Final ID: P1049
Screen Time and Social-Emotional Skills in Michigan Middle School Students Participating in Project Healthy Schools
Abstract Body: Introduction
Time spent on electronic devices, specifically mobile devices and computers, amongst adolescents has increased in the past decade. While there is agreement that too much recreational screen time (ST) can have negative effects on physiological and behavioral health, studies examining the impact on social-emotional (SE) skills are sparse. This study aims to assess the relationship between ST and SE skills among adolescents. We hypothesized that students with higher daily recreational ST will experience more difficulty across SE skills.
Methods
We examined baseline self-reported survey responses (N = 362) from 6th grade students attending a Project Healthy Schools-participating middle school from 2022-2024.
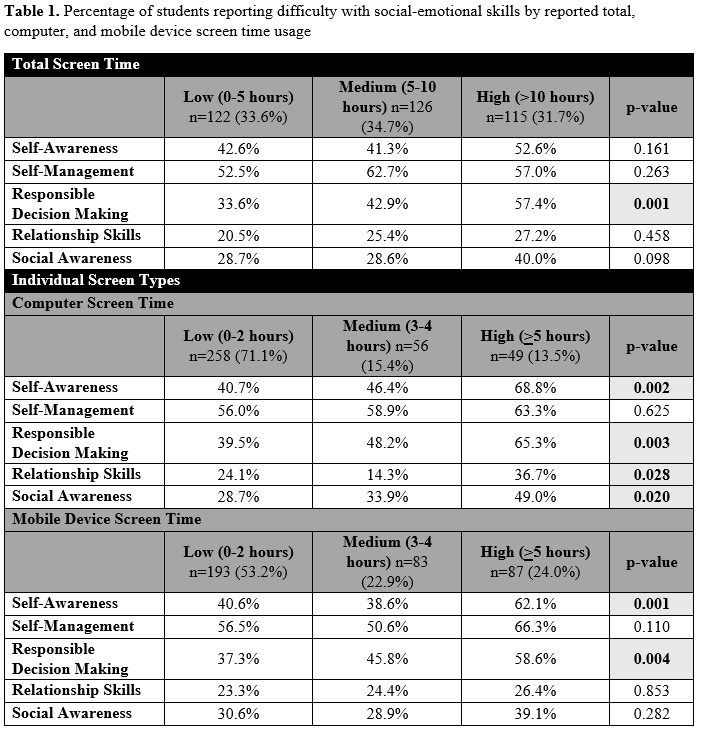
SE skills (self-awareness, self-management, responsible decision making, relationship skills, social awareness) were compared among tertiles of total daily ST (low [0-5 hours], medium [>5-10], and high [>10]) based on chi-squared tests. Students’ total daily ST was calculated by summing the 4 ST modalities (TV/movie, computer, video games, mobile device). SE skills were also examined separately for computer and mobile device ST (low [0-2 hours], medium [3-4], and high [5+]).
Results
Total ST was positively associated with students reporting greater difficulty with responsible decision making (p=0.001). High mobile device ST was positively associated with increased indicated difficulty with self-awareness (p=0.001) and responsible decision making (p=0.004). High computer ST was positively associated with more difficulty for self-awareness (p=0.002), responsible decision making (p=0.003), relationship skills (p=0.028), and social awareness (p=0.02).
Conclusions
Higher ST, including total, computer, and mobile device ST were associated with increased difficulty with several SE skills, in particular responsible decision making. These results suggest that limiting ST may assist middle-school students in SE competencies.
Time spent on electronic devices, specifically mobile devices and computers, amongst adolescents has increased in the past decade. While there is agreement that too much recreational screen time (ST) can have negative effects on physiological and behavioral health, studies examining the impact on social-emotional (SE) skills are sparse. This study aims to assess the relationship between ST and SE skills among adolescents. We hypothesized that students with higher daily recreational ST will experience more difficulty across SE skills.
Methods
We examined baseline self-reported survey responses (N = 362) from 6th grade students attending a Project Healthy Schools-participating middle school from 2022-2024.
SE skills (self-awareness, self-management, responsible decision making, relationship skills, social awareness) were compared among tertiles of total daily ST (low [0-5 hours], medium [>5-10], and high [>10]) based on chi-squared tests. Students’ total daily ST was calculated by summing the 4 ST modalities (TV/movie, computer, video games, mobile device). SE skills were also examined separately for computer and mobile device ST (low [0-2 hours], medium [3-4], and high [5+]).
Results
Total ST was positively associated with students reporting greater difficulty with responsible decision making (p=0.001). High mobile device ST was positively associated with increased indicated difficulty with self-awareness (p=0.001) and responsible decision making (p=0.004). High computer ST was positively associated with more difficulty for self-awareness (p=0.002), responsible decision making (p=0.003), relationship skills (p=0.028), and social awareness (p=0.02).
Conclusions
Higher ST, including total, computer, and mobile device ST were associated with increased difficulty with several SE skills, in particular responsible decision making. These results suggest that limiting ST may assist middle-school students in SE competencies.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acceptability and Feasibility Of A Digital Health Intervention For Adults with Congenital Heart Disease
Valente Joseph, Reardon Leigh, Moons Philip, Okumura Megumi, Gurvitz Michelle, Agarwal Anushree, Banala Keerthana, Buenrostro Karina, Alano Lindsay, Duan Rong, Parang Kim, Manyan Karina, Bravo-jaimes Katia, Norris Mark
Association of sedentary behavior with cardiovascular risk biomarkers in a population with overweight or obesity: the PREDIMED-Plus trialLi Linzi, Romaguera Dora, Alonso-gomez Angel M, Toledo Estefania, Martinez-gonzalez Miguel, Fito Montserrat, Alonso Alvaro