Final ID: MDP734
Health Status Outcomes of Nicorandil in Patients With Angina Pectoris: A Prospective, Multicenter, Registry-Based Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Coronary artery disease (CAD) exerts a considerable impact on mortality from cardiovascular disease. Approximately half of patients with CAD initially present with angina pectoris. The GREAT study is designed to establish a large cohort of Chinese patients with angina pectoris and compare the effectiveness of different anti-angina regimens, using the Seattle Angina Questionnaire.
Method: The GREAT (reGistRy study of medical thErapy in patients with Angina pecToris) Registry is a multicenter, prospective, observational, cohort study that enrolled 1556 adult CAD patients with angina pectoris from nine hospitals in China. The study included patients currently receiving or eligible to receive oral anti-anginal regimens. The cohort was classified into nicorandil and non-nicorandil groups based on the treatment therapies. The primary outcome was the Seattle Angina Questionnaire summary score (SAQ-SS) changes from baseline to 12 months. The SAQ-SS averages the domains of physical limitation, angina frequency, and quality-of-life scores.
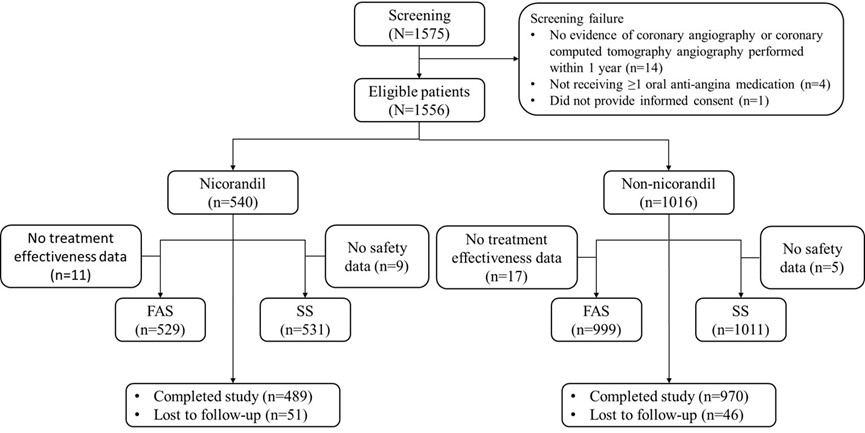
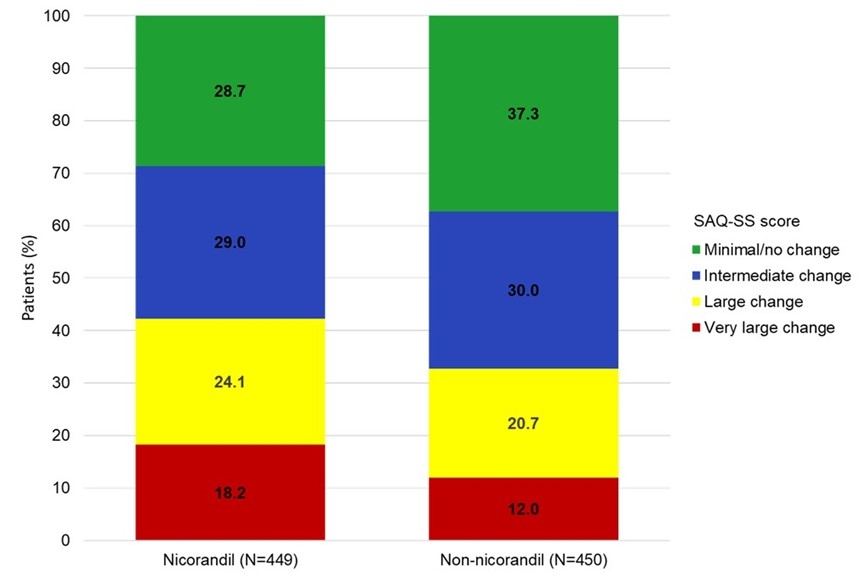
Results: From September 2021 to May 2022, a total of 1575 patients were screened, of whom 1556 met the inclusion criteria and were included (Figure 1). Among the patients at the full analysis set (FAS, N=1528), 28.5% were women, and the median age was 61 years. Baseline variables were well balanced after propensity score matching, with both groups containing 450 patients. In the nicorandil group, patients showed a significantly greater increase in mean SAQ-SS score at Month 12 compared to the non-nicorandil group (17.6±14.0 vs 15.1±13.0; difference: 0.19; 95% CI, 0.05-0.32; p=0.003). In addition, patients in the nicorandil versus the non-nicorandil group reported a significantly greater mean improvement in the SAQ-QoL domain (18.9±21.4 vs 16.3±20.4; p=0.042) and SAQ-PL domain (11.7±16.9 vs 10.0±17.0; p=0.001). Over 12 months, a higher proportion of patients in the nicorandil group, compared to the non-nicorandil group, reported substantial improvements in SAQ-SS, with 24.1% experiencing large improvements (20-29 points) and 18.2% reporting very large improvements (≥30 points) versus 20.7% and 12.0%, respectively (p=0.005 across all categories) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: This real-world data indicates that nicorandil-based anti-angina regimens are associated with a greater health status outcome improvement compared to those not using nicorandil in CAD patients.
Method: The GREAT (reGistRy study of medical thErapy in patients with Angina pecToris) Registry is a multicenter, prospective, observational, cohort study that enrolled 1556 adult CAD patients with angina pectoris from nine hospitals in China. The study included patients currently receiving or eligible to receive oral anti-anginal regimens. The cohort was classified into nicorandil and non-nicorandil groups based on the treatment therapies. The primary outcome was the Seattle Angina Questionnaire summary score (SAQ-SS) changes from baseline to 12 months. The SAQ-SS averages the domains of physical limitation, angina frequency, and quality-of-life scores.
Results: From September 2021 to May 2022, a total of 1575 patients were screened, of whom 1556 met the inclusion criteria and were included (Figure 1). Among the patients at the full analysis set (FAS, N=1528), 28.5% were women, and the median age was 61 years. Baseline variables were well balanced after propensity score matching, with both groups containing 450 patients. In the nicorandil group, patients showed a significantly greater increase in mean SAQ-SS score at Month 12 compared to the non-nicorandil group (17.6±14.0 vs 15.1±13.0; difference: 0.19; 95% CI, 0.05-0.32; p=0.003). In addition, patients in the nicorandil versus the non-nicorandil group reported a significantly greater mean improvement in the SAQ-QoL domain (18.9±21.4 vs 16.3±20.4; p=0.042) and SAQ-PL domain (11.7±16.9 vs 10.0±17.0; p=0.001). Over 12 months, a higher proportion of patients in the nicorandil group, compared to the non-nicorandil group, reported substantial improvements in SAQ-SS, with 24.1% experiencing large improvements (20-29 points) and 18.2% reporting very large improvements (≥30 points) versus 20.7% and 12.0%, respectively (p=0.005 across all categories) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: This real-world data indicates that nicorandil-based anti-angina regimens are associated with a greater health status outcome improvement compared to those not using nicorandil in CAD patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Recalled Experience of Death Among Cardiac Arrest Survivors Is Associated with Improved Psychological Outcomes
Goins Imani, Ingram Cambell, Wei Lijing, Gonzales Anelly, He Tun, Moore Sacha, Parnia Sam
A Case of Myocardial Infarction with Non-obstructive Coronary Arteries (MINOCA) Complicated by a Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)Thai Theresa, Lipinski Jerry, Sola Michael, El Rafei Abdelghani, Desai Aken, Sailer Christine