Final ID: P2135
Nicorandil improves health status outcomes in patients with angina pectoris: a prospective, multicenter, cohort study (GREAT)
Abstract Body: Background: Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a major contributor to cardiovascular mortality, with angina pectoris affecting nearly half of CAD patients. The GREAT study aims to establish a large cohort of Chinese patients with angina pectoris, evaluating the effectiveness of anti-anginal treatments through the Seattle Angina Questionnaire (SAQ).
Methods: This multicenter, prospective cohort study included 1556 adult CAD patients with angina pectoris receiving or eligible for oral anti-anginal therapy. Patients were observed over 12 months. All participants were registered on an ePRO system via a WeChat Mini program, allowing them to submit questionnaires and clinic visit data. The primary outcome was the 12-month change in the SAQ summary score (SAQ-SS) from baseline. Secondary outcomes included changes in SAQ-SS at 3, 6, and 9 months. Patients were categorized into two groups: those treated with nicorandil (nicorandil group) and those not receiving it (non-nicorandil group). Propensity score matching (PSM) was used to reduce bias and control for confounding factors.
Results: A total of 1528 patients were analyzed (FAS), of which 529 (34.6%) were in the nicorandil group and 999 (65.4%) in the non-nicorandil group. Following PSM, 450 matched pairs were identified. Baseline characteristics were well-balanced. The median age was 60 years in the nicorandil group and 61 years in the non-nicorandil group, and most patients were male (74.2% and 73.3%, respectively). β-blockers were widely used (68.7% and 70.2%, respectively). Both groups showed improvements in mean SAQ-SS across all follow-up points, but the nicorandil group had significantly greater improvements (P<0.05). At 12 months, the nicorandil group had a mean SAQ-SS improvement of 17.6 points, compared to 15.1 points in the non-nicorandil group (P=0.003). Furthermore, nicorandil users had significantly greater improvements in the SAQ quality-of-life (18.9 vs 16.3; P=0.042) and physical limitation (11.7 vs 8.4; P=0.001) domains (Table 1).
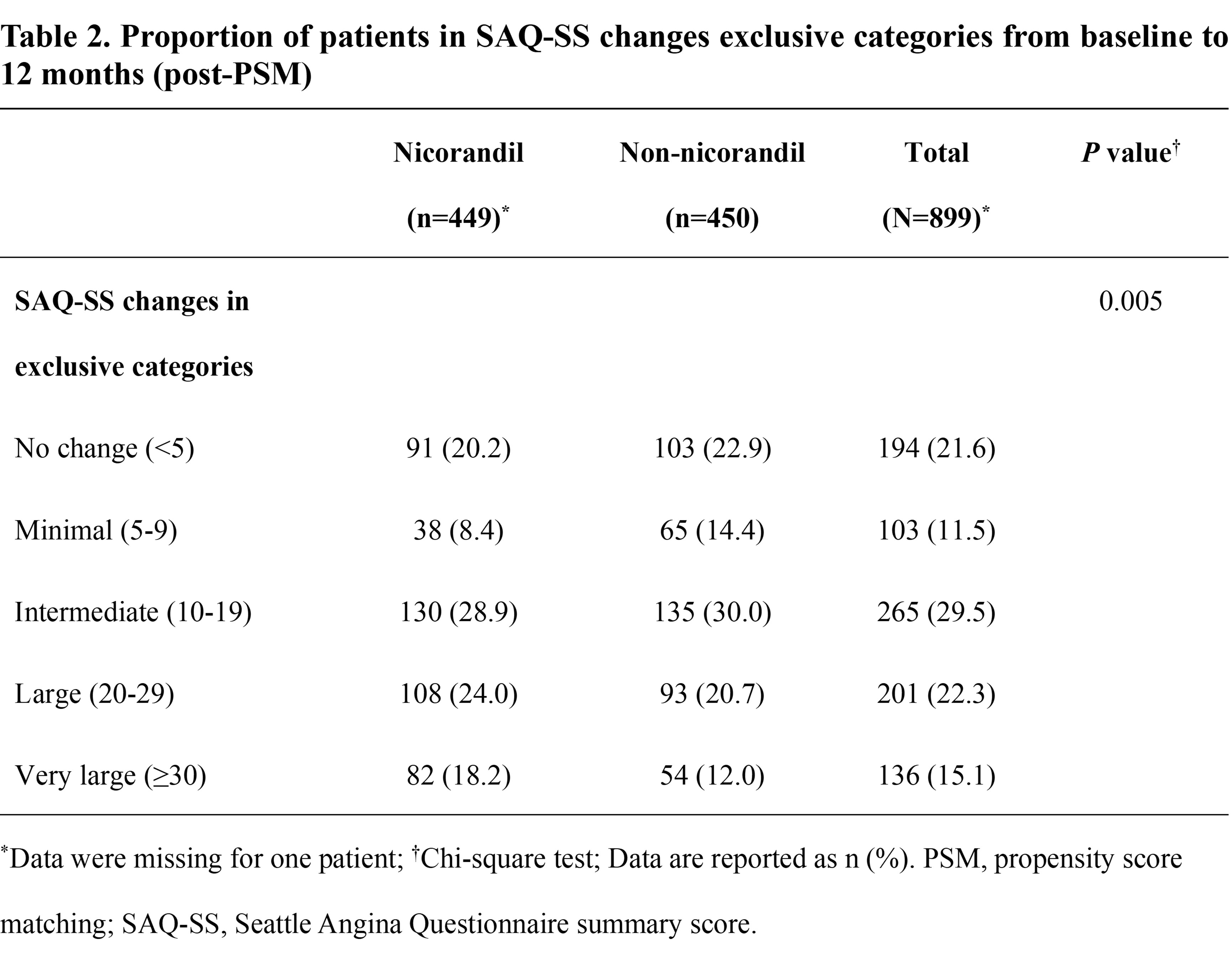
In terms of clinical benefit, a higher proportion of patients in the nicorandil group experienced large or very large improvements in SAQ-SS at 12 months (24.0% vs 20.7% for 20–29 points; 18.2% vs 12.0% for ≥30 points; P=0.005) (Table 2).
Conclusion: This real-world evidence demonstrates that nicorandil-based regimens lead to superior health status improvements in patients with angina pectoris compared to non-nicorandil treatments.
Methods: This multicenter, prospective cohort study included 1556 adult CAD patients with angina pectoris receiving or eligible for oral anti-anginal therapy. Patients were observed over 12 months. All participants were registered on an ePRO system via a WeChat Mini program, allowing them to submit questionnaires and clinic visit data. The primary outcome was the 12-month change in the SAQ summary score (SAQ-SS) from baseline. Secondary outcomes included changes in SAQ-SS at 3, 6, and 9 months. Patients were categorized into two groups: those treated with nicorandil (nicorandil group) and those not receiving it (non-nicorandil group). Propensity score matching (PSM) was used to reduce bias and control for confounding factors.
Results: A total of 1528 patients were analyzed (FAS), of which 529 (34.6%) were in the nicorandil group and 999 (65.4%) in the non-nicorandil group. Following PSM, 450 matched pairs were identified. Baseline characteristics were well-balanced. The median age was 60 years in the nicorandil group and 61 years in the non-nicorandil group, and most patients were male (74.2% and 73.3%, respectively). β-blockers were widely used (68.7% and 70.2%, respectively). Both groups showed improvements in mean SAQ-SS across all follow-up points, but the nicorandil group had significantly greater improvements (P<0.05). At 12 months, the nicorandil group had a mean SAQ-SS improvement of 17.6 points, compared to 15.1 points in the non-nicorandil group (P=0.003). Furthermore, nicorandil users had significantly greater improvements in the SAQ quality-of-life (18.9 vs 16.3; P=0.042) and physical limitation (11.7 vs 8.4; P=0.001) domains (Table 1).
In terms of clinical benefit, a higher proportion of patients in the nicorandil group experienced large or very large improvements in SAQ-SS at 12 months (24.0% vs 20.7% for 20–29 points; 18.2% vs 12.0% for ≥30 points; P=0.005) (Table 2).
Conclusion: This real-world evidence demonstrates that nicorandil-based regimens lead to superior health status improvements in patients with angina pectoris compared to non-nicorandil treatments.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Transient Cortical Blindness occurring during Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angiography for Acute Coronary Syndrome.
Adelakun Adeniyi, Farouji Iyad, Haddad Ahmad, Szwed Stanley
A Synthetic Small Molecule Efficiently Sequesters Carbon Monoxide from Hemoglobin and Red Blood Cells In VitroCorrenti Jacob, Ai Yong, Gladwin Mark, Xue Fengtian, Rose Jason, Demartino Anthony