Final ID: MP30
Estimated Health Benefits, Costs, and Cost-Effectiveness of Eliminating Dietary Industrial Trans-fatty Acids in China
Abstract Body: Objectives: To estimate the potential health benefits, costs, and cost-effectiveness of mandating a limit on industrial trans-fatty acids (iTFA) in all foods, fats, and oils in China.
Methods: A multiple cohort proportional multistate life table model was used to project the impact of eliminating dietary iTFA on ischemic heart disease (IHD) burden and costs over different time horizons (5 years, 10 years, and population lifetime). Nationally representative data on iTFA intake were derived from the 2015-2018 China Total Diet Study and China National Health and Nutrition Survey 2011. The health benefits were modelled as averted IHD deaths, events, and health-adjusted life years (HALYs) gained. Net costs were estimated by combining healthcare costs and policy implementation costs, which included government monitoring and industry reformulation costs. Cost-effectiveness was assessed through incremental cost-effectiveness ratios, with both costs and HALYs discounted at 3%.
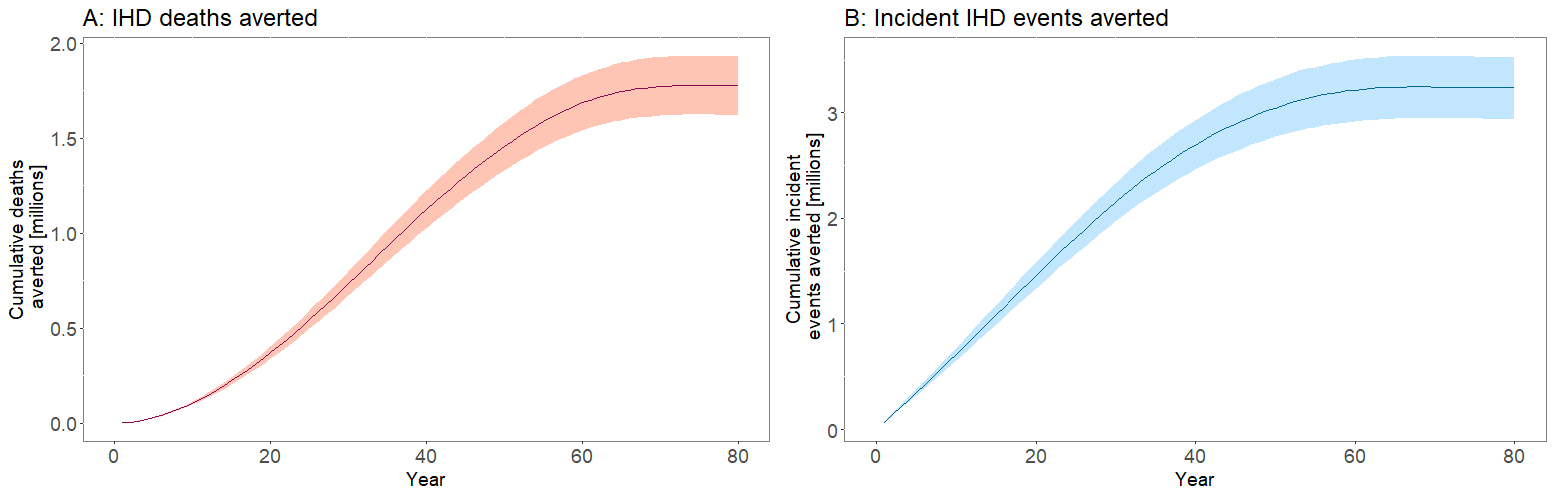
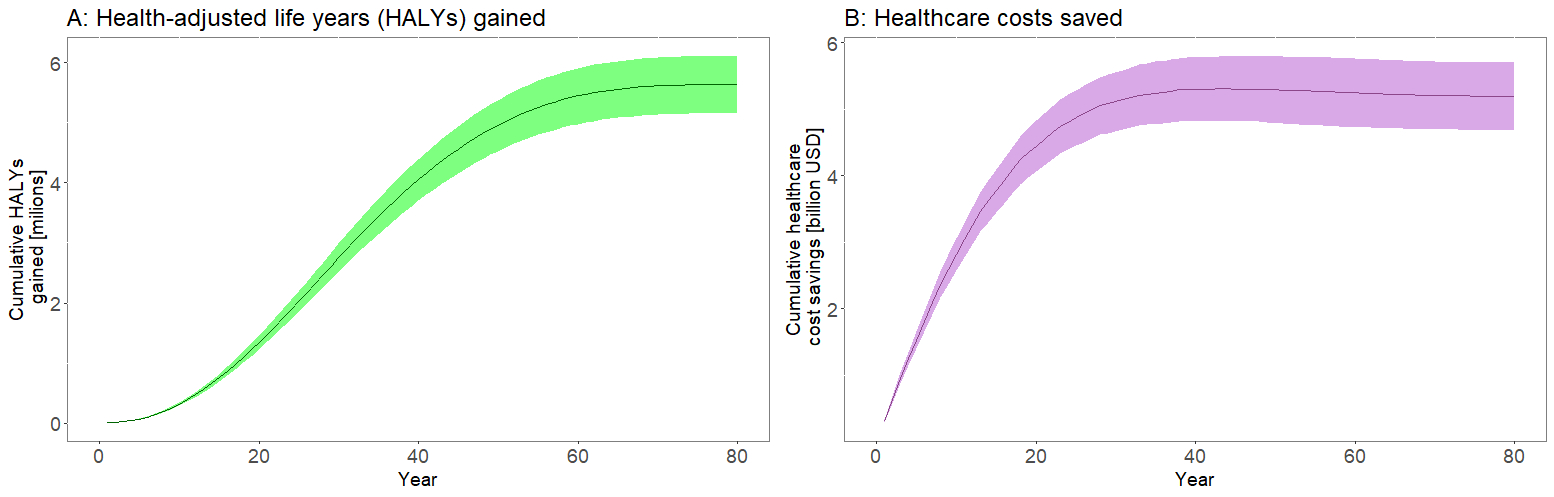
Results: Over 10 years, the mandatory iTFA limit was estimated to prevent approximately 111K IHD deaths (95% uncertainty interval [UI]: 101K-120K), 744K IHD events (95% UI: 678K-807K), 330K HALYs (95% UI: 301K-357K), resulting in a healthcare cost saving of around 2.8 billion USD (95% UI: 2.5-3.0). Over the population lifetime, the intervention was projected to avert 1.9 million (95% UI: 1.7-2.0) IHD deaths, 3.4 million (95% UI: 3.0-3.7) IHD events, and 5.9 million (95% UI: 5.4-6.4) HALYs, saving approximately 5.1 billion USD (95% UI: 4.6-5.7) Policy implementation costs were estimated at 165 million USD (95% UI: 132-198) over the first 10 years and 295 million USD (95% UI: 261-329) over the population lifetime (Figures 1-2). The intervention was estimated to be cost-saving regardless of the time horizon, with robust findings across sensitivity analyses.
Conclusions These findings suggest that legislating a mandatory limit on iTFAs could be a cost-saving strategy to prevent a substantial number of IHD events and deaths in China.
Methods: A multiple cohort proportional multistate life table model was used to project the impact of eliminating dietary iTFA on ischemic heart disease (IHD) burden and costs over different time horizons (5 years, 10 years, and population lifetime). Nationally representative data on iTFA intake were derived from the 2015-2018 China Total Diet Study and China National Health and Nutrition Survey 2011. The health benefits were modelled as averted IHD deaths, events, and health-adjusted life years (HALYs) gained. Net costs were estimated by combining healthcare costs and policy implementation costs, which included government monitoring and industry reformulation costs. Cost-effectiveness was assessed through incremental cost-effectiveness ratios, with both costs and HALYs discounted at 3%.
Results: Over 10 years, the mandatory iTFA limit was estimated to prevent approximately 111K IHD deaths (95% uncertainty interval [UI]: 101K-120K), 744K IHD events (95% UI: 678K-807K), 330K HALYs (95% UI: 301K-357K), resulting in a healthcare cost saving of around 2.8 billion USD (95% UI: 2.5-3.0). Over the population lifetime, the intervention was projected to avert 1.9 million (95% UI: 1.7-2.0) IHD deaths, 3.4 million (95% UI: 3.0-3.7) IHD events, and 5.9 million (95% UI: 5.4-6.4) HALYs, saving approximately 5.1 billion USD (95% UI: 4.6-5.7) Policy implementation costs were estimated at 165 million USD (95% UI: 132-198) over the first 10 years and 295 million USD (95% UI: 261-329) over the population lifetime (Figures 1-2). The intervention was estimated to be cost-saving regardless of the time horizon, with robust findings across sensitivity analyses.
Conclusions These findings suggest that legislating a mandatory limit on iTFAs could be a cost-saving strategy to prevent a substantial number of IHD events and deaths in China.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Qualitative Study of Perspectives on South Asian Dietary Practices: Exploring a Framework for Culturally Tailored Food-is-Medicine Interventions
Kaloth Srivarsha, Fitzgerald Nurgul, Bacalia Karen Mae, Kalbag Aparna, Setoguchi Soko
Cardiology Medications and Medicare Spending: Opportunities for Savings Using Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company and Costco Member Prescription Program PricingSchoeffler Katherine, Day Stephanie, Sanjamala Hemanth, Danesh Alireza, Rosales Isaac, Fennell Zachary, Aguilar Atticus, Parikh Suparshva, Nipp Ryan