Final ID: MP66
Sex Differences in the Association of Baseline and Longitudinal Changes in Cardiac Biomarkers with Risk of Heart Failure subtypes – a post-hoc analysis of the Look AHEAD trial
Abstract Body: Background: Elevated levels of biomarkers of neurohormonal stress (NT-proBNP) and myocardial injury (hs-TnT) are associated with an increased risk of heart failure (HF) in diabetes. While sex differences in these biomarker profiles and the HF epidemiology are well-established, it is unclear if the prognostic association of biomarkers with the risk of HF differs by sex.
Methods: The study included participants of the LookAHEAD trial with overweight/obesity and T2DM. NT-proBNP and hs-TnT were measured at baseline, 1- and 4-year follow-up. HFpEF (LV EF> 50%) and HFrEF (LV EF <50) incidence were adjudicated based on HF hospitalization reports using a well-established protocol. Separate adjusted Cox models were constructed to assess the associations of baseline and longitudinal biomarker changes with the risk of HF subtypes, including sex*biomarker interaction terms.
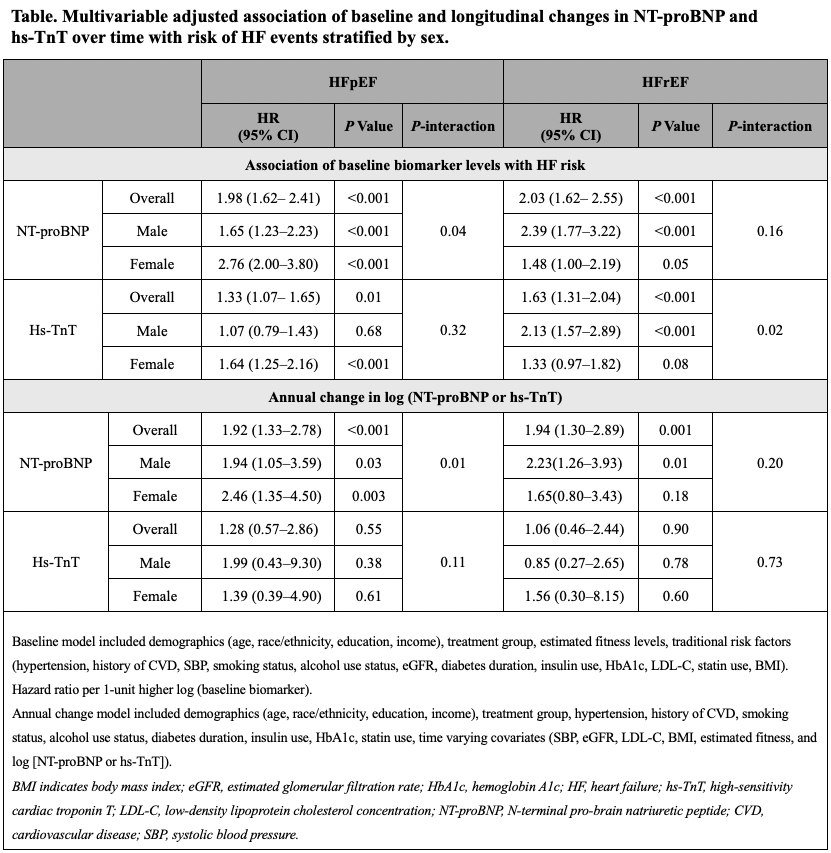
Results: The study included 3959 participants (age: 59 years, 59.3% women, BMI=36 kg/m2) with 108 HFpEF (men vs women: 3.3% vs 2.3%) and 84 HFrEF (men vs women: 2.9% vs 1.6%) events over 12.4 years of follow-up. At baseline, higher NT-proBNP levels were more strongly associated with the risk of HFpEF in females than males (P-int=0.02). In contrast, the association between NT-proBNP and the HFrEF risk was significant and comparable for both sexes (Table). The association of elevated hs-TnT levels with the risk of HFpEF did not differ by sex. In contrast, the risk of HFrEF associated with hs-TnT was significantly modified by sex, with a greater risk noted among males (vs. females, Table). Among those with biomarker assessment on follow-up, an increase in NT-proBNP levels over time was more strongly associated with risk of HFpEF in females than males (P-int=0.01). In contrast, the association between an increase in NT-proBNP levels over time and HFrEF risk did not differ by sex. Repeated measures of hs-TnT over time were not associated with the risk of either HF subtype, with no significant interaction by sex.
Conclusion: Among individuals with T2DM with overweight/obesity, the prognostic relevance of cardiac biomarkers for HF outcomes varies by sex. Elevated baseline levels and increase in NT-proBNP over time are more strongly associated with HFpEF risk in females than males. In contrast, elevated hs-TnT is more strongly associated with the risk of HFrEF in males. Further research is needed to determine if sex-specific biomarker screening strategies can inform HF prevention in high-risk individuals.
Methods: The study included participants of the LookAHEAD trial with overweight/obesity and T2DM. NT-proBNP and hs-TnT were measured at baseline, 1- and 4-year follow-up. HFpEF (LV EF> 50%) and HFrEF (LV EF <50) incidence were adjudicated based on HF hospitalization reports using a well-established protocol. Separate adjusted Cox models were constructed to assess the associations of baseline and longitudinal biomarker changes with the risk of HF subtypes, including sex*biomarker interaction terms.
Results: The study included 3959 participants (age: 59 years, 59.3% women, BMI=36 kg/m2) with 108 HFpEF (men vs women: 3.3% vs 2.3%) and 84 HFrEF (men vs women: 2.9% vs 1.6%) events over 12.4 years of follow-up. At baseline, higher NT-proBNP levels were more strongly associated with the risk of HFpEF in females than males (P-int=0.02). In contrast, the association between NT-proBNP and the HFrEF risk was significant and comparable for both sexes (Table). The association of elevated hs-TnT levels with the risk of HFpEF did not differ by sex. In contrast, the risk of HFrEF associated with hs-TnT was significantly modified by sex, with a greater risk noted among males (vs. females, Table). Among those with biomarker assessment on follow-up, an increase in NT-proBNP levels over time was more strongly associated with risk of HFpEF in females than males (P-int=0.01). In contrast, the association between an increase in NT-proBNP levels over time and HFrEF risk did not differ by sex. Repeated measures of hs-TnT over time were not associated with the risk of either HF subtype, with no significant interaction by sex.
Conclusion: Among individuals with T2DM with overweight/obesity, the prognostic relevance of cardiac biomarkers for HF outcomes varies by sex. Elevated baseline levels and increase in NT-proBNP over time are more strongly associated with HFpEF risk in females than males. In contrast, elevated hs-TnT is more strongly associated with the risk of HFrEF in males. Further research is needed to determine if sex-specific biomarker screening strategies can inform HF prevention in high-risk individuals.
More abstracts on this topic:
4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal Alters Alternative Polyadenylation to Regulate mRNA Isoform Diversity in the Transition from Human Cardiac Fibroblasts to Myofibroblasts
Natarajan Kartiga, Neupane Rahul, Yalamanchili Hari Krishna, Palaniyandi Suresh, Wagner Eric, Guha Ashrith, Amirthalingam Thandavarayan Rajarajan
β1-adrenergic autoantibodies (β1-AA) augment macropinocytosis in CD4+ T cells, leading to the expansion of CD4+CD28− T cell subsets in heart failure.Sun Fei, Yao Junyan, Li Bingjie, Zhang Suli, Liu Huirong