline prediabetes (fasting glucose [FG] 100-125 mg/dL without diabetes). We used multivariable logistic regressions to examine protein associations with 3-year progression from prediabetes to diabetes (physician diagnosis, medication, or FG ≥126 mg/dL) or remission (FG <100 mg/dL). Analyses were adjusted for demographics, cardiometabolic risk factors, and baseline glucose. Statistical significance was based on p<10-5. We explored biologic pathways enriched among top proteins and calculated the delta-AUC for models with (and without) the associated proteins.
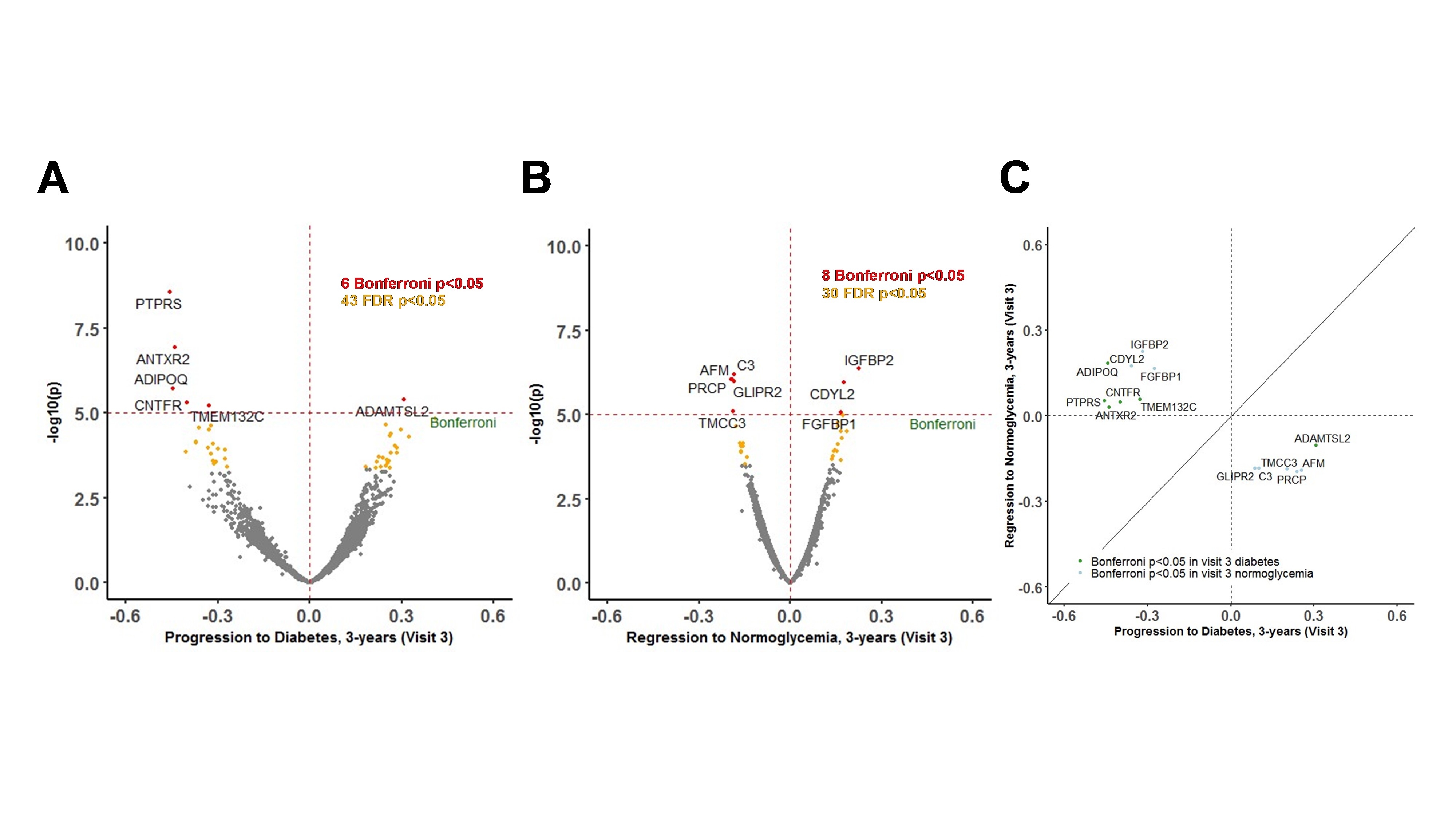
Results: The 3,788 participants with prediabetes were mean aged 57 years (SD:6), 52% were women, 18% self-identified as Black. The 3-year cumulative incidence of diabetes was 6% and was 40% for prediabetes remission. We identified 6 proteins associated with 3-year progression to diabetes (e.g., lower adiponectin [ADIPOQ]) and 8 proteins (e.g., higher insulin growth factor binding protein 2 [IGFBP2], lower complement C3 [C3]) associated with prediabetes remission. Adipogenesis and Jak/STAT signaling were among the pathways enriched in diabetes-associated proteins. Regulation of IGF transport and uptake by IGFBPs and C3/C5 activation were pathways for remission-associated proteins. The 6 proteins collectively improved diabetes progression prediction (covariate only AUC=0.798; delta-AUC=0.03 p<0.001). The 8 proteins collectively improved remission prediction (covariate only AUC=0.722; delta-AUC=0.03 p<0.001).
Conclusions: In persons with prediabetes, we identified known and novel proteins that were associated with 3-year progression to diabetes and remission. Proteins associated with remission relate to reduced inflammation and improved insulin sensitivity.
Objective: To identify proteomic predictors of 3-year progression from prediabetes to diabetes and remission.
Method: We used data from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study visit 2 (1990-2) and visit 3 (1993-5). We examined associations of 4,955 plasma proteins (SOMAScan v4.0) in participants with baseline prediabetes (fasting glucose [FG] 100-125 mg/dL without diabetes). We used multivariable logistic regressions to examine protein associations with 3-year progression from prediabetes to diabetes (physician diagnosis, medication, or FG ≥126 mg/dL) or remission (FG <100 mg/dL). Analyses were adjusted for demographics, cardiometabolic risk factors, and baseline glucose. Statistical significance was based on p<10-5. We explored biologic pathways enriched among top proteins and calculated the delta-AUC for models with (and without) the associated proteins.
Results: The 3,788 participants with prediabetes were mean aged 57 years (SD:6), 52% were women, 18% self-identified as Black. The 3-year cumulative incidence of diabetes was 6% and was 40% for prediabetes remission. We identified 6 proteins associated with 3-year progression to diabetes (e.g., lower adiponectin [ADIPOQ]) and 8 proteins (e.g., higher insulin growth factor binding protein 2 [IGFBP2], lower complement C3 [C3]) associated with prediabetes remission. Adipogenesis and Jak/STAT signaling were among the pathways enriched in diabetes-associated proteins. Regulation of IGF transport and uptake by IGFBPs and C3/C5 activation were pathways for remission-associated proteins. The 6 proteins collectively improved diabetes progression prediction (covariate only AUC=0.798; delta-AUC=0.03 p<0.001). The 8 proteins collectively improved remission prediction (covariate only AUC=0.722; delta-AUC=0.03 p<0.001).
Conclusions: In persons with prediabetes, we identified known and novel proteins that were associated with 3-year progression to diabetes and remission. Proteins associated with remission relate to reduced inflammation and improved insulin sensitivity.
More abstracts on this topic:
Correlations Between VeggieMeter and Self-reported Carotenoid, Fruit and Vegetable Intake Among Older Adults: Results from Bringing the Diabetes Prevention Program to Geriatric Populations
Johnston Emily, Dudzik Josephine, Chen Jack Yanming, Adams Taj, Kulkarni Adeep, Yi Stella, Barua Souptik, Chodosh Joshua, Beasley Jeannette
Associations of Adipokines with 6-Year Progression of Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) StudyAryee Ebenezer, Selvin Elizabeth, Ballantyne Christie, Coresh Joe, Ndumele Chiadi, Wallace Amelia, Zhang Sui, Ozkan Bige, Abushamat Layla, Nambi Vijay, Echouffo Justin, Blumenthal Roger, Matsushita Kunihiro